===================================================================================
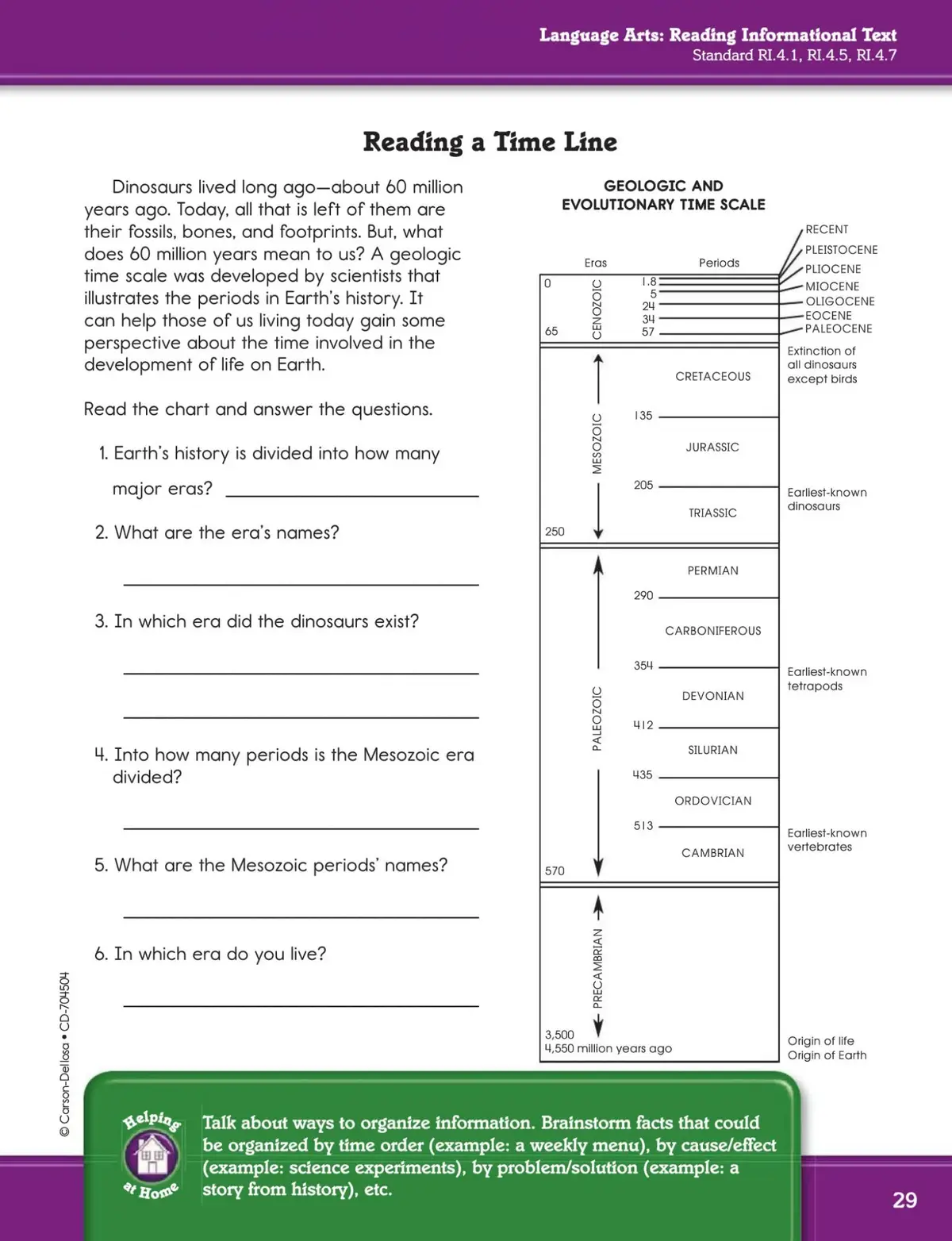
Introduction
Momentum trading is a core strategy used by quantitative traders to take advantage of trending assets in the financial markets. By identifying and capitalizing on the continued direction of price movement, traders can unlock significant profits. In the world of quantitative trading, momentum techniques are an essential tool for making data-driven decisions. Advanced momentum techniques enable traders to go beyond basic trend-following strategies, incorporating machine learning, statistical analysis, and high-frequency trading algorithms to enhance profitability.
In this article, we will explore advanced momentum techniques for quants, the mathematical principles behind momentum strategies, and how you can apply them to improve your trading edge. We’ll also look at the latest trends, compare different momentum-based strategies, and share expert recommendations for traders looking to deepen their understanding of momentum trading.
- What is Momentum in Quantitative Trading?
————————————————
1.1 Understanding Momentum in Financial Markets
Momentum refers to the tendency of an asset’s price to persist in the same direction for some time. In quantitative trading, momentum is often used to create predictive models that suggest when to buy or sell an asset. A simple way to think about it is that “what goes up, tends to go up”, and “what goes down, tends to go down”.
1.2 The Mathematical Concept Behind Momentum
Momentum can be quantified by examining price changes over a given period, often using indicators like Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD). These indicators measure the speed and strength of price movements and help traders gauge whether an asset is overbought or oversold.
In quantitative finance, we go a step further and use sophisticated models, such as machine learning algorithms, to detect and predict momentum. These models use historical price data, volume information, and other financial metrics to develop momentum-based strategies.
- Advanced Momentum Techniques for Quants
———————————————-
2.1 Machine Learning for Momentum Detection
2.1.1 Using Supervised Learning for Momentum Prediction
Machine learning has taken momentum trading to a new level. By employing supervised learning techniques like linear regression, support vector machines (SVM), and decision trees, quants can model price momentum more accurately. These models are trained on historical data to identify patterns and predict future price movements.
2.1.2 Reinforcement Learning in Momentum Trading
Reinforcement learning (RL) is an advanced machine learning technique where an agent learns how to make trading decisions by interacting with the market environment. The RL agent can optimize momentum strategies by continuously adjusting its parameters based on market feedback, creating a more adaptive and efficient trading system.
2.2 Statistical Arbitrage and Momentum
2.2.1 Cointegration and Pairs Trading
In quantitative trading, cointegration refers to a statistical relationship between two assets whose prices move in a consistent pattern over time. By using this technique, quants can identify momentum pairs trading opportunities, where one asset may show stronger momentum than another.
2.2.2 Multi-Factor Momentum Models
Rather than relying on price alone, multi-factor models incorporate various market signals like earnings reports, interest rates, and economic indicators to enhance momentum trading strategies. By adding multiple factors to a momentum model, quants can improve their predictive power and reduce risk.
2.3 High-Frequency Momentum Trading
High-frequency trading (HFT) is a technique that involves executing a large number of trades in fractions of a second. Momentum trading can be applied to HFT by utilizing ultra-low latency algorithms that detect micro-trends in real-time. These systems identify short-term momentum shifts and can capitalize on them before other traders react, offering a significant edge in the market.
2.3.1 Market Microstructure and Momentum
The study of market microstructure plays a critical role in HFT momentum strategies. Understanding the dynamics of order flow, liquidity, and bid-ask spreads allows quants to fine-tune their algorithms to take advantage of momentum-based opportunities that last only a few milliseconds.
- Comparing Different Momentum Techniques: A Deep Dive
———————————————————–
3.1 Traditional vs. Advanced Momentum Strategies
3.1.1 Traditional Momentum Techniques
Traditional momentum techniques, such as moving averages and RSI, are often used in manual trading. These techniques rely on basic statistical analysis of price movements over set periods. While effective in many cases, these strategies are typically slow and may not capitalize on short-term momentum shifts.
3.1.2 Advanced Techniques Using Machine Learning
In contrast, advanced momentum techniques leverage machine learning models to predict and act upon momentum shifts. These models can analyze far more data and incorporate non-traditional indicators, such as sentiment analysis and macro-economic factors, providing a more holistic view of the market.
3.2 Momentum in Trend Following vs. Mean Reversion
3.2.1 Trend-Following Momentum Strategies
Trend-following momentum strategies assume that a prevailing trend will continue. These strategies aim to capture sustained price movements in the same direction. Common tools for trend-following momentum include moving averages and MACD.
3.2.2 Mean Reversion and Momentum
Contrary to trend-following, mean reversion strategies assume that prices will return to their historical averages. In the context of momentum, mean reversion is often used to identify points where a trend has become overextended and may soon reverse.
- Expert Recommendations: How to Improve Your Momentum Trading Strategy
—————————————————————————-
4.1 Leverage Multi-Asset Momentum Models
Incorporating multiple asset classes into your momentum strategy can help diversify risk and improve overall returns. For instance, combining stocks, bonds, and commodities into a single momentum model allows you to capture different types of market movements and reduce exposure to any single asset class.
4.2 Combine Momentum with Volatility Strategies
Pairing momentum with volatility measures like Bollinger Bands or Average True Range (ATR) can improve the timing of trades. When a momentum signal aligns with a period of low volatility, the potential for a strong price move increases.
4.3 Adapt Your Strategy for Different Market Conditions
Momentum strategies work well in trending markets but may underperform during sideways or highly volatile conditions. Quants must develop adaptive strategies that can adjust to different market environments, potentially incorporating volatility measures or using machine learning to detect changing market conditions.
- FAQ: Expert Answers to Common Questions
———————————————-
1. What is the difference between momentum and trend-following?
While both momentum and trend-following focus on riding the wave of price movements, momentum specifically looks at the speed and strength of a trend, whereas trend-following seeks to capture the overall direction of the market. Momentum strategies are more focused on timing the market’s acceleration or deceleration, while trend-following simply seeks to profit from sustained price movements.
2. How can machine learning improve momentum strategies?
Machine learning allows quants to process vast amounts of data, including non-traditional factors like social media sentiment and macro-economic events. This enables quants to create more sophisticated models that can predict momentum more accurately than traditional technical indicators. Machine learning models can also adapt to changing market conditions, making them highly flexible.
3. Is high-frequency momentum trading effective for retail traders?
High-frequency momentum trading is typically reserved for large institutional players with access to advanced infrastructure and data. However, retail traders can still benefit from momentum strategies by using less frequent but still effective algorithms. These might involve strategies that capitalize on momentum over a few minutes or hours rather than milliseconds.

Conclusion
Advanced momentum techniques are transforming the way quants approach market trends. By integrating machine learning, multi-factor models, and high-frequency trading, quants can develop highly effective momentum strategies that outperform traditional approaches. Whether you’re a novice quant or an experienced trader, understanding and applying these advanced techniques can significantly enhance your trading performance.
Ready to elevate your momentum trading game? Share this article with fellow traders, and don’t forget to explore our other articles on momentum trading strategies and quantitative analysis for deeper insights into these cutting-edge techniques.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| What is Momentum? | Momentum refers to the tendency of an asset’s price to persist in the same direction, used to create predictive models in quantitative trading. |
| Mathematical Concept | Momentum is quantified using indicators like RSI and MACD, measuring speed and strength of price movements to identify overbought or oversold conditions. |
| Machine Learning for Momentum | Supervised learning (e.g., linear regression, SVM) and reinforcement learning (RL) are used to predict momentum and adapt strategies based on market feedback. |
| Statistical Arbitrage & Momentum | Cointegration and pairs trading identify momentum opportunities between correlated assets. Multi-factor models incorporate economic signals to enhance momentum strategies. |
| High-Frequency Trading (HFT) | HFT applies momentum strategies by detecting micro-trends and executing trades in milliseconds using low-latency algorithms, optimizing profits in real-time. |
| Comparing Strategies | Traditional strategies rely on simple technical analysis like moving averages, while advanced methods use machine learning and macro-economic factors for more holistic predictions. |
| Trend-Following vs. Mean Reversion | Trend-following assumes trends will continue, using tools like moving averages. Mean reversion assumes prices will revert to averages, used to identify overextended trends. |
| Expert Recommendations | Leverage multi-asset models to diversify risk, combine momentum with volatility strategies to improve timing, and adapt strategies for different market conditions using machine learning or volatility measures. |
| Momentum vs. Trend-Following | Momentum focuses on the speed and strength of a trend, whereas trend-following focuses on the overall direction, with momentum timing market acceleration or deceleration. |
| Machine Learning’s Role | Machine learning enhances momentum strategies by analyzing vast data, including non-traditional factors, allowing more accurate predictions and adaptation to changing conditions. |
| High-Frequency Trading for Retail | High-frequency trading is more suited for institutional traders due to infrastructure needs, but retail traders can use less frequent momentum algorithms for short-term opportunities. |

0 Comments
Leave a Comment