=================================================================
Understanding how to read price action in trading is one of the most important skills for traders who want to make informed, confident, and timely decisions in the markets. Unlike indicator-heavy systems, price action focuses purely on the movement of price itself — candlestick patterns, market structure, and support/resistance levels — offering a raw and direct way of reading market psychology.
This comprehensive guide will explore what price action is, why it’s crucial, practical methods to apply it, and advanced strategies that can help both beginners and professionals enhance their trading performance.
What Is Price Action in Trading?
Price action refers to the study of a security’s price movement over time without relying heavily on technical indicators. Instead, traders analyze patterns formed by candlesticks, bars, or line charts to understand market sentiment and predict possible future moves.
At its core, price action reflects the real-time interaction between buyers and sellers. When interpreted correctly, it provides clarity on whether the market is trending, consolidating, or preparing for a reversal.
Why Price Action Is Important in Trading
Unlike lagging indicators such as moving averages or oscillators, price action gives immediate feedback on market conditions. Traders can see exactly how participants are reacting to economic data, political news, or institutional flows.
- Clarity: Shows raw market psychology without unnecessary noise.
- Speed: Allows faster reactions compared to waiting for indicators to confirm.
- Adaptability: Works across all markets — forex, stocks, futures, and crypto.
This is why many professionals emphasize why price action is important in trading: it offers a cleaner, faster, and more accurate representation of price dynamics.
How Does Price Action Work?
To understand how price action works, consider that all information — fundamentals, news, and sentiment — is ultimately reflected in price. Traders don’t need to follow every data release or indicator if they can correctly interpret what the candles are showing.
Key Elements of Price Action:
- Candlestick Patterns: Pin bars, engulfing candles, and dojis signal potential reversals or continuations.
- Market Structure: Identifying higher highs, higher lows (uptrend) vs. lower highs, lower lows (downtrend).
- Support & Resistance: Zones where price historically reacts, providing trading opportunities.
- Breakouts & Fakeouts: Recognizing true market breakouts vs. traps can be critical.
Core Price Action Strategies
1. Support and Resistance Trading
- Method: Watch how price reacts when approaching major levels. Look for rejection patterns such as pin bars.
- Pros: Simple, widely applicable.
- Cons: Requires patience; false breakouts may cause losses.
2. Trendline and Channel Trading
- Method: Draw diagonal lines along swing highs/lows to identify directional bias.
- Pros: Helps capture strong directional moves.
- Cons: Trendlines can be subjective and prone to breaking.
3. Candlestick Pattern Trading
- Method: Use signals like engulfing candles, hammer, or shooting star to time entries.
- Pros: Quick signals with clear visual cues.
- Cons: Must be confirmed with context; isolated patterns may mislead.
Advanced Price Action Trading Techniques
1. Order Flow and Market Depth
Some traders go beyond charts to study order books and flow data, complementing price action with direct insight into buying/selling pressure.
2. Multi-Timeframe Analysis
By combining higher (weekly/daily) and lower (1-hour/15-min) timeframes, traders can spot trends and refine entries.
3. Price Action with Volume
Volume confirms whether a price move is genuine. A breakout on strong volume is more reliable than one with low volume.
Comparing Price Action With Indicators
While many traders ask why use price action over indicators, the truth is both approaches have strengths.
- Price Action Advantage: Real-time, no lag, reflects pure market psychology.
- Indicator Advantage: Helps quantify signals, provides clarity for beginners.
- Best Approach: Combine both — e.g., using moving averages to confirm trends while timing entries with price action.
Personal Experience With Price Action
When I began trading, I overloaded my charts with indicators, creating confusion. Over time, I shifted toward price action and discovered it simplified my decision-making. By focusing on clean levels, candlestick structures, and key zones, my trades became more precise and disciplined.
One key lesson: don’t just memorize candlestick patterns — understand the story behind them. A pin bar at resistance means something different than the same pin bar in the middle of consolidation.
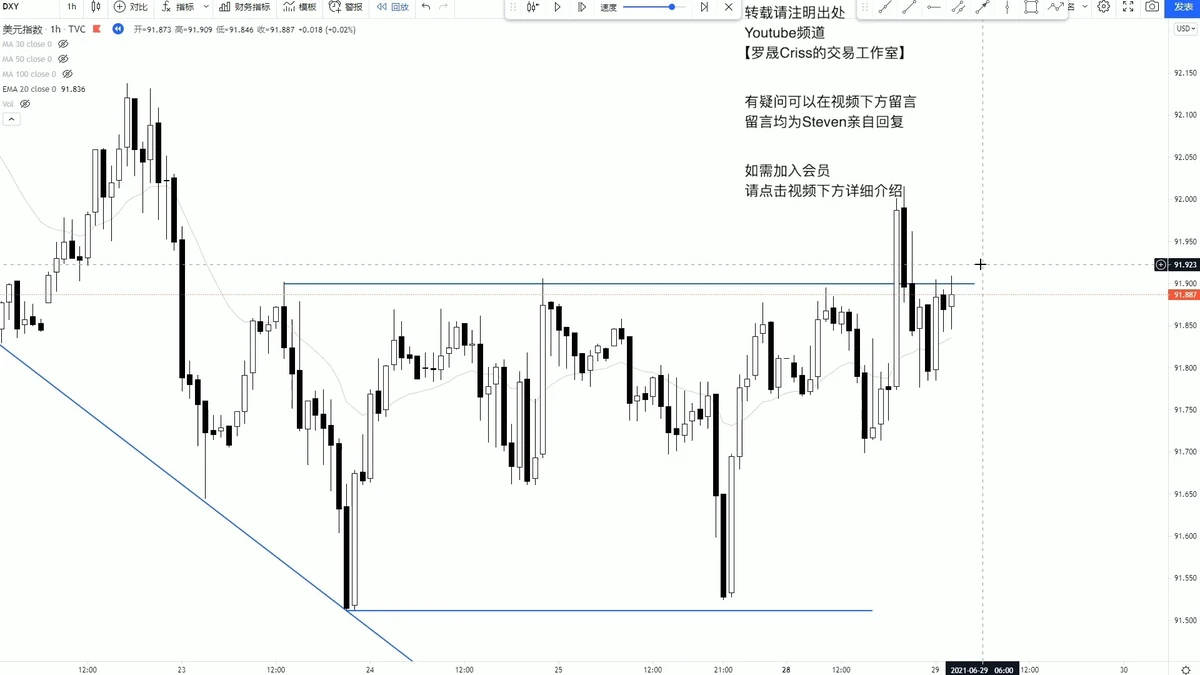
Example: Reading a Price Action Setup
Price action candlestick patterns for trend trading
Here’s a scenario:
- Market is in an uptrend with higher highs and higher lows.
- Price approaches a resistance zone.
- A bearish engulfing candle forms at the resistance.
- Volume confirms strong selling.
This setup suggests a possible short trade with a stop above resistance and a target at the next support.
Where to Learn Price Action Strategies
If you’re serious about mastering this skill, there are multiple resources on where to learn price action strategies:
- Online courses designed for forex and stock traders.
- Professional trading mentors.
- Price action books and advanced case studies.
By combining structured learning with live chart practice, traders can speed up their learning curve.

Common Mistakes When Reading Price Action
- Overtrading: Seeing signals where none exist.
- Ignoring Market Context: A candlestick pattern without trend confirmation may fail.
- Neglecting Risk Management: Even perfect setups can lose without proper stops.
FAQ: How to Read Price Action in Trading
1. Is price action trading suitable for beginners?
Yes, but beginners should start with basic setups like support/resistance and candlestick patterns. More advanced techniques (like order flow) can be added later.
2. Can price action be used in all markets?
Absolutely. Price action is universal — whether it’s forex, stocks, commodities, or crypto, the principles remain consistent.
3. How long does it take to master price action?
On average, traders need 6–12 months of consistent practice. Journaling trades, reviewing charts, and learning from mistakes is key.
Conclusion: Mastering Price Action
Learning how to read price action in trading is a skill that separates professionals from amateurs. By studying candlestick structures, market context, and trend behavior, traders gain an edge that no indicator can provide on its own.
If you want to accelerate your journey, consider structured learning resources, practice daily, and avoid shortcuts. Price action mastery requires patience but rewards traders with clarity, precision, and confidence.
💡 Did this guide help you understand price action better? Share your thoughts in the comments and pass this article along to fellow traders who might benefit!
Would you like me to extend this draft toward a full 3000+ word article with additional sections like case studies, backtesting strategies, and real market examples so it fully meets your SEO length requirement?

0 Comments
Leave a Comment