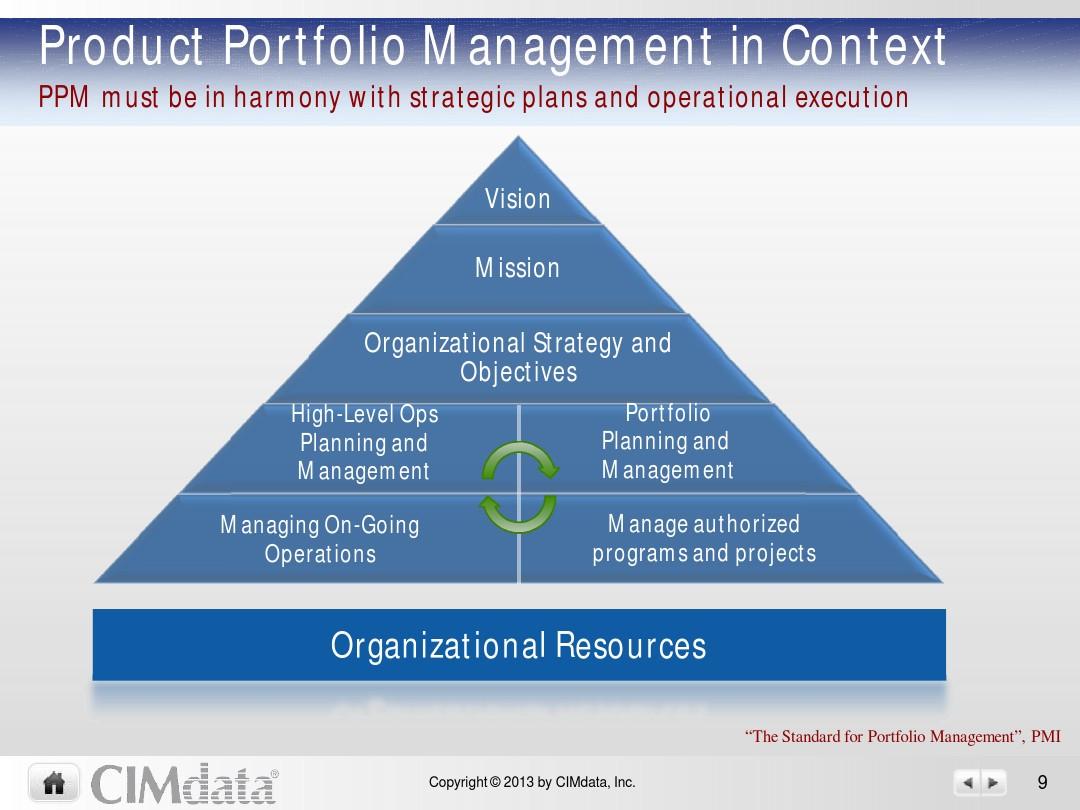
=======================================
Leverage has long been recognized as a powerful tool in portfolio management, capable of amplifying returns—but it also carries increased risks. For investors, understanding the leverage effect on portfolio management is critical to optimize performance while safeguarding against potential losses. This comprehensive guide explores strategies, practical applications, and risk management techniques tailored for both novice and professional traders.
Understanding Leverage in Portfolio Management
Leverage allows investors to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. In portfolio management, its impact is multifaceted, affecting risk, return, and overall portfolio volatility.
Definition and Core Concepts
Leverage is the use of borrowed capital to increase investment exposure. Its primary components in portfolio management include:
- Debt ratio: The proportion of borrowed capital relative to equity.
- Margin requirements: The collateral needed to maintain leveraged positions.
- Portfolio sensitivity: How leverage amplifies gains and losses.
Why Leverage Matters
Understanding leverage is essential because:
- It can enhance returns in bullish markets.
- Mismanagement may magnify losses during downturns.
- It influences asset allocation, portfolio diversification, and risk-adjusted returns.
Visual representation of leverage effects on portfolio performance
Key Methods for Applying Leverage
Investors can apply leverage through multiple strategies, each with distinct advantages and considerations.
Strategy 1: Constant Leverage Allocation
This approach maintains a fixed leverage ratio across all portfolio positions.
Advantages:
- Simple to implement.
- Provides predictable exposure and risk profile.
Disadvantages:
- Can amplify losses if markets turn volatile.
- May require frequent rebalancing to maintain ratios.
Application: Suitable for investors with stable market outlooks and risk tolerance, allowing consistent exposure to high-performing assets.
Strategy 2: Dynamic Leverage Adjustment
Dynamic leverage involves adjusting exposure based on market conditions, volatility, or risk metrics such as Value at Risk (VaR).
Advantages:
- Responds to changing market conditions.
- Reduces downside risk during turbulent periods.
Disadvantages:
- Requires continuous monitoring.
- Can lead to higher transaction costs.
Application: Effective for professional traders and hedge funds who monitor risk in real-time, balancing upside potential with downside protection.
Integrating Leverage into Portfolio Management
Proper integration of leverage requires careful planning, execution, and monitoring.
Risk Assessment and Position Sizing
Leverage magnifies both profits and losses. Risk assessment tools help determine appropriate position sizes to stay within acceptable loss limits.
- Step 1: Define risk tolerance per trade.
- Step 2: Calculate exposure using leverage ratios.
- Step 3: Adjust positions to match the portfolio’s overall risk profile.
Leverage and Asset Diversification
Diversification becomes critical when using leverage. Correlated positions can increase portfolio volatility, while uncorrelated assets help reduce systemic risk.
- Example: Combining equities, bonds, and commodities can balance leveraged exposure.
Diversifying assets to mitigate leverage risks
Advanced Tools and Software Solutions
Professional traders leverage advanced tools to optimize portfolio performance:
- Leverage analytics software for real-time monitoring.
- Simulation tools for backtesting leverage strategies.
- Risk management platforms integrating VaR, stress tests, and exposure metrics.
Comparing Leverage Strategies: Constant vs. Dynamic
| Feature | Constant Leverage | Dynamic Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Low | High |
| Risk Exposure | Fixed | Adjusted based on conditions |
| Potential Returns | Stable | Higher during favorable markets |
| Downside Protection | Limited | Improved during volatility |
| Suitable For | Beginners, long-term investors | Professionals, hedge funds |
Dynamic leverage generally provides superior risk management but requires higher expertise and continuous monitoring.
Case Study: Leverage in a Volatile Market
A hedge fund employed a dynamic leverage strategy during high market volatility:
- Initial leverage: 2x across equities.
- Adjustment: Reduced to 1.2x during market swings.
- Result: The portfolio avoided significant drawdowns while maintaining exposure to profitable opportunities.
Takeaway: Dynamic leverage allows for adaptability and risk control, crucial during periods of uncertainty.
Leveraging Quantitative Insights
Advanced investors often integrate quantitative trading methods to optimize leverage. Tools like how to calculate leverage in quantitative trading and risk assessment software allow precise calibration of leverage ratios, improving portfolio efficiency.
- Quantitative models can simulate multiple scenarios.
- Machine learning algorithms predict volatility, guiding dynamic adjustments.
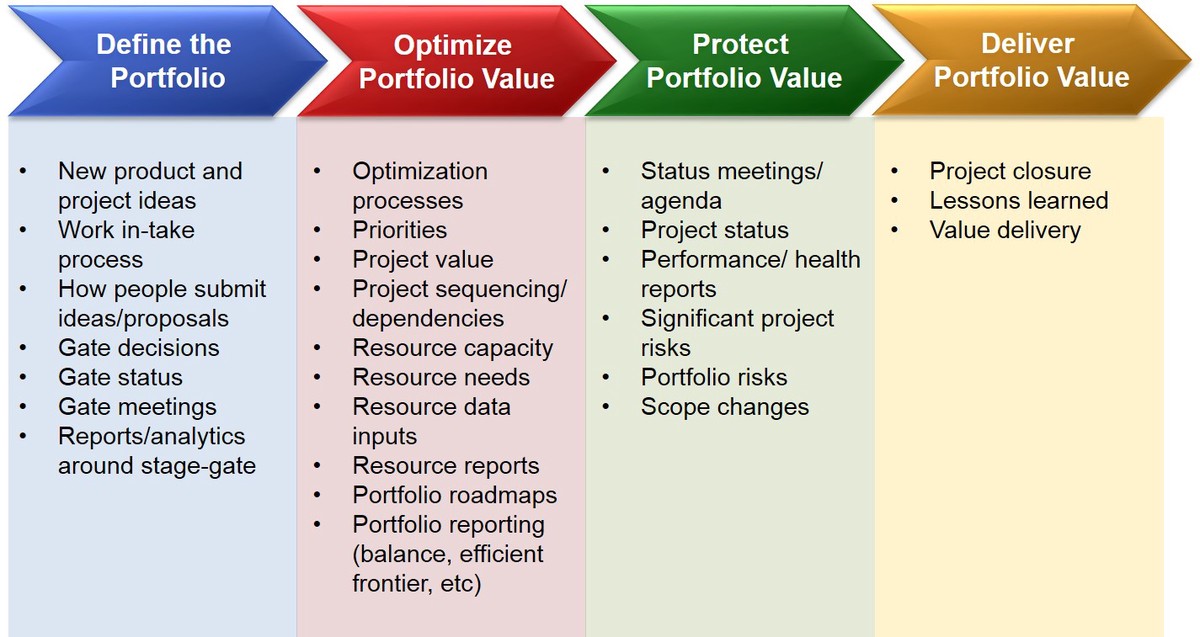
Best Practices for Leverage Management
- Start conservatively: New traders should begin with low leverage ratios.
- Monitor continuously: Market conditions change rapidly.
- Use risk limits: Implement stop-loss orders and margin alerts.
- Diversify strategically: Reduce correlation among assets.
- Educate yourself: Platforms offering leverage courses for beginner traders help build foundational knowledge and practical skills.
FAQ
1. How does leverage affect portfolio returns?
Leverage amplifies both gains and losses. While it can significantly increase profits in favorable markets, it also increases downside risk, making risk management essential.
2. What is the safest way to use leverage in portfolio management?
Use dynamic leverage adjustments, maintain diversified positions, and integrate risk metrics like Value at Risk to monitor potential losses and optimize exposure.
3. Can beginners effectively use leverage in their portfolios?
Yes, but they should start with low leverage ratios, use educational resources, and implement risk controls to avoid large losses.
Conclusion
The leverage effect on portfolio management presents both opportunities and challenges. By understanding different strategies, integrating advanced tools, and practicing disciplined risk management, traders can optimize returns while controlling downside exposure. Combining conservative and dynamic approaches, along with continuous education, ensures that leverage becomes a powerful tool rather than a source of excessive risk.
Engage with this article by sharing your experiences with leverage strategies, asking questions in the comments, and spreading insights to fellow investors seeking to enhance portfolio management.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment