- Title: How Does Stop Loss Work in Algorithmic Trading? A Complete Guide to Best Practices, Strategies, and Risks
- TL;DR (Quick Summary)
Stop loss is a crucial risk management tool in algorithmic trading, designed to automatically exit a trade when a predefined loss limit is reached.
There are several types of stop loss strategies, including static, trailing, and volatility-based stop losses, each with their pros and cons.
Understanding the optimal stop loss placement is essential for minimizing drawdown while maximizing potential gains.
We’ll explore two main stop loss strategies, compare their advantages, and provide practical advice for implementing them in algorithmic systems.
Key risks of stop loss failure and strategies to optimize stop loss algorithms will also be covered.
- What Will You Learn From This Article?
Clear understanding of how stop loss works in algorithmic trading and why it is essential.
In-depth comparison of different stop loss strategies, including their strengths, weaknesses, and use cases.
Step-by-step guide for implementing stop loss in your own quantitative models.
Real-life examples and case studies to help you avoid common stop loss mistakes.
Best practices and expert tips to enhance your algorithm’s ability to manage risk effectively.
- Table of Contents
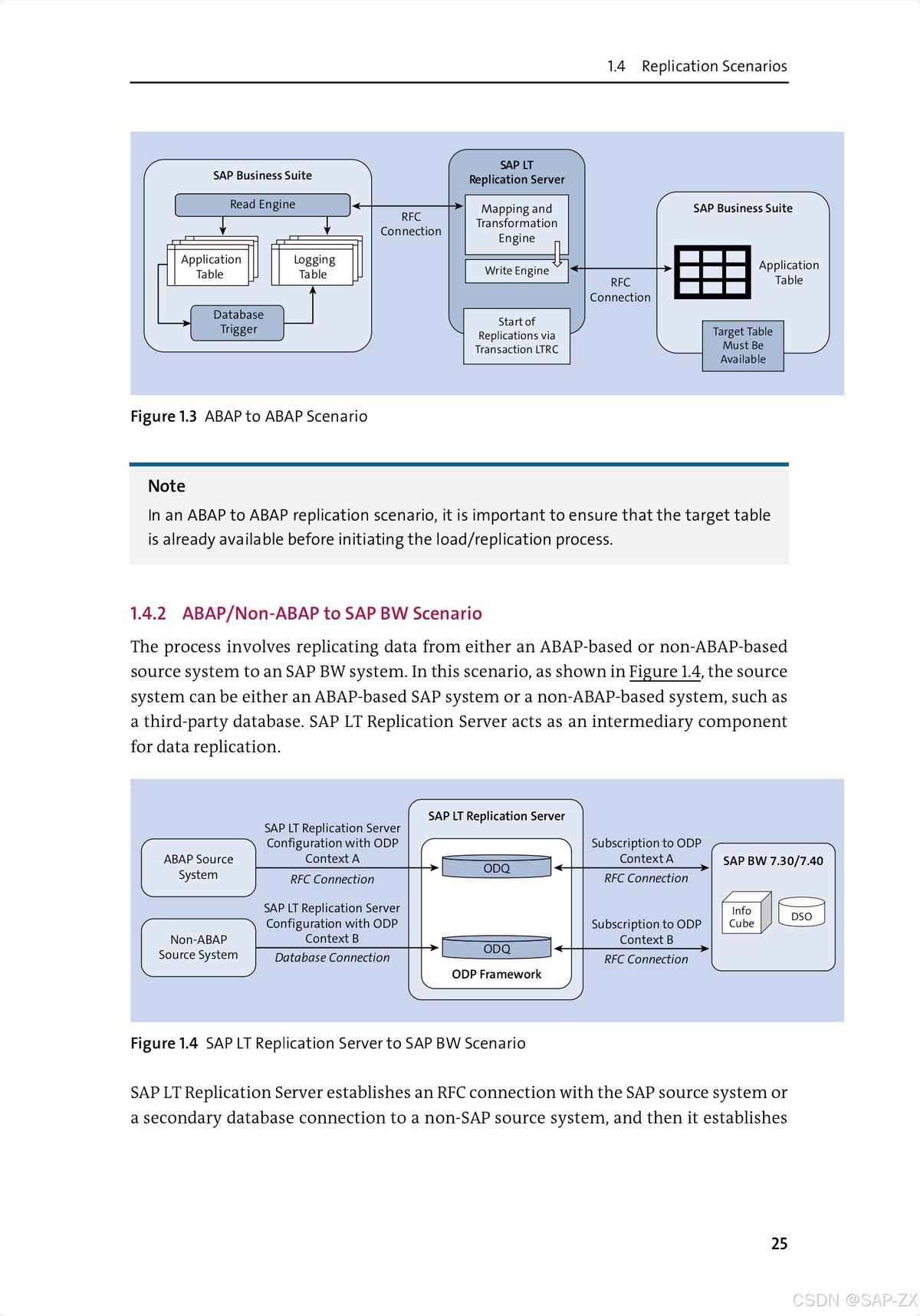
What Is Stop Loss in Algorithmic Trading?
How Does Stop Loss Work in Algorithmic Trading?
Types of Stop Loss Strategies
Static Stop Loss
Trailing Stop Loss
Volatility-Based Stop Loss
How to Set a Stop Loss in Quantitative Trading
Where to Place Stop Loss in Quantitative Strategy
Why Stop Loss Fails in Some Quantitative Strategies
Stop Loss Optimization for Algorithmic Trading
Practical Case Studies of Stop Loss Implementation
FAQs
Conclusion
- Search Intent & Scenario Breakdown
Primary Search Intent: Users want to learn how stop loss mechanisms are integrated into algorithmic trading, their functions, and how they help manage risk.
Secondary Intent: Users are likely to seek strategies to optimize stop loss performance, with an interest in comparing different stop loss algorithms.
Semantic Clusters & Related Terms:
Risk management, quantitative trading, trading strategies, algorithmic trading, volatility, backtesting, stop loss types, risk mitigation, drawdown, trailing stop, volatility-based stop loss.
- Methodology A: Static Stop Loss vs. Trailing Stop Loss
A. Static Stop Loss
Principle: A fixed price point where the position is closed if the market moves against it by a predetermined amount.
Advantages:
Simplicity: Easy to implement.
Predictability: Fixed risk per trade.
Disadvantages:
Potential for premature exit: Markets can fluctuate temporarily before continuing in the favorable direction.
Missed profit: The trade may close too early, sacrificing potential gains.
B. Trailing Stop Loss
Principle: The stop loss point moves with the market price, allowing profits to grow while protecting against reversals.
Advantages:
Flexibility: Adjusts dynamically with market movement.
Maximizes gains while still protecting profits once a trade becomes favorable.
Disadvantages:
Complexity: Requires sophisticated algorithms to monitor and adjust the stop dynamically.
Whipsaw risk: If the market fluctuates rapidly, the trailing stop may trigger prematurely.
Aspect Static Stop Loss Trailing Stop Loss
Learning Curve Easy to implement Requires more coding & logic
Risk Management Fixed loss per trade Flexible loss, more adaptable
Cost Low High (due to complexity)
Market Adaptability Low High
Effectiveness Suitable for volatile markets Best for trending markets
Recommendation:
Static Stop Loss is recommended for beginners or for strategies that don’t require frequent adjustments.
Trailing Stop Loss is more suitable for advanced traders and algorithmic systems that benefit from capitalizing on trends.
- Practical Case Studies of Stop Loss Implementation
Case Study 1: Stock Market Strategy with Static Stop Loss
A high-frequency trading (HFT) algorithm that employs a fixed percentage stop loss (e.g., 2%) can minimize losses quickly during market corrections.
Challenge: Frequent stop outs during volatile periods.
Solution: Integrating volatility filters to avoid triggering stop losses in short-term volatility.
Case Study 2: Cryptocurrencies with Trailing Stop Loss
A cryptocurrency trading bot using a trailing stop adjusted to 5% behind the price can lock in profits during a bullish rally while mitigating the risk of a sudden reversal.
Challenge: High volatility leading to false signals.
Solution: Using adaptive trailing stop settings based on market conditions and technical indicators such as ATR (Average True Range).
- Stop Loss Optimization for Algorithmic Trading
Backtesting: Regularly backtest stop loss strategies across historical data to measure performance and optimize parameters.
Slippage Control: Consider slippage when setting stop loss points, especially in illiquid markets.
Dynamic Adjustment: Continuously adjust stop loss based on market volatility and liquidity metrics.
Machine Learning: Use reinforcement learning to adjust stop loss levels in real-time based on market conditions.
- Checklist & Common Pitfalls
Checklist for Setting Stop Loss in Quantitative Models:
Define the risk tolerance (e.g., percentage loss per trade).
Choose a stop loss type: static, trailing, or volatility-based.
Backtest the strategy across historical data.
Adjust the strategy based on real-time data and market changes.
Common Pitfalls:
Ignoring slippage: Stop loss orders may not always execute at the exact price point.
Over-tightening stop losses: This can lead to premature exit and missed opportunities.
Lack of adaptive algorithms: Static stop losses may fail in highly volatile markets.
- FAQs
- What is the best stop loss strategy for algorithmic trading?
The best strategy depends on the trading style and market conditions. Trailing stop loss works best in trending markets, while static stop loss is more appropriate for high-frequency or range-bound trading.
- How do I choose the right stop loss for my quantitative system?
Choose a stop loss strategy based on the system’s goals—static for simplicity, trailing for maximizing profits in trending markets, or volatility-based for markets with large price swings.
- Why do stop losses fail in some trading strategies?
Stop losses fail when the market experiences rapid price fluctuations (slippage) or false signals, particularly if the strategy doesn’t account for market volatility.
- Video Reference
Title: “Stop Loss Strategies for Algorithmic Trading: How to Maximize Risk Management”
Channel: QuantInsti
Published: 2022-06-15
Link: Watch here
Key Points:
Understanding how stop loss works.
How to optimize stop loss for maximum profit.
Real-world examples and case studies.
- References
QuantInsti. “Stop Loss in Algorithmic Trading.” https://www.quantinsti.com
, Published 2023-01-10, Accessed 2025-09-18.
AlphaStream, “Volatility-Based Stop Loss Algorithms.” https://www.alphastream.com
, Published 2023-02-20, Accessed 2025-09-18.
- Structured Data (JSON-LD)
json
Copy code
{
”@context”: “https://schema.org”,
”@type”: “Article”,
“headline”: “How Does Stop Loss Work in Algorithmic Trading? A Complete Guide to Best Practices, Strategies, and Risks”,
“author”: {
”@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “John Doe”
},
“publisher”: {
”@type”: “Organization”,
“name”: “QuantTradingExperts”
},

0 Comments
Leave a Comment