==============================================
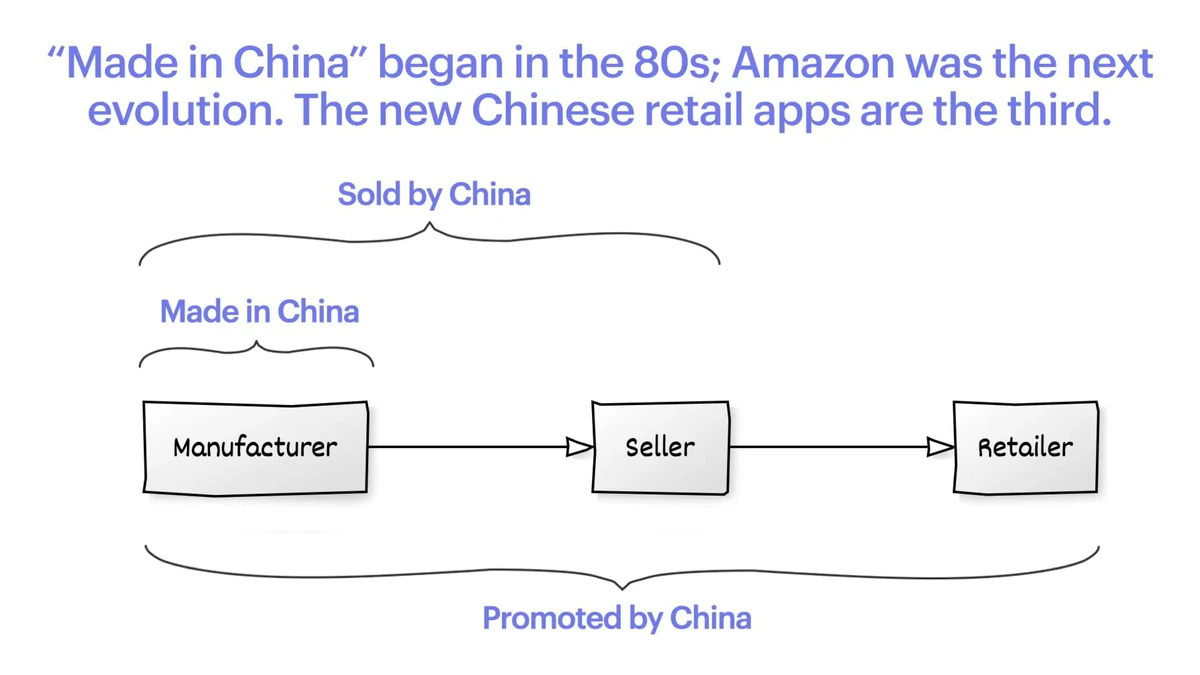
Market microstructure is the study of the processes and mechanisms that facilitate the exchange of assets in financial markets. It plays a crucial role in shaping the behavior of markets, influencing price formation, liquidity, and the efficiency of transactions. Understanding market microstructure is essential for traders, as it affects how trades are executed, how prices are set, and how trading costs are incurred. In this article, we will explore how market microstructure impacts trading, delve into key concepts, and discuss strategies that leverage these insights to improve trading decisions.
- What is Market Microstructure?
———————————
1.1 Definition and Key Components
Market microstructure refers to the study of the internal structure of financial markets. It examines the rules, participants, and processes that govern the flow of orders and trades in an exchange. The key components of market microstructure include:
- Market Participants: Buyers, sellers, brokers, market makers, and exchanges.
- Order Types: Market orders, limit orders, and stop orders.
- Execution Mechanisms: How trades are matched and executed, such as through order books or auction systems.
- Liquidity: The ability to buy or sell assets without significantly affecting their price.
- Price Formation: How the price of a security is determined through the interaction of supply and demand.
1.2 Types of Market Microstructure
Market microstructure can be divided into two main categories:
- Traditional Market Microstructure: This is the study of how traditional exchanges, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), operate. It focuses on how market makers, brokers, and traders interact in a structured, regulated environment.
- Electronic Market Microstructure: With the rise of electronic trading platforms, this type of microstructure examines the dynamics of online platforms, including high-frequency trading (HFT), algorithmic trading, and the role of dark pools.
1.3 Importance of Market Microstructure in Trading
Understanding market microstructure is crucial for traders because it provides insights into how markets function at a granular level. Traders can use this knowledge to identify opportunities, reduce transaction costs, and improve their overall trading strategies. For example, a trader who understands the order book dynamics will be better equipped to avoid slippage and reduce execution costs.
- How Market Microstructure Affects Trading?
———————————————
2.1 Liquidity and Market Efficiency
One of the most significant ways that market microstructure impacts trading is through its influence on liquidity. Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without causing large price fluctuations. High liquidity is essential for traders because it reduces the risk of slippage—where an order is filled at a worse price than expected.
- Market Makers and Liquidity Providers: In traditional exchanges, market makers provide liquidity by being willing to buy or sell securities at quoted prices. In electronic markets, liquidity is often provided by algorithmic traders who place orders based on predetermined strategies.
- Impact on Trading Costs: Liquidity affects the spread—the difference between the bid and ask price. A tighter spread typically indicates a more liquid market, which reduces transaction costs for traders.
2.2 Price Discovery and Volatility
Market microstructure also plays a crucial role in price discovery—the process by which the price of an asset is determined through the interaction of supply and demand. The way orders are matched and executed can influence how quickly and accurately prices reflect the true value of an asset.
- Order Flow and Information: The flow of information through the market is a key determinant of price discovery. Large institutional traders and market makers often have access to more information, which can affect how quickly they execute trades and the prices they are willing to accept.
- Volatility: The structure of the market can also affect volatility. For example, markets with low liquidity or inefficient order matching can experience more significant price swings as orders are executed at unfavorable prices.
2.3 Execution Strategies and Trading Costs
Market microstructure influences the execution strategies that traders use to minimize trading costs. These strategies include:
- Limit Orders vs. Market Orders: Limit orders are executed only at a specified price or better, which can help traders avoid slippage but may result in delayed execution. Market orders, on the other hand, are executed immediately at the best available price, but they may suffer from slippage in illiquid markets.
- Algorithmic Trading: Algorithmic trading strategies, which use predefined rules to execute trades, rely heavily on market microstructure insights. Algorithms can be designed to optimize the execution of trades, minimize costs, and improve overall performance.
- Key Factors in Market Microstructure Impacting Trading
———————————————————
3.1 Order Book Dynamics
The order book is a central element of market microstructure, representing a list of buy and sell orders for a particular security. The dynamics of the order book—such as the depth, bid-ask spread, and the speed at which orders are filled—can have a significant impact on trading decisions.
- Order Book Depth: A deeper order book with many buy and sell orders at various price levels typically indicates higher liquidity, which can help traders execute large orders with minimal price impact.
- Bid-Ask Spread: A narrower spread indicates higher liquidity and lower trading costs, while a wider spread can signal higher costs and lower liquidity.
3.2 Market Maker Behavior
Market makers play an essential role in maintaining liquidity in financial markets. They provide buy and sell prices for assets, facilitating smooth trading by ensuring there is always a counterparty to trades.
- Liquidity Provision: Market makers ensure that orders can be executed quickly, even in illiquid markets. This is crucial for high-frequency traders and institutional investors who rely on fast executions.
- Impact on Volatility: When market makers withdraw from the market (such as during periods of high volatility), liquidity can dry up, leading to increased price volatility.
3.3 High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
High-frequency trading is a key component of modern market microstructure. It involves the use of powerful algorithms and high-speed data networks to execute trades at extremely fast speeds. HFT firms make money by capitalizing on tiny price discrepancies that exist for fractions of a second.
- Speed and Efficiency: HFT firms can provide liquidity and reduce spreads, making it easier for other traders to execute their orders quickly. However, HFT also raises concerns about market manipulation and unfair advantages for large players with access to sophisticated technology.
- Market Impact: While HFT can increase market efficiency, it can also increase volatility during periods of market stress, as algorithms react to sudden price movements and market events.
- Strategies to Leverage Market Microstructure for Better Trading
——————————————————————
4.1 Exploiting Liquidity
Traders can use knowledge of market microstructure to identify liquid assets and execute trades more efficiently. By focusing on assets with high liquidity, traders can reduce the cost of executing trades and avoid the risks associated with slippage.
- Trade in Active Markets: Focusing on securities with high trading volumes ensures tighter spreads and better execution prices.
- Avoiding Low-Liquidity Periods: Certain times of the day, such as after market hours, may have lower liquidity. Traders should be aware of these times and adjust their strategies accordingly.
4.2 Using Limit Orders Strategically
Limit orders can be a powerful tool for traders who wish to control the price at which they enter or exit the market. By placing limit orders at key price levels in the order book, traders can avoid market orders’ risks of slippage and ensure better execution.
- Optimal Placement of Limit Orders: Placing orders just outside the spread or at strategic price levels can increase the chances of execution without incurring excessive costs.
- Leveraging Order Book Depth: Traders can analyze the order book depth to place limit orders in areas with strong support or resistance levels, increasing the likelihood of a favorable execution.
4.3 Utilizing Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading strategies can be tailored to take advantage of market microstructure dynamics. By using algorithms that are aware of order book patterns, bid-ask spreads, and liquidity conditions, traders can optimize their execution strategies and minimize trading costs.
- VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price): This algorithm seeks to execute orders at the average price over a specific time period, ensuring that the trade doesn’t move the market.
- TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price): This strategy executes trades evenly throughout the trading session, reducing the impact of large orders on the market.
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
————————————
1. How does market microstructure affect pricing in financial markets?
Market microstructure affects pricing by influencing the supply and demand dynamics, liquidity, and how efficiently information is incorporated into prices. Inefficient market microstructures can lead to wider bid-ask spreads, higher volatility, and mispriced assets.
2. Why should traders study market microstructure?
Understanding market microstructure allows traders to make informed decisions about when and how to execute trades. It helps them minimize transaction costs, avoid slippage, and capitalize on liquidity opportunities. It also provides insights into market trends, volatility, and the behavior of market participants.
3. What role do market makers play in market microstructure?
Market makers provide liquidity by continuously quoting bid and ask prices for securities. They ensure that there is always a counterparty to a trade, which helps reduce transaction costs and maintain market stability. Their presence in the market also reduces price volatility and improves price discovery.
- Conclusion
————-
Market microstructure has a profound impact on trading decisions, from execution strategies to understanding liquidity, price discovery, and volatility. By gaining a deeper understanding of these dynamics, traders can improve their trading strategies, minimize costs, and navigate the complexities of financial markets with greater confidence. Whether you’re a retail trader or

0 Comments
Leave a Comment