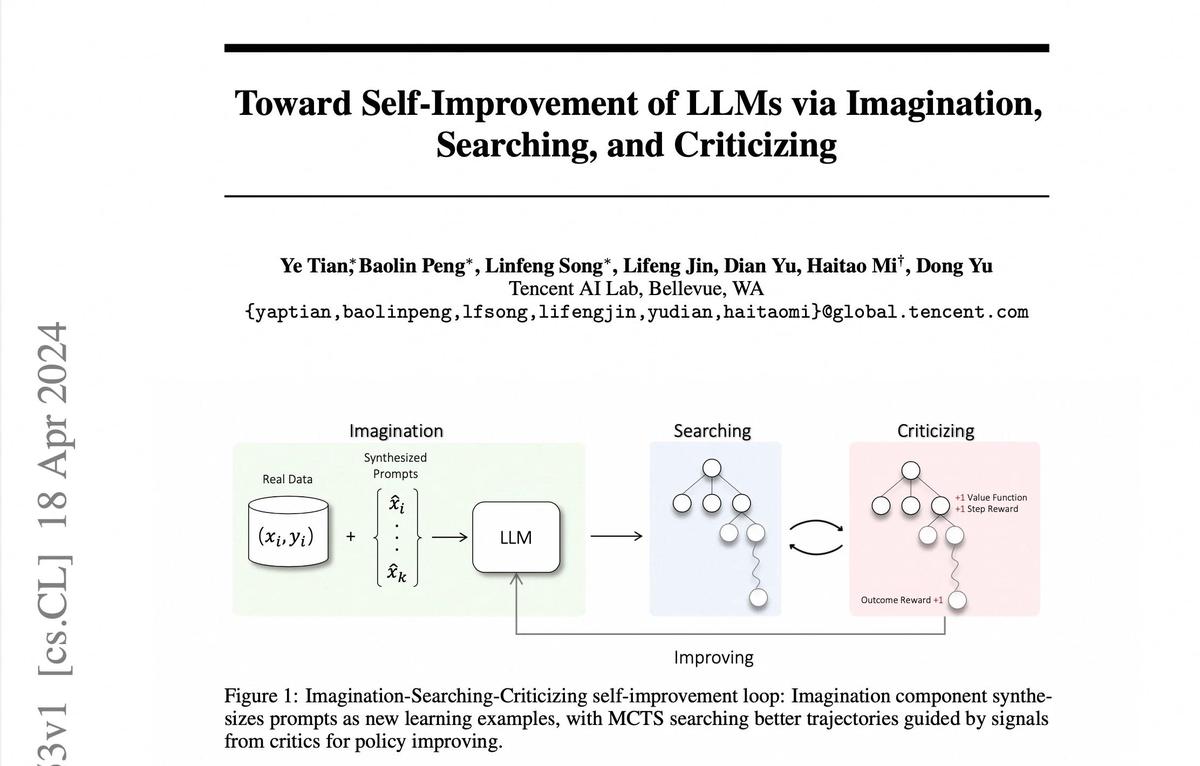
Introduction
As a beginner trader, the concept of alpha can seem both intriguing and complex. In simple terms, alpha refers to the excess return an investment generates over a benchmark or market index, adjusting for risk. For traders, generating positive alpha is the ultimate goal, as it signifies that their strategies are outperforming the broader market. This article will walk you through the basics of alpha strategies for beginner traders, exploring effective methods and techniques to help you maximize your returns. Along the way, we will discuss two primary alpha strategies: quantitative models and fundamental analysis, and help you decide which might be the best fit for your trading style.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid understanding of alpha, how it impacts your trading performance, and actionable steps you can take to implement alpha strategies that work for you.
What is Alpha in Trading?
Understanding Alpha
In trading, alpha represents the excess return that an asset or portfolio achieves compared to its benchmark index. For example, if the S&P 500 returns 10% in a year, and your investment portfolio returns 15%, your alpha would be 5%, signaling that your strategy outperformed the market by 5%.
Alpha is one of the most important metrics used by investors and traders to assess performance. A positive alpha means you are generating returns above what is expected given the level of risk you are taking, while a negative alpha indicates underperformance.
Why Alpha is Important for Traders
Alpha matters because it allows traders to distinguish between skill and luck. Generating consistent alpha means you’re not just riding market trends but are actively creating value with your strategies. Whether you’re using quantitative trading models, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both, understanding how to generate alpha can significantly improve your trading results.
Key Alpha Strategies for Beginner Traders
There are many strategies that can be used to generate alpha, but beginner traders should start with a solid foundation. The following sections will explore two of the most popular approaches: quantitative trading models and fundamental analysis. Both strategies offer distinct advantages and can help you create a diversified approach to generating alpha.
- Quantitative Trading Models
Quantitative trading involves using mathematical models and algorithms to make trading decisions. These models rely on historical data, statistical methods, and risk analysis to predict future price movements and identify opportunities for alpha generation. For beginner traders, here are a few common strategies within quantitative trading:
1.1. Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage (or stat-arb) involves using mathematical models to identify pricing inefficiencies between related assets. By taking long and short positions simultaneously, traders can exploit these inefficiencies to generate alpha. For example, if two stocks are historically correlated, but one diverges from the other, a trader might take a long position in the undervalued stock and short the overvalued one, betting that the prices will converge again.
Pros: Can be highly profitable with a well-designed model.
Cons: Requires substantial knowledge of programming, data analysis, and risk management.
1.2. Momentum Strategies
Momentum trading is a quantitative strategy based on the idea that assets that have performed well in the past will continue to perform well in the future. By identifying strong upward or downward trends, traders can take positions that benefit from these movements, generating alpha by riding trends.
Pros: Works well in trending markets.
Cons: Momentum can reverse quickly, leading to potential losses.
1.3. Machine Learning for Alpha Generation
Machine learning (ML) is becoming increasingly popular in quantitative trading. ML algorithms can process large datasets to identify patterns and make predictions that are difficult to capture using traditional methods. By applying ML techniques such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning, traders can develop sophisticated models that predict asset movements and generate alpha.
Pros: Can adapt to changing market conditions and process vast amounts of data.
Cons: Requires knowledge of coding and ML algorithms, as well as significant computational resources.
- Fundamental Analysis for Alpha Generation
Fundamental analysis involves analyzing the intrinsic value of an asset by studying its financials, industry, and macroeconomic factors. Beginner traders can apply fundamental analysis to generate alpha by identifying undervalued or overvalued assets based on economic indicators, company performance, and market trends.
2.1. Value Investing
Value investing is a strategy that focuses on identifying undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals. By purchasing these stocks at a discount to their intrinsic value, traders can generate alpha when the market eventually recognizes their true worth. This strategy relies on metrics such as price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, price-to-book (P/B) ratio, and dividend yield to find assets that are underpriced.
Pros: Long-term focus, relatively low risk if done correctly.
Cons: Requires patience and the ability to withstand market volatility.
2.2. Growth Investing
Growth investing focuses on investing in companies with strong potential for future growth. These companies may not be profitable yet, but they are expected to achieve rapid earnings growth in the future. Traders using this strategy look for signs of high revenue growth, expanding market share, and strong management.
Pros: Can generate high returns in high-growth industries.
Cons: Higher risk, especially if the company fails to meet growth expectations.
2.3. Macroeconomic Analysis
Macroeconomic analysis looks at broader economic factors that affect entire markets or sectors. By analyzing economic indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, interest rates, and inflation, traders can identify trends and anticipate market movements that provide opportunities for alpha generation.
Pros: Provides a broader view of the market, allowing for better long-term predictions.
Cons: Can be difficult to predict how macroeconomic factors will impact individual assets.
Comparing Quantitative Models and Fundamental Analysis
Both quantitative models and fundamental analysis can generate alpha, but they offer different approaches. Here’s a comparison to help you decide which is best for your trading style:
Aspect Quantitative Models Fundamental Analysis
Approach Data-driven, uses mathematical models and algorithms Based on company and economic fundamentals
Time Horizon Short-term to medium-term Long-term, but can also work for short-term trades
Risk Management Often uses statistical measures for risk control Relies on understanding market cycles and financials
Skill Set Requires coding, statistics, and model development Requires understanding of financial statements, markets, and economics
Tools Algorithms, backtesting software, statistical models Financial statements, economic indicators, and reports
Which Strategy is Best for Beginners?
For beginners who are more comfortable with understanding economic trends and company fundamentals, fundamental analysis may be easier to start with. It offers a more intuitive understanding of market movements.
For tech-savvy beginners who are willing to dive into programming and data analysis, quantitative models can offer more precision and scalability in identifying trading opportunities.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the best way for a beginner to learn about alpha generation?
The best way to learn is by starting with the basics of fundamental analysis and gradually incorporating quantitative models as you become more comfortable. You can begin by reading books, taking online courses, and practicing with demo accounts before moving to real-money trading.
- How do I calculate alpha in trading?
Alpha can be calculated using the formula:
Alpha=Actual Return−Expected Return
Alpha=Actual Return−Expected Return
Where the expected return is usually calculated using a benchmark model like CAPM (Capital Asset Pricing Model) or APT (Arbitrage Pricing Theory).
- Can machine learning help generate alpha in trading?
Yes, machine learning can help generate alpha by identifying patterns in large datasets and predicting market movements. Techniques like supervised learning and reinforcement learning are commonly used in quantitative trading strategies to enhance alpha generation.
Conclusion
| Aspect | Quantitative Models | Fundamental Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses mathematical models and algorithms to predict price movements | Analyzes intrinsic value via financials, industry, and macro factors |
| Key Strategies | Statistical arbitrage, momentum, machine learning | Value investing, growth investing, macroeconomic analysis |
| Pros | Can be precise, scalable, adapt to data trends | Intuitive, long-term focus, identifies undervalued assets |
| Cons | Requires coding, data analysis, computational resources | Requires patience, market volatility can affect returns |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term | Long term, but applicable short term |
| Risk Management | Statistical measures and model-based controls | Understanding market cycles and financials |
| Skills Needed | Programming, statistics, model development | Financial statement analysis, market knowledge, economics |
| Tools | Algorithms, backtesting software, statistical models | Financial statements, economic indicators, reports |
| Best for Beginners | Tech-savvy, comfortable with coding and data | Those preferring intuitive, fundamentals-based approach |
| Alpha Calculation | Alpha = Actual Return − Expected Return using models like CAPM | Alpha = Actual Return − Expected Return via benchmark |
| Machine Learning | Enhances prediction and alpha generation in quantitative models | Less commonly used, mainly for data-driven insights |

0 Comments
Leave a Comment