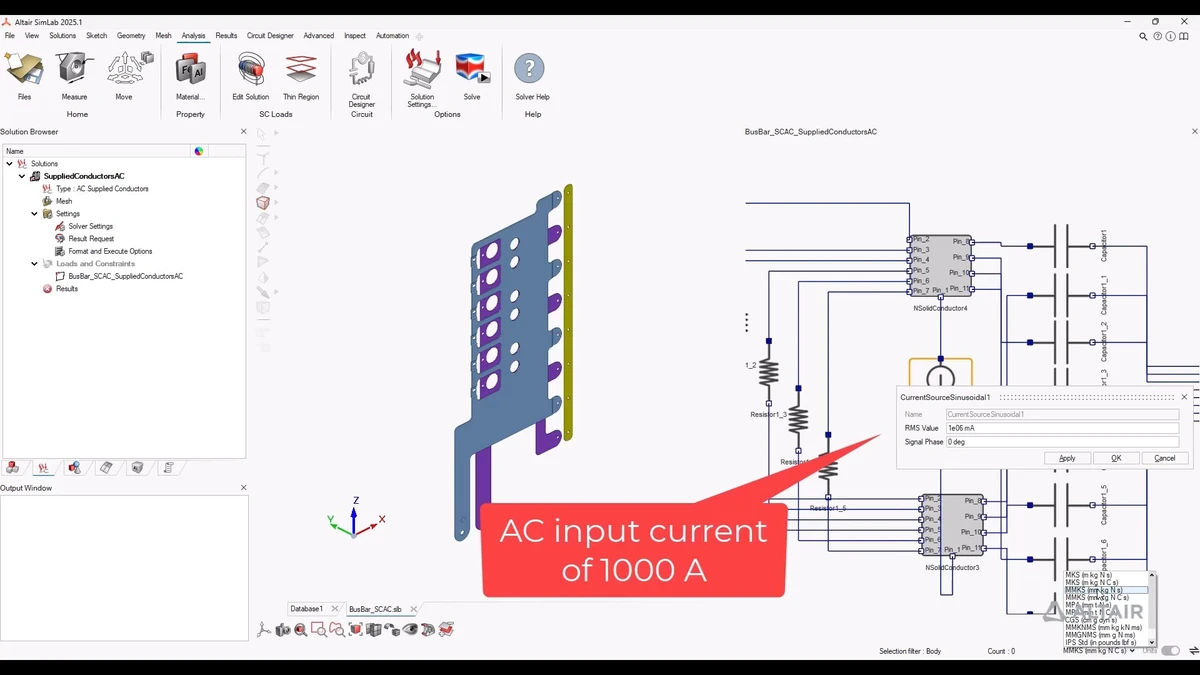
Quantitative trading has become an integral part of modern financial markets, with strategies based on mathematical models, statistical analysis, and algorithmic decision-making. For quantitative trading experts, the ability to simulate trading strategies is essential for refining models, testing hypotheses, and enhancing performance before going live. In this article, we explore the role of advanced simulation for quantitative trading experts, the tools and techniques that make simulations effective, and how these simulations can elevate your trading strategies.
What is Quantitative Trading Simulation?
Quantitative trading simulation is the process of using computer-based models to replicate the dynamics of financial markets and test trading strategies under various conditions. By simulating market behavior, quantitative traders can assess the effectiveness of their strategies, identify potential weaknesses, and refine their models without risking real capital.
Simulations help experts validate their algorithms by testing them against historical data, adjusting parameters, and tweaking models based on performance. This process not only reduces the risks associated with live trading but also provides valuable insights into market behavior and algorithm performance.
Importance of Simulation for Quantitative Trading
Simulating trading strategies before execution is critical for several reasons:
Risk Management: Testing strategies on simulated data allows traders to identify risks and weaknesses in their algorithms before using real money. By optimizing risk parameters, traders can reduce the chances of large drawdowns and improve the robustness of their strategies.
Strategy Evaluation: A well-executed simulation enables traders to evaluate various strategies under different market conditions. This gives them an idea of how the strategy would perform during periods of high volatility, low liquidity, or other market stresses.
Performance Improvement: Simulation allows traders to experiment with different techniques, test multiple variations of their models, and optimize parameters to improve overall strategy performance. By doing so, they can uncover new ways to enhance returns.
Backtesting: Advanced simulations are often used for backtesting, where traders can apply their strategies to historical data to assess how well they would have performed in the past. This process provides confidence in the strategy’s potential profitability in real-market conditions.
Real-Time Testing: In some advanced simulations, traders can test strategies with live market data but with simulated trades. This gives them real-time insights into the viability of their strategies while preventing any exposure to actual financial risk.
Techniques for Advanced Simulation in Quantitative Trading
- Monte Carlo Simulation
Monte Carlo simulation is a powerful technique used to model the probability of different outcomes in a process that cannot easily be predicted due to the intervention of random variables. This method is particularly useful in finance for simulating the random paths of asset prices or market conditions.
For example, using Monte Carlo methods, a trader can simulate the price movements of an asset like Bitcoin or Ethereum under different scenarios, taking into account volatility, liquidity, and market sentiment. This helps determine the probability distribution of potential outcomes and allows for better risk management.
- Agent-Based Simulation
Agent-based simulation involves modeling the behavior of individual market participants, or “agents,” and observing how their interactions can create larger market phenomena. Each agent is programmed with a set of rules or strategies that guide its behavior, such as buying, selling, or holding assets based on certain conditions.
In the context of cryptocurrency markets, agent-based simulations are particularly useful in replicating the decentralized, highly dynamic behavior of these markets. By simulating various market participants (traders, bots, and institutions), experts can observe how different strategies and trading volumes affect overall market liquidity and price movements.
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT) Simulation
High-frequency trading relies on algorithms that execute a large number of orders within milliseconds. Simulating HFT strategies is crucial for ensuring that the algorithms work efficiently and effectively in ultra-low-latency environments.
Advanced simulation tools allow traders to test how their HFT strategies will perform under extreme market conditions, such as during significant price movements or sudden liquidity shocks. This helps traders optimize their algorithms for speed and ensure that they can execute orders quickly and with minimal slippage.
- Factor-Based Simulations
Factor-based simulation involves testing trading strategies that rely on predefined factors (such as momentum, value, or volatility) to drive trading decisions. By simulating how different factors affect asset prices over time, traders can refine their models to focus on the most predictive variables.
For example, using factor-based simulation, a trader could test a strategy that buys assets with low volatility and sells those with high volatility. This type of simulation helps identify the effectiveness of each factor and how it impacts overall strategy performance.
- Portfolio Simulation
Quantitative traders often manage large portfolios of multiple assets. Portfolio simulation helps evaluate the performance of a portfolio under different market scenarios and conditions. These simulations can factor in correlations between assets, risk management rules, and liquidity constraints.
Advanced portfolio simulations allow traders to assess the diversification benefits of holding various assets, measure portfolio risk using Value-at-Risk (VaR), and optimize asset allocation to minimize risk and maximize returns.
Tools for Advanced Quantitative Trading Simulation
Several tools and platforms have been developed to help quantitative traders run advanced simulations:
QuantConnect: A cloud-based algorithmic trading platform that allows for backtesting and simulating strategies on historical data. It provides access to both traditional financial instruments and cryptocurrencies, making it ideal for multi-asset simulations.
Backtrader: A popular Python-based framework for backtesting and simulating trading strategies. It offers advanced features like data handling, risk management, and order execution simulation.
TradeStation: A platform known for its powerful backtesting and simulation tools, TradeStation is widely used by professionals to test complex trading strategies and optimize their performance.
AlgoTrader: A quantitative trading platform that supports both live trading and advanced simulation. It allows for backtesting, strategy optimization, and the ability to simulate multi-asset portfolios.
Simul8: A tool often used for agent-based simulations, Simul8 is ideal for creating models of market participants and understanding how their collective behavior can impact market conditions.
Best Practices for Quantitative Trading Simulation
- Realistic Data Input
For simulations to be effective, it is important to use high-quality, realistic data. This includes historical price data, market depth, trading volumes, and order book data. Traders should also incorporate factors like transaction costs, slippage, and latency into their simulations to better mirror real-world conditions.
- Parameter Optimization
Advanced simulation allows for fine-tuning model parameters. For example, adjusting moving averages, stop-loss levels, or other trading indicators can drastically affect performance. Using grid search or genetic algorithms can help find the optimal set of parameters for a given strategy.
- Stress Testing
Simulations should include stress testing, which involves testing strategies under extreme conditions, such as market crashes, sudden volatility spikes, or liquidity shortages. This helps identify potential weaknesses in a strategy and adjust it for better robustness.
- Iterative Testing and Refinement
Rather than testing a strategy only once, successful quantitative traders iterate on their models. After each simulation, analyze the results and make adjustments. This iterative process helps uncover patterns, optimize parameters, and improve strategy performance.
- Simulation with Live Data
To get the most realistic results, traders should test their strategies with live data feeds, running simulations with real-time market data to better understand how strategies perform in actual market conditions.
FAQs about Advanced Simulation for Quantitative Trading
- What is the difference between backtesting and simulation?
Backtesting refers to testing a trading strategy using historical data, while simulation often involves testing a strategy with real-time data or market conditions. Simulations may also incorporate agent-based models, Monte Carlo simulations, or stress tests to better replicate market behavior.
- Can simulations predict future market movements?
Simulations cannot predict future movements with certainty. They are tools for testing hypotheses and strategies under different scenarios. However, they can help identify profitable strategies and optimize parameters to improve future performance.
- What programming languages are commonly used for quantitative trading simulation?
Python is one of the most popular languages for quantitative trading simulation due to its rich ecosystem of libraries (such as NumPy, pandas, and SciPy). Other languages like R, C++, and Java are also used, particularly for high-frequency trading simulations or when performance is critical.
Conclusion
Advanced simulation plays a critical role in the development and refinement of quantitative trading strategies. By simulating real-world market conditions, traders can better understand the risks, optimize their models, and gain valuable insights into how their strategies will perform in various market scenarios. Whether using Monte Carlo, agent-based models, or high-frequency trading simulations, experts can take advantage of these tools to fine-tune their approaches and improve their chances of success in the competitive world of quantitative trading.
Internal Links:
How to use simulation in quantitative trading
| Topic | Description | Key Strategies | Advantages | Disadvantages | Tips for Beginners |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day Trading | Buying and selling financial instruments within a single day. | Scalping, Breakout Trading | Quick results, exciting, small capital required. | High risk, most retail traders lose money. | Start small, focus on one or two strategies. |
| Scalping Strategy | Make numerous trades to capture small price movements. | Timeframes: 1–5 minutes, Indicators: VWAP, EMA | Quick profits, reduces overnight risks, many trades. | Requires high focus, fees can eat into profits. | Ideal for fast-paced traders. |
| Breakout Trading Strategy | Trade when price breaks key support/resistance levels with strong momentum. | Timeframes: 5–15 minutes, Tools: Trendlines, Bollinger Bands | Captures big moves, works well in volatile markets. | False breakouts, requires patience. | Better for traders preferring fewer, higher-quality trades. |
| Quantitative Day Trading | Uses algorithms and mathematical models to automate decision-making. | RSI, automated entry and exit points | Removes emotions, automates decisions. | Can be complex for beginners, requires coding skills. | Start with drag-and-drop tools for non-coders. |
| Backtesting Importance | Testing strategies on historical data to validate performance. | Use platforms like TradingView, MetaTrader | Helps to understand win/loss ratio, drawdowns. | Historical data may not reflect future conditions. | Always backtest before using real money. |
| Common Mistakes | Trading without a plan, over-leveraging, letting emotions control decisions. | Focus on a plan, risk management, avoid overtrading | Improved discipline, controlled risk. | Can be hard to stick to the plan under pressure. | Avoid over-leveraging and emotional trading. |
| Best Strategy for Beginners | Breakout trading is usually better due to clear signals and fewer trades. | Focus on breakout trades with clear momentum | Clearer setups, fewer trades per day. | False breakouts, requires patience. | Start with breakout trading for clarity. |
| Required Capital | Minimum capital to start day trading varies by market (stocks, forex, crypto). | Stocks: \(25,000, Forex/Crypto: \)500–$1,000 | Lower capital required for forex/crypto. | Stock market requires higher initial capital. | Start with small capital and focus on risk management. |

0 Comments
Leave a Comment