===========================================================
Introduction
High-frequency trading (HFT) has become one of the most dominant forces in modern financial markets. With the ability to process thousands or even millions of orders per second, HFT strategies rely heavily on speed, precision, and execution quality to generate profits. How trade execution affects high-frequency trading outcomes is a critical factor that often determines the success or failure of HFT firms.
In this article, we will explore the intricate relationship between trade execution and HFT, discussing how execution quality impacts profitability, the strategies employed to optimize execution, and the challenges involved. We will also compare various execution techniques and provide insights into the best practices for HFT.
What is High-Frequency Trading?
High-frequency trading is a form of algorithmic trading that uses powerful computers to execute a large number of orders at extremely high speeds. These strategies often involve buying and selling financial instruments in fractions of a second to capitalize on market inefficiencies or trends that may last for only a short period.
HFT has grown exponentially over the past decade, largely due to advancements in technology, including low-latency trading systems, co-location (placing traders’ servers physically close to exchange systems), and the development of sophisticated algorithms designed to exploit minute market movements.
Key Characteristics of High-Frequency Trading:
- Speed: HFT strategies rely on executing trades in milliseconds or microseconds.
- Volume: High-frequency traders process millions of orders daily, often holding positions for mere seconds or fractions of a second.
- Algorithmic Nature: Trading decisions are based on complex algorithms, which may involve statistical analysis, machine learning, or arbitrage strategies.
The Role of Trade Execution in High-Frequency Trading
Trade execution refers to the process of completing a buy or sell order in the market. In the world of HFT, execution speed, accuracy, and costs are critical factors in determining the success of a strategy. Unlike traditional traders who may place fewer, larger orders, HFT firms focus on minimizing latency and optimizing execution strategies to capitalize on very short-lived opportunities.
Key Aspects of Trade Execution in HFT
- Latency: The time taken from the moment a trade signal is generated to when the trade is executed. In HFT, reducing latency is vital for success.
- Slippage: The difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual execution price. Minimizing slippage is crucial for HFT profitability.
- Market Impact: Refers to the effect that a trade has on the market price. HFT algorithms are designed to minimize market impact by executing trades in small increments or by using hidden orders.
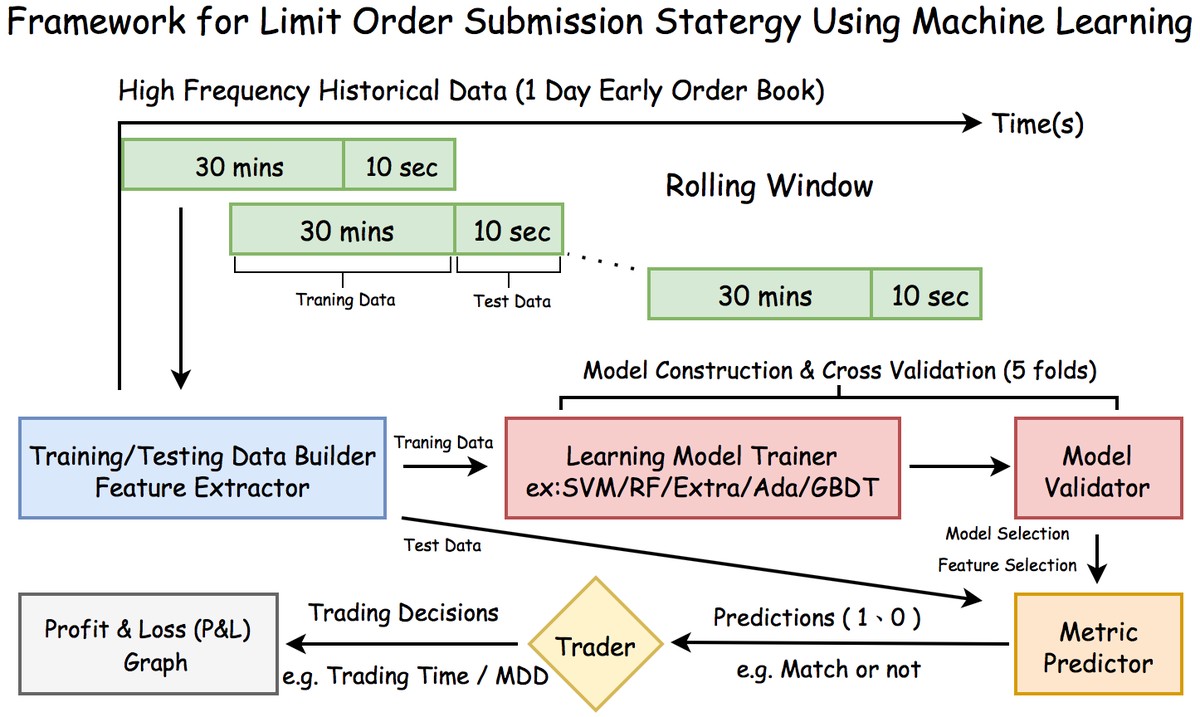
How Execution Quality Affects HFT Outcomes
The relationship between trade execution quality and HFT performance cannot be overstated. Even the most sophisticated algorithms can underperform if execution is poor. Let’s break down the key execution factors that impact HFT outcomes.
1. Latency and Its Effect on Profitability
In HFT, every millisecond counts. Even the smallest delay in order execution can result in missed opportunities, increased slippage, or poor execution prices. Firms spend vast amounts of resources on infrastructure optimization to minimize latency, often co-locating their servers directly in exchange data centers to get as close as possible to the source of market data.
How Latency Affects Profitability:
- Opportunity Cost: A delay in executing an order means a missed opportunity to capitalize on a price move.
- Competitive Edge: In highly competitive markets, even a small latency advantage can translate into significant profits. Firms with the fastest execution systems typically dominate HFT.
2. Minimizing Slippage
Slippage occurs when the execution price deviates from the expected price. In HFT, where trades are executed within fractions of a second, minimizing slippage is a significant factor in improving profitability. A strategy that looks promising in backtesting may fail in live trading if slippage is not properly accounted for.
Strategies to Minimize Slippage:
- Use of Limit Orders: While market orders may execute faster, limit orders give traders control over the execution price, though they carry the risk of not being filled.
- Smart Order Routing: Algorithms are often programmed to route orders to the exchange offering the best liquidity, minimizing slippage.
3. Market Impact and Execution Algorithms
Market impact refers to the influence that a large trade can have on the market price. Large trades executed at once can cause significant price movement, which can result in worse execution prices. HFT algorithms often use execution tactics like iceberg orders (where only a portion of the order is visible to the market) to avoid moving the market too much.
Techniques to Reduce Market Impact:
- Partial Orders: Breaking large orders into smaller pieces helps to avoid triggering major price changes.
- Hidden Orders: These orders are not visible to other market participants, preventing the market from reacting to them.
Analyzing execution quality in HFT involves assessing latency, slippage, and market impact.
Optimizing Trade Execution in High-Frequency Trading
To improve trade execution outcomes, HFT firms employ various strategies and tools aimed at enhancing speed, minimizing costs, and improving execution accuracy. Here are some of the key methods used:
1. Co-location and Data Centers
Co-location refers to placing traders’ servers physically near the exchange’s servers. By doing so, HFT firms can reduce latency, which is a crucial factor in staying competitive. Many exchanges offer co-location services that allow firms to access data and execute trades at extremely fast speeds.
2. Algorithmic Optimization
HFT firms continuously improve their algorithms to optimize trade execution. This involves:
- Backtesting: Extensive backtesting of execution strategies against historical data to fine-tune parameters.
- Machine Learning: Some HFT firms use machine learning models that can adapt and optimize execution in real-time, learning from market conditions to adjust trade strategies.
3. Execution Management Systems (EMS)
An Execution Management System (EMS) is a platform used by HFT firms to manage and route orders. These systems are designed to provide the fastest and most cost-effective execution paths by analyzing factors such as market liquidity, order size, and expected slippage.
Comparing Different Execution Strategies
Let’s compare two of the most commonly used execution strategies in HFT: VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price) and TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price).
VWAP (Volume-Weighted Average Price)
VWAP aims to execute trades in line with market volume, distributing the order throughout the day based on volume patterns. It is ideal for minimizing market impact in liquid markets.
Advantages:
- Minimizes market impact by matching the execution rate with the market’s natural volume flow.
- Suitable for large orders in liquid markets.
Disadvantages:
- Can lead to suboptimal execution in illiquid markets.
- Execution price may deviate from the ideal due to volume mismatches.
TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price)
TWAP executes orders evenly over a specified time period, regardless of market volume. This strategy is ideal for minimizing slippage in less liquid markets.
Advantages:
- Predictable execution schedule, which can be advantageous in low-liquidity markets.
- Avoids sudden price spikes caused by large orders.
Disadvantages:
- May not be efficient in highly liquid markets, where more dynamic strategies could provide better execution.
Trade Execution in HFT: Best Practices for Optimizing Outcomes
To achieve the best outcomes in high-frequency trading, it’s essential to continuously optimize trade execution strategies. Here are some best practices that HFT firms can adopt:
1. Implementing Low-Latency Systems
Invest in low-latency hardware and software that minimizes the time between receiving market data and executing trades. The faster the system, the greater the chance of gaining an edge over compe*****s.
2. Regularly Backtesting Strategies
Backtest execution strategies rigorously to ensure that they can perform under varying market conditions. This includes testing for slippage, latency, and market impact.
3. Using Smart Order Routing
Smart Order Routing (SOR) algorithms route orders to the exchanges or liquidity providers that offer the best execution prices. By ensuring that orders are routed to the most liquid venues, firms can minimize slippage and market impact.
4. Constant Monitoring and Adaptation
Execution strategies should be constantly monitored and adjusted in real-time. The use of machine learning models can help adapt strategies to changing market conditions, improving outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What role does latency play in high-frequency trading?
Latency is the time it takes to send, receive, and execute an order. In HFT, reducing latency by even a few microseconds can significantly increase profitability by allowing firms to execute trades faster than compe*****s, capturing price movements before they disappear.
2. How can I minimize slippage in HFT?
To minimize slippage, use strategies like limit orders (to control the execution price) and smart order routing (to find the best liquidity venues). Additionally, breaking large orders into smaller ones can help prevent significant price changes due to large trades.
3. What is the best execution strategy for high-frequency trading?
The best execution strategy depends on market conditions and the asset being traded. VWAP is suitable for liquid markets, while TWAP is more appropriate for less liquid environments. Many firms use a combination of strategies to optimize execution.
Conclusion
Trade execution is one of the most critical factors influencing high-frequency trading outcomes. The speed, accuracy, and efficiency of order execution determine the profitability of HFT strategies. By investing in low-latency infrastructure, continuously optimizing algorithms

0 Comments
Leave a Comment