============================================================================
Executing a limit order successfully is a crucial skill for traders, whether you’re in stocks, forex, crypto, or any other financial market. Limit orders provide you with more control over your trades and allow you to enter or exit positions at specific prices. But to truly master limit orders, you need to understand how to implement them efficiently, manage them strategically, and avoid common pitfalls.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the concept of limit orders, explore the best strategies for executing them, and help you optimize your trading approach. We’ll also cover the key differences between limit orders and market orders, and answer some common FAQs about limit order placement.
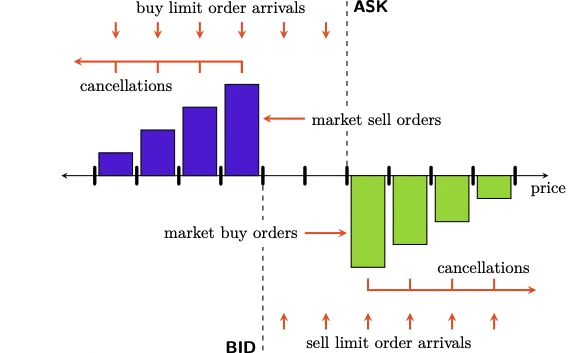
What is a Limit Order?
A limit order is an order to buy or sell a security at a specific price or better. It ensures that you won’t pay more than a preset amount when buying, or sell for less when exiting a position. The key advantage of using limit orders is that they allow you to control the price at which your trade is executed. However, there is no guarantee that the order will be filled, especially if the market price does not reach your limit price.
Types of Limit Orders
- Buy Limit Orders: These orders are placed below the current market price, ensuring that you’re purchasing at a price that is favorable to you.
- Sell Limit Orders: These orders are placed above the current market price, ensuring that you sell at a price that meets your profit targets.
How Does a Limit Order Work?
When you place a limit order, your broker will queue it in the market until the price reaches your specified level. Once the price matches your limit price or better, the order is executed. If the price doesn’t reach the limit, the order remains open until it’s either filled, canceled, or expires, depending on the conditions you’ve set.

Best Practices for Executing Limit Orders
To successfully execute a limit order, you must understand when to place it, how to optimize the order size, and how to ensure the best chances of the order being filled. Below are two proven strategies for executing limit orders effectively:
Strategy 1: Time-Based Limit Orders
Time-based limit orders are used to control the duration of your limit order. Traders often use this strategy to ensure that their orders are only active during certain market conditions. There are several types of time-based limits:
- Day Orders: This order is valid only for the day. If the price isn’t met by the end of the trading day, the order will be canceled.
- Good Till Canceled (GTC) Orders: This order remains active until it is filled or canceled. GTC orders are useful for traders who are willing to wait for an optimal price over multiple trading days.
Pros:
- You have more control over the trade execution.
- It aligns well with both short-term and long-term trading strategies.
Cons:
- There’s a risk of missing out on opportunities if the market moves rapidly and doesn’t reach your limit price.
Strategy 2: Price-Based Limit Orders
Price-based limit orders involve setting a specific price at which you’re willing to buy or sell. A well-executed price-based limit order can be an effective way to ensure that you don’t overpay or undersell a security.
Example: You set a buy limit order at \(50 for a stock currently trading at \)52. If the stock price falls to $50 or below, your order will be executed. If it doesn’t, your order remains unfilled.
Pros:
- You protect yourself from market volatility by ensuring that you enter or exit positions at your desired price.
Cons:
- There’s no guarantee that the order will be filled, especially in fast-moving markets.
Key Considerations When Using Limit Orders
To execute a limit order successfully, consider the following:
1. Market Liquidity
Liquidity plays a significant role in the success of limit orders. In highly liquid markets, limit orders are more likely to be filled because prices tend to move more predictably. However, in less liquid markets, it may take longer for your order to fill, or it may not fill at all.
Tip: Consider setting limit orders during periods of high market activity or when liquidity is at its peak.
2. Spread Between Bid and Ask
The difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay (bid) and the lowest price a seller will accept (ask) is critical to the success of a limit order. A narrow spread increases the likelihood of your order being filled.
Tip: Place buy limit orders near the ask price and sell limit orders near the bid price to increase the chances of execution.
3. Order Size
The size of your limit order also influences whether it will be filled. Larger orders in illiquid markets may not be completely filled at your limit price. Break larger orders into smaller ones if necessary, and place them strategically over time.
How to Avoid Mistakes with Limit Orders
Limit orders are powerful tools, but they come with the risk of mistakes if not used carefully. Here are some common mistakes and how to avoid them:
1. Setting Unrealistic Prices
Avoid placing a limit order at an unrealistic price. If you’re too aggressive with your price expectations, your order might never get filled.
Tip: Set your limit price based on realistic price targets, and avoid setting it too far from the current market price unless you’re willing to wait for a longer time.
2. Ignoring Order Expiration
If you don’t specify the duration of your order, you may find that it sits unfilled for an indefinite period.
Tip: Always set an expiration time that suits your trading strategy. Whether it’s for the day or a longer-term order, know when you want your order to expire.
3. Failing to Monitor Market Conditions
Market conditions can change rapidly. If you place a limit order and don’t monitor market movements, you might miss out on better execution prices or have your order stay unfilled.
Tip: Regularly review your limit orders, especially during volatile market conditions, to ensure they remain aligned with your strategy.
FAQ: Common Questions About Limit Orders
1. How Often Do Limit Orders Get Filled?
Limit orders are more likely to be filled in liquid markets with a narrow bid-ask spread. In slower markets or with larger orders, they may go unfilled. For high-frequency traders, it’s essential to adjust limit orders dynamically based on real-time market data.
2. Can I Modify or Cancel My Limit Order?
Yes, most brokers allow you to modify or cancel limit orders at any time before they are filled. However, if you’ve placed a limit order as part of a time-sensitive strategy, it’s essential to monitor your trades closely.
3. How Do I Know Which Limit Order to Use?
The best limit order to use depends on your trading strategy. A day order is typically used for short-term trades, while a GTC order might be more appropriate for long-term trades. Always align the type of limit order with your broader market strategy.
Conclusion: Optimizing Limit Orders for Success
Executing a limit order successfully involves understanding your market, setting the right prices, and choosing the appropriate order type based on your strategy. Whether you’re using limit orders for short-term trading or long-term investment, they offer significant control and the potential for improved execution compared to market orders. By applying the strategies outlined above and avoiding common mistakes, you can enhance your trading experience and increase your chances of success.
For more advanced insights on how limit orders can improve your trading strategy, consider exploring topics like how to set a limit order in quantitative trading, or why use limit orders in trading.
Remember, successful limit order execution requires a combination of technical knowledge, market awareness, and strategic planning. Stay informed, adjust your orders as needed, and practice to perfect this essential trading skill.
Feel free to share your thoughts on limit order strategies or any experiences you’ve had with them in the comments below!

0 Comments
Leave a Comment