=========================================================================================
Mean reversion is a cornerstone concept in trading and investment, allowing investors to capitalize on temporary price deviations from an asset’s historical average. For both retail and institutional investors, mean reversion techniques for investors provide a structured framework to enhance returns while controlling risk. This article explores practical strategies, advanced methods, and real-world applications to leverage mean reversion effectively.
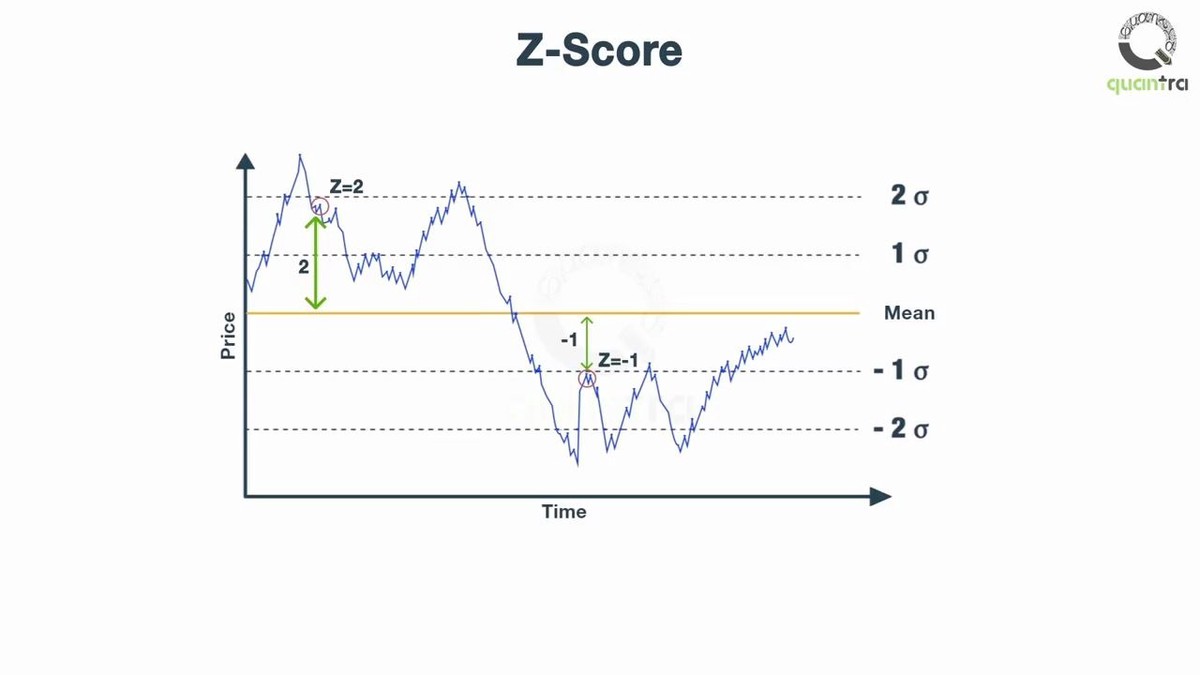
Understanding Mean Reversion
What is Mean Reversion?
Mean reversion is the financial principle that asset prices tend to revert to their historical average over time. It implies that periods of extreme price movements are often followed by corrections toward the mean.
Core Concepts:
- Historical Mean: Average price or return over a defined period
- Deviation: Difference between current price and the mean
- Reversion Signal: Indicator that price may revert to the mean
Internal Link Integration: Understanding how does mean reversion work in quantitative trading provides a foundation for developing algorithmic strategies that exploit temporary mispricings.
Why Mean Reversion is Effective
- Market Inefficiencies: Prices temporarily deviate due to overreaction or underreaction.
- Predictable Patterns: Statistical evidence supports recurring price corrections.
- Portfolio Stabilization: Helps manage volatility by targeting assets trading far from intrinsic value.
Core Mean Reversion Techniques
1. Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage involves identifying pairs of correlated assets whose prices diverge temporarily. Investors go long on the undervalued asset and short on the overvalued one, expecting convergence toward the mean.
Steps:
- Identify correlated pairs using historical data
- Calculate spread deviation from mean
- Establish thresholds for entry and exit
- Execute trades when divergence exceeds the threshold
Pros:
- Exploits relative mispricing efficiently
- Works across multiple asset classes
Cons:
- Requires rigorous statistical modeling
- Correlation breakdown can lead to losses
2. Bollinger Bands Strategy
Bollinger Bands use moving averages and standard deviations to define upper and lower price boundaries. Price movements near the bands can signal mean reversion opportunities.
Application:
- Buy when price touches lower band, expecting upward correction
- Sell when price reaches upper band, anticipating downward adjustment
Pros:
- Simple visualization of price extremes
- Effective for intraday and swing trading
Cons:
- Can produce false signals in strong trends
- Requires calibration for different market conditions
Illustration showing a stock price reverting to its mean within Bollinger Bands.
Advanced Implementation Strategies
Algorithmic Mean Reversion
Algorithmic trading enables precise execution of mean reversion strategies at scale. Techniques include:
- Mean Reversion in High-Frequency Trading: Exploiting micro-level deviations across stocks or derivatives
- Portfolio Mean Reversion: Balancing positions across multiple securities to maintain overall risk-adjusted returns
Internal Link Integration: Investors can learn how to implement mean reversion in trading algorithms to automate decision-making and enhance speed of execution.
Risk Management Techniques
- Dynamic Position Sizing: Adjust trade size based on volatility
- Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Rules: Protect against extended deviations
- Diversification: Apply mean reversion across multiple assets to reduce idiosyncratic risk
Practical Examples and Case Studies
Case Study 1: Equity Pairs Trading
- Scenario: Two historically correlated tech stocks diverge in price
- Action: Go long on undervalued stock and short overvalued stock
- Outcome: Convergence occurs within three weeks, generating 5% risk-adjusted return
Case Study 2: Commodity Mean Reversion
- Scenario: Crude oil prices spike due to temporary supply disruption
- Action: Buy on dip when price drops below historical mean
- Outcome: Price returns to mean over one month, capturing profitable trade
Comparison of actual price movement vs historical mean showing successful mean reversion trade.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Why Mean Reversion Fails Sometimes
- Extended Trends: Strong market momentum can prevent price from reverting quickly
- Incorrect Mean Calculation: Using inappropriate timeframes can skew mean estimates
- Market Regime Changes: Shifts in volatility or correlation patterns reduce predictability
Solutions:
- Backtest strategies across multiple market conditions
- Use dynamic means (e.g., moving averages) instead of fixed historical averages
- Combine with other indicators to confirm signals
FAQ: Mean Reversion for Investors
1. How does mean reversion differ from momentum trading?
Momentum trading follows the trend, betting that price will continue moving in the same direction, whereas mean reversion expects correction toward historical averages. Combining both can create balanced strategies.
2. Where to find mean reversion strategies?
Reliable sources include algorithmic trading platforms, financial research publications, and specialized trading courses offering step-by-step guidance.
3. How to backtest mean reversion models effectively?
Use historical price data to simulate trades, incorporate transaction costs, and test across various market regimes to ensure robustness and realistic performance evaluation.
Best Practices for Investors
- Apply mean reversion across diversified assets
- Integrate quantitative and qualitative analysis
- Continuously monitor and adjust thresholds and parameters
- Use technology for efficient execution and risk management
Flowchart outlining key steps for executing a mean reversion investment strategy.
Conclusion
Mean reversion techniques for investors offer structured ways to exploit price anomalies while managing risk. By combining statistical methods, Bollinger Bands, and algorithmic execution, investors can enhance returns and reduce exposure to adverse market conditions.
Engage & Share: Experiment with mean reversion strategies, discuss insights with your network, and leverage these techniques to optimize portfolio performance.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment