=============================

Introduction
Mean reversion is one of the most widely used trading strategies in quantitative finance. The core concept revolves around the assumption that asset prices tend to revert to their historical average over time. This mean reversion strategy guide explores the fundamentals, practical implementations, advanced techniques, and risk management strategies for traders ranging from beginners to professionals.
By integrating insights from how does mean reversion work in quantitative trading and how to backtest mean reversion models, this guide provides actionable steps to design, implement, and optimize mean reversion strategies.
Understanding Mean Reversion
The Concept of Mean Reversion
Mean reversion assumes that prices oscillate around a statistical mean. When prices deviate significantly from this mean, there is a tendency for them to revert, providing trading opportunities. Key elements include:
- Historical Average (Mean): The reference point for expected price levels.
- Deviation Measures: Standard deviation or Bollinger Bands are commonly used to detect anomalies.
- Time Horizon: Mean reversion may occur over short-term (intraday) or long-term (weeks/months) periods.
Illustration of mean reversion showing price oscillation around the average
Why Mean Reversion Works
Mean reversion is effective due to:
- Market Overreactions: Temporary price spikes or drops often correct themselves.
- Behavioral Biases: Investors’ irrational behavior creates deviations from fundamental values.
- Liquidity Effects: Excessive buying or selling pressure eventually stabilizes prices.
Note: Mean reversion is not guaranteed and may fail during strong trends or structural market changes.
Types of Mean Reversion Strategies
Strategy 1: Statistical Arbitrage
Overview
Statistical arbitrage involves identifying correlated or cointegrated assets and trading deviations from historical relationships. Typical steps include:
- Identify Pairs or Portfolios: Use correlation or cointegration tests.
- Detect Divergence: Measure spread deviation from historical mean.
- Execute Trades: Go long undervalued and short overvalued assets.
Advantages:
- Exploits market inefficiencies.
- Can be automated and scaled across multiple assets.
Limitations:
- Requires robust statistical modeling.
- Sensitive to changes in correlation structures.
Example of a mean reversion pair trading scenario
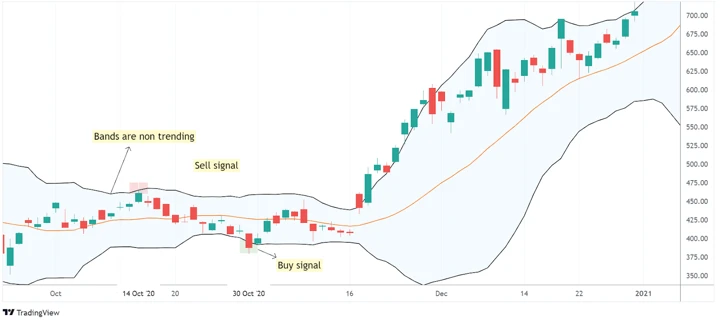
Strategy 2: Bollinger Bands Trading
Overview
Bollinger Bands are a popular technical tool for mean reversion:
- Setup: Middle band represents the moving average; upper and lower bands represent ±2 standard deviations.
- Entry Signals: Buy when price touches the lower band; sell when it hits the upper band.
- Exit Rules: Close positions when price reverts to the mean or middle band.
Advantages:
- Easy to visualize and implement.
- Works well in range-bound markets.
Limitations:
- Can produce false signals in trending markets.
- Requires careful selection of lookback periods and standard deviation multipliers.
Backtesting and Implementation
Step 1: Data Preparation
- Collect historical price data and calculate moving averages, standard deviations, or spreads.
- Clean data to remove outliers or anomalies.
Step 2: Strategy Testing
- Use backtesting frameworks to simulate trades.
- Analyze key performance metrics: Sharpe ratio, drawdown, win/loss ratio.
- Adjust parameters based on historical performance.
Step 3: Risk Management
- Set maximum position sizes and stop-loss thresholds.
- Incorporate volatility-adjusted sizing to reduce exposure during high-risk periods.
- Monitor ongoing performance to detect strategy decay.
Flowchart of backtesting mean reversion strategies
Advanced Techniques
Strategy 1: Adaptive Mean Reversion
- Adjust mean and thresholds dynamically using exponentially weighted moving averages.
- Benefits: Responsive to changing market volatility.
- Limitations: More complex to implement and backtest.
Strategy 2: Machine Learning Integration
- Use ML models to detect patterns of deviation and predict reversion likelihood.
- Benefits: Potentially higher accuracy and adaptability.
- Limitations: Requires significant data and expertise.
Comparative Analysis
| Strategy | Pros | Cons | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical Arbitrage | Exploits correlations, scalable | Model sensitive, data-intensive | Pair trading across equities or ETFs |
| Bollinger Bands | Simple, visual | False signals in trends | Range-bound markets |
| Adaptive Mean Reversion | Responds to volatility | Complex implementation | Highly volatile markets |
| ML Integration | Predictive, adaptable | Requires data & expertise | Multi-asset portfolios |
FAQ
1. How does mean reversion differ from momentum trading?
Momentum strategies exploit trends, assuming assets will continue moving in the same direction. Mean reversion assumes prices revert to a historical average, capitalizing on overreactions or deviations.
2. Why use mean reversion in forex trading?
Forex markets often exhibit cyclical behavior and temporary overshooting due to economic announcements, making them suitable for mean reversion strategies.
3. How to backtest mean reversion models effectively?
Use historical price data, simulate trades with realistic execution costs, and evaluate performance metrics like Sharpe ratio, maximum drawdown, and consistency across market regimes. Include out-of-sample testing to validate robustness.

Conclusion
Mean reversion offers a systematic way to capture market inefficiencies and overreactions. From statistical arbitrage to Bollinger Bands trading, and extending to adaptive or machine learning-enhanced techniques, traders have multiple approaches to implement mean reversion. By combining robust backtesting, dynamic risk management, and careful strategy selection, mean reversion strategies can become a reliable component of a diversified trading portfolio.
Summary of key mean reversion strategies and their applications

0 Comments
Leave a Comment