====================================
Introduction
In financial markets, one of the most critical decisions traders face is choosing between a limit order and a market order. While both order types allow investors to buy or sell securities, their execution mechanics, risks, and strategies differ significantly. Understanding these differences is vital for building an efficient trading approach, especially in highly volatile markets such as equities, futures, forex, and cryptocurrencies.
This article offers a comprehensive limit order vs market order analysis, including practical examples, benefits, drawbacks, and expert recommendations. By the end, you will understand not only the theory but also how to apply these concepts in real-world trading.
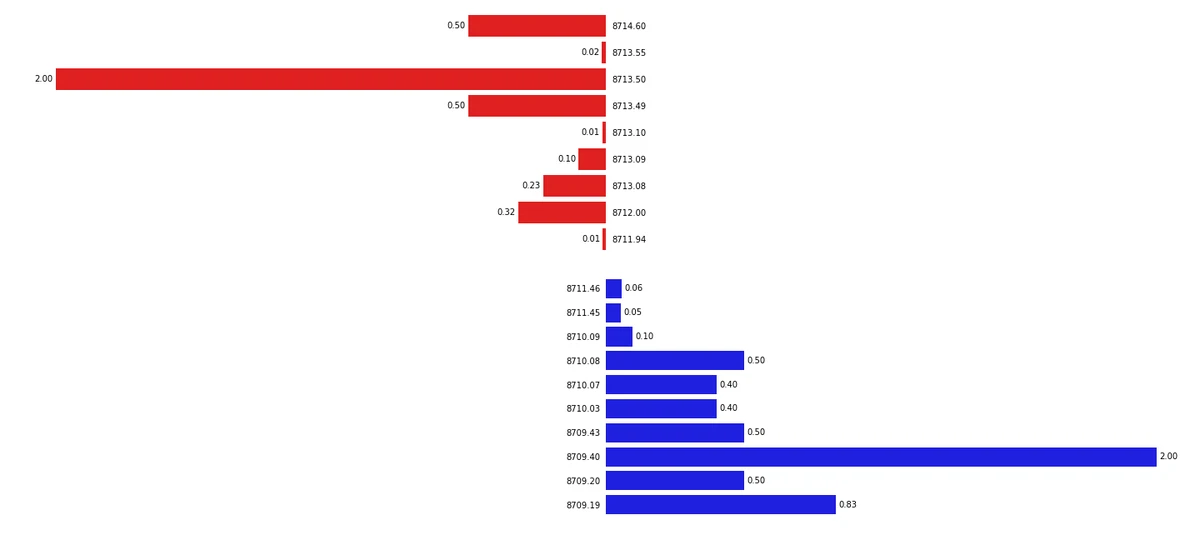
What Is a Market Order?
A market order is an instruction to buy or sell a security immediately at the best available current price.
Key Features
- Execution is instantaneous.
- Prioritizes speed over price precision.
- Best used when liquidity is high, and execution certainty is more important than the exact price.
Pros of Market Orders
- Guaranteed execution (as long as the market is open and liquid).
- Suitable for fast-moving markets where delays could lead to missed opportunities.
- Simplicity—ideal for beginner traders.
Cons of Market Orders
- Execution price may vary from the expected price due to slippage.
- Can be expensive in illiquid markets.
- Not suitable for strategies that require precise entry and exit levels.
What Is a Limit Order?
A limit order specifies the maximum price at which you are willing to buy or the minimum price at which you are willing to sell. Unlike a market order, execution is not guaranteed—it depends on whether the market reaches your limit price.
Key Features
- Execution occurs only at or better than the specified price.
- Prioritizes price control over speed.
- Offers more flexibility for strategic traders.
Pros of Limit Orders
- Full control over entry and exit prices.
- Prevents unexpected losses caused by slippage.
- Essential for traders who build structured trading systems or use algorithmic strategies.
Cons of Limit Orders
- Execution is not guaranteed.
- Orders may remain unfilled if the market never reaches the target price.
- Requires more active monitoring or automation.
Comparison of execution mechanics between limit and market orders
Limit Order vs Market Order Analysis
Execution Speed vs Price Certainty
- Market orders offer speed, but limit orders offer price precision.
- In highly volatile markets, a market order may lead to unfavorable fills, whereas limit orders may prevent execution altogether.
Cost Implications
- Market orders can cause higher trading costs due to slippage.
- Limit orders may reduce costs but at the risk of missed opportunities.
Use Case Scenarios
- Market orders: Best when execution certainty matters, e.g., breaking news events or entering/exiting high-frequency trades.
- Limit orders: Best when building systematic strategies where entry price is part of the edge, such as mean reversion or breakout setups.
Practical Applications in Trading
Algorithmic and Quantitative Trading
Algorithmic traders often rely heavily on limit orders because they provide predictability in execution. Knowing the exact price helps when backtesting and building models. This connects to the idea of how to set a limit order in quantitative trading, where precise parameters define the success of the strategy.
Retail and Discretionary Trading
Retail traders often use a mix: market orders for urgent trades, and limit orders for planned entries. This is particularly important for those exploring limit orders for retail investors, where cost efficiency and discipline are key.
Institutional and High-Frequency Trading
Institutions typically combine both order types:
- Market orders for speed in large transactions.
- Limit orders for gradual accumulation or liquidation without affecting market prices.
Scenarios where traders may prefer limit vs market orders
Strategies for Using Market Orders
1. News-Based Trading
When market-moving news breaks, execution speed becomes critical. Market orders ensure you enter immediately before prices adjust.
2. Momentum Trading
Market orders work well in momentum setups, where missing an entry may result in significant opportunity cost.
3. Emergency Exit
If markets move sharply against you, market orders provide a fast exit to minimize further losses.
Strategies for Using Limit Orders
1. Breakout Confirmation Entries
Placing a buy stop-limit just above resistance ensures entry only when price confirms the breakout.
2. Mean Reversion Entries
Limit orders allow traders to buy at perceived support or sell at resistance, aligning with statistical edge strategies.
3. Scaling into Positions
Institutions often use multiple limit orders at different levels to build positions gradually without moving the market.
Which Is Better: Limit Order or Market Order?
There is no universal “best” choice. The decision depends on trading style, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
- Short-term scalpers may favor market orders for execution certainty.
- Swing traders and algorithmic systems may prefer limit orders for price accuracy.
- Experienced traders often use a hybrid approach, blending both order types depending on context.
Limit Order vs Market Order in Different Markets
Stocks
- Market orders may cause problems in low-volume small-cap stocks.
- Limit orders are ideal for controlling entry in illiquid names.
Forex
- Due to high liquidity, market orders typically have minimal slippage.
- Limit orders remain essential for structured strategies.
Futures
- Market orders are common during roll periods.
- Limit orders dominate intraday trading due to precision requirements.
Crypto
- Market orders can result in massive slippage during high volatility.
- Limit orders are critical to avoid overpaying, especially on smaller exchanges.
Visualization of how limit and market orders interact in order books
Expert Recommendation
Based on years of professional trading experience, the optimal strategy is a context-driven hybrid approach:
- Use market orders when speed is critical (news events, emergency exits).
- Use limit orders when precision matters (systematic entries, scaling positions).
- Always consider liquidity, volatility, and time horizon when choosing order types.
FAQ: Limit Order vs Market Order Analysis
1. How can a limit order improve trading strategy?
A limit order provides better control over entry price, which is often a key factor in risk/reward setups. It allows traders to stick to their planned strategies without emotional decision-making.
2. How often do limit orders get filled?
It depends on market liquidity, order size, and price level. In liquid markets, small orders have a high probability of filling. However, in illiquid assets or far-from-market prices, orders may remain unfilled.
3. Why use limit orders instead of market orders?
Limit orders protect traders from slippage and ensure trades are executed only at favorable levels. They are especially useful in volatile markets or for traders who rely on precise price levels.
Conclusion
The limit order vs market order analysis reveals that neither order type is universally superior. Instead, the effectiveness depends on the trader’s objectives, strategy, and market environment. Professional traders often combine both methods, using market orders for speed and limit orders for control.
For retail and institutional traders alike, mastering when and how to use these order types is a cornerstone of sustainable trading.
📢 Have you faced challenges deciding between limit and market orders? Share your experiences in the comments and forward this guide to other traders who might benefit from learning about order execution strategies.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment