
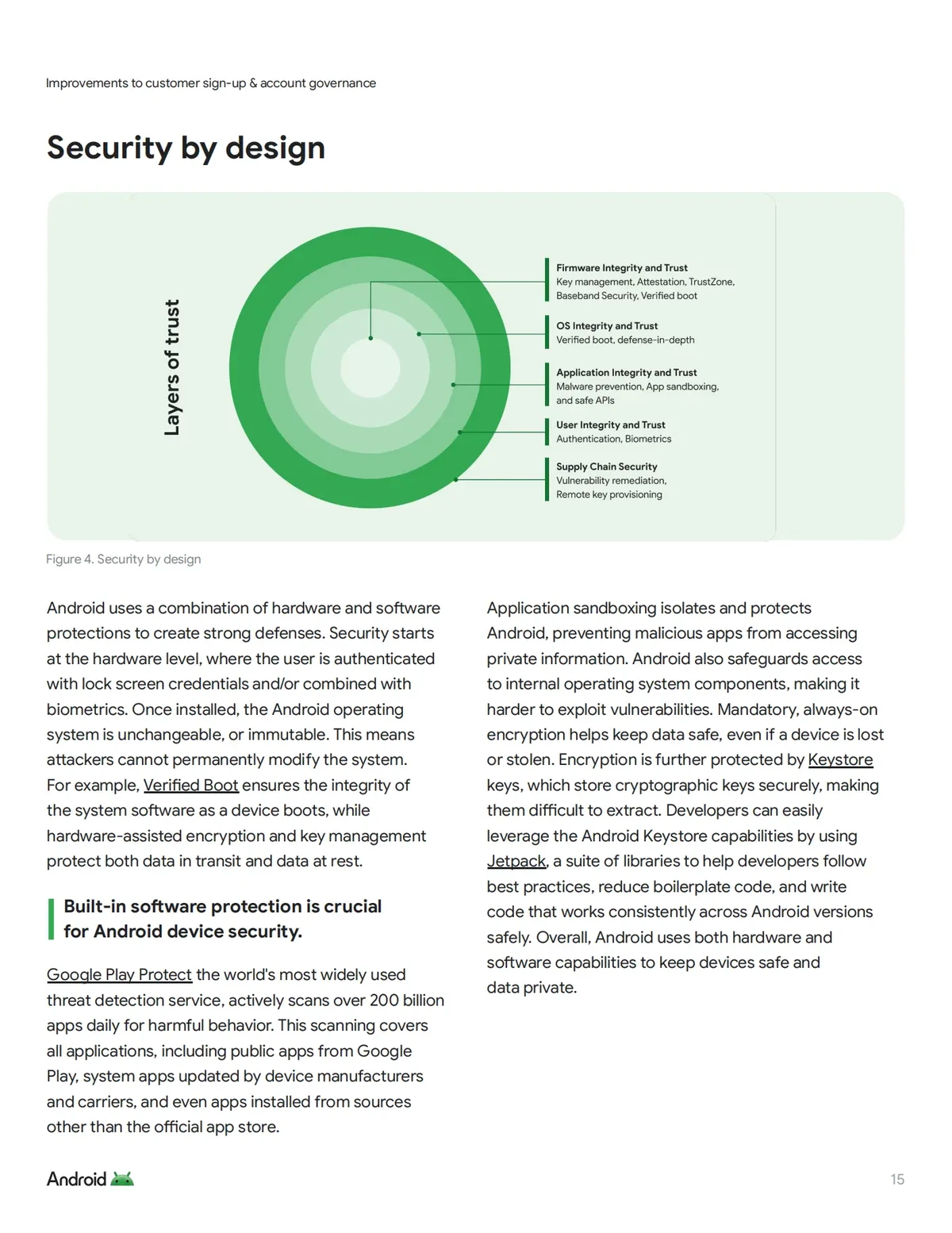
Introduction
For forex traders, backtesting is an indispensable tool that allows them to assess the effectiveness of their trading strategies before committing real money to the markets. This process involves applying a trading strategy to historical data to see how it would have performed in the past. While it’s not a guarantee of future performance, backtesting helps traders make informed decisions based on past market behavior.
In this guide, we’ll explore the critical aspects of backtesting for forex traders, comparing different methods and strategies, discussing tools and platforms, and providing real-world examples. By the end of this guide, you will understand how to use backtesting to improve your trading decisions, reduce risk, and increase profitability.
Table of Contents
Why Backtesting is Important for Forex Traders
How to Perform Backtesting in Forex Trading
2.1. Manual Backtesting
2.2. Automated Backtesting
Backtesting Strategies for Forex Traders
3.1. Trend Following Strategies
3.2. Mean Reversion Strategies
Backtesting Tools and Platforms for Forex Traders
Common Backtesting Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Analyzing Backtesting Results
FAQ: Backtesting for Forex Traders
Conclusion
Why Backtesting is Important for Forex Traders
In forex trading, making decisions based on technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and market sentiment is part of the daily routine. However, without testing these strategies against historical data, traders may not have a reliable benchmark for performance. Here’s why backtesting is a crucial practice:
Validation of Strategies: Backtesting allows traders to validate whether their trading ideas or strategies are likely to be profitable under real-world conditions.
Risk Management: By analyzing past performance, traders can estimate the potential drawdowns and risk involved in the strategy. This information helps in setting stop-loss orders and risk-reward ratios.
Optimization: Backtesting helps traders optimize their strategies by tweaking parameters (e.g., moving averages, RSI thresholds, or trade sizes) to maximize profitability.
Confidence: Having a strategy that has been tested with historical data increases confidence, reducing the emotional aspect of trading.
Backtesting Tools and Platforms for Forex Traders
To backtest your strategies efficiently, you need the right tools and platforms. Some popular backtesting platforms used by forex traders include:
MetaTrader 4 (MT4): A widely used platform with built-in backtesting tools for manual and automated testing.
TradingView: Provides a user-friendly interface for backtesting, along with a wide range of charting options.
NinjaTrader: Known for its powerful automated backtesting and optimization capabilities.
Amibroker: Offers advanced backtesting tools and data analysis features.
How to Perform Backtesting in Forex Trading
Backtesting can be done in several ways, depending on the resources and tools you have. The two most common approaches are manual backtesting and automated backtesting. Below, we’ll compare the two and explain their advantages and disadvantages.
2.1. Manual Backtesting
Manual backtesting involves going through historical data and executing trades based on the rules of your strategy. Traders usually do this by manually placing trades on charts, recording the results, and analyzing performance.
Steps for Manual Backtesting:
Choose a time period: Select the historical period you want to test.
Apply your strategy: Use your trading strategy to identify trade setups on the charts.
Record the trades: Note the entry and exit points, as well as any stop losses and take profits.
Analyze results: After completing the test, analyze the performance of your trades (win rate, profit factor, maximum drawdown, etc.).
Pros:
Helps you deeply understand your strategy’s performance.
Ideal for beginners who are learning the ropes of trading and backtesting.
Cons:
Extremely time-consuming.
Prone to human errors and biases.
2.2. Automated Backtesting
Automated backtesting involves using backtesting software or programming to run the strategy against historical data. It’s more efficient and less error-prone than manual testing, especially for large datasets.
Steps for Automated Backtesting:
Choose a backtesting platform (like MT4, TradingView, or NinjaTrader).
Program the strategy: Code your strategy’s rules into the platform using its specific scripting language (e.g., MQL4 for MT4).
Run the test: Let the software run the strategy against historical data and generate a detailed performance report.
Analyze the results: The platform will provide detailed analytics, including equity curve, win rate, drawdowns, and more.
Pros:
Faster and more efficient than manual backtesting.
Reduces human errors and biases.
Ideal for testing complex strategies on large datasets.
Cons:
Requires knowledge of coding (e.g., MQL4, Pine Script).
Limited to the platform’s capabilities.
Backtesting Strategies for Forex Traders
When performing backtesting, the type of strategy you test plays a significant role in the results. Below, we’ll explore two common strategies used by forex traders: trend-following and mean-reversion.
3.1. Trend Following Strategies
Trend-following strategies aim to capitalize on the momentum of the market. These strategies often involve indicators like Moving Averages, MACD, and ADX to identify and follow market trends.
Example: Moving Average Crossover Strategy
In this strategy, traders use a short-term moving average (e.g., 50-period) and a long-term moving average (e.g., 200-period). A bullish crossover occurs when the short-term moving average crosses above the long-term moving average, signaling a buy. Conversely, a bearish crossover happens when the short-term moving average crosses below the long-term moving average, signaling a sell.
Backtesting Trend Following:
Test the crossover strategy using historical data from different market conditions (e.g., trending, ranging).
Analyze key performance metrics like win rate, profit factor, and drawdowns.
Use the results to tweak the strategy for better risk management and profitability.
3.2. Mean Reversion Strategies
Mean reversion strategies are based on the idea that prices tend to return to their average over time. These strategies often use indicators like the Bollinger Bands or RSI to identify when a currency pair is overbought or oversold.
Example: RSI-Based Mean Reversion Strategy
In this strategy, traders look for an RSI above 70 (overbought) for a potential sell or RSI below 30 (oversold) for a potential buy.
Backtesting Mean Reversion:
Backtest the RSI strategy on currency pairs known for mean-reverting behavior.
Track entry and exit points, and evaluate the results across multiple time frames.
Modify parameters to optimize the strategy for varying market conditions.
Common Backtesting Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
While backtesting is essential for refining trading strategies, traders often make several mistakes during the process. These include:
Overfitting: Creating a strategy that performs well on historical data but fails in real-market conditions.
Avoid it: Keep the strategy simple and robust by testing it on different market periods.
Ignoring Transaction Costs: Not factoring in spreads, commissions, and slippage can lead to unrealistic results.
Avoid it: Always include transaction costs in your backtesting calculations.
Data Snooping: Using the same data multiple times or optimizing parameters until the results look too good to be true.
Avoid it: Use out-of-sample testing to validate the strategy on unseen data.
Analyzing Backtesting Results
Once you have completed the backtest, it’s crucial to analyze the results to determine whether the strategy is worth trading with real money. Key metrics to consider include:
Win rate: Percentage of winning trades.
Profit Factor: Ratio of gross profit to gross loss.
Maximum Drawdown: The largest peak-to-trough decline in the equity curve.
Sharpe Ratio: Measure of risk-adjusted return.
By analyzing these metrics, you can identify strengths and weaknesses in your strategy and make adjustments as needed.
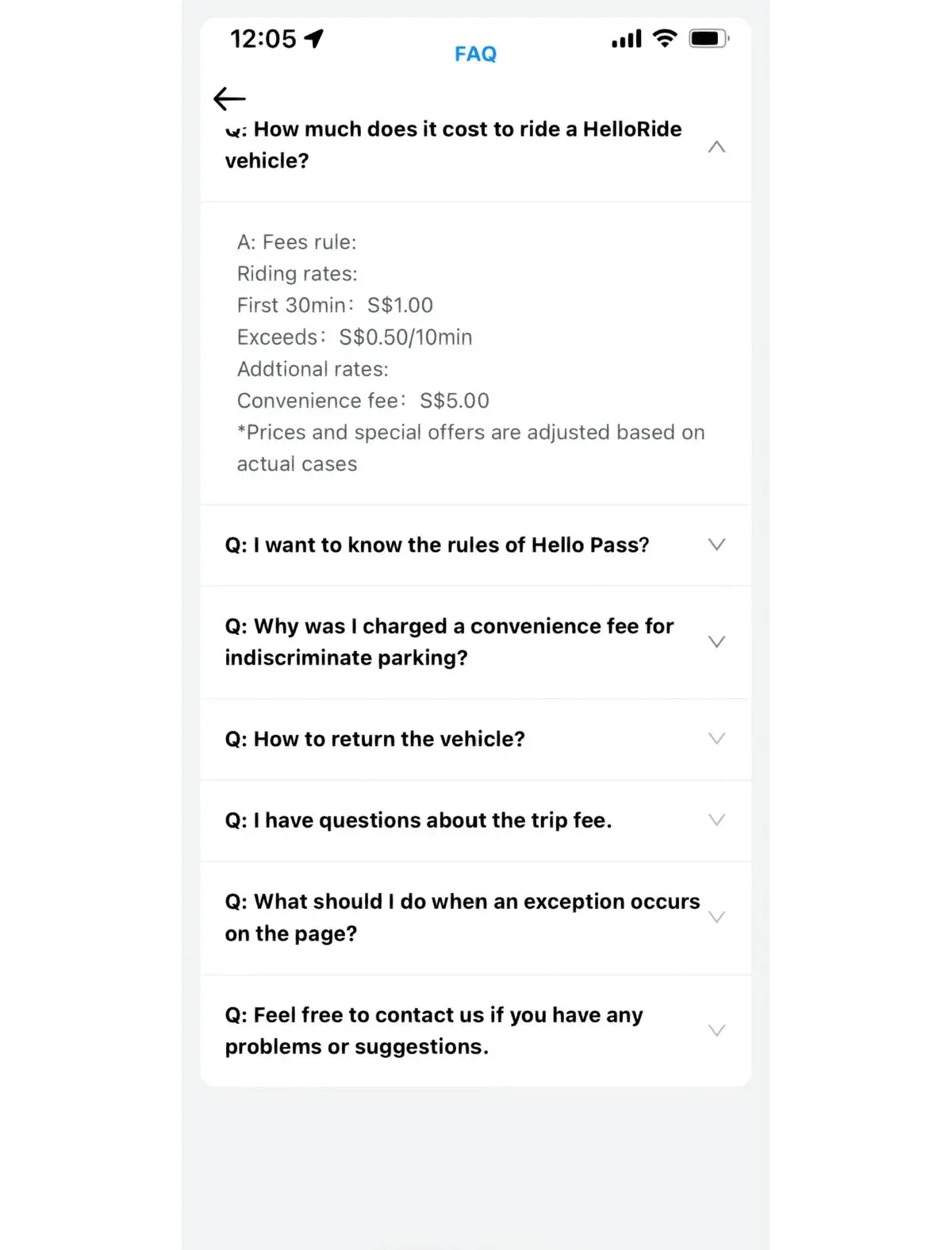
FAQ: Backtesting for Forex Traders
- How do I choose the right backtesting platform for forex trading?
Choosing the right platform depends on your trading strategy and needs. For beginners, MetaTrader 4 (MT4) offers simple backtesting tools, while more advanced traders may prefer NinjaTrader or TradingView for their advanced features and custom scripting options.
- Can backtesting guarantee future profitability?
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| What is an API in Crypto Trading? | API connects crypto exchanges to external applications for tasks like retrieving market data, automating trades, and tracking portfolios. |
| Importance for Beginners | 1. Efficiency: Automates tasks 2. Speed: Faster than humans 3. Customization: Tailored strategies 4. Market Data: Access to real-time info for decision-making. |
| Core Functions of Crypto APIs | 1. Market Data Access 2. Trade Execution 3. Risk Management 4. Portfolio Tracking |
| Strategy 1: SMA Crossover Bot | Monitors moving averages (e.g., 10-day vs 50-day) and places trades on crossovers. Easy but may generate false signals. |
| Strategy 2: Arbitrage via API | Monitors price differences across exchanges and executes trades. Requires fast execution and multiple exchange accounts. |
| Choosing the Right API | 1. Ease of Integration 2. Security Features 3. Exchange Compatibility 4. Support & Community |
| Risks of Using APIs | 1. Security Risks 2. Over-Reliance on Automation 3. Exchange Downtime 4. Coding Errors |
| Personal Experience | Started with a simple SMA crossover bot on Binance API. Key lessons: test strategies, start small, monitor trades closely. |
| Best Practices for Beginner Traders | 1. Secure API Keys 2. Limit Permissions 3. Use Testnets 4. Set Realistic Expectations 5. Track Performance |
| FAQ: Starting with APIs | 1. Register on an exchange, generate API key, follow guides. 2. API trading is safe with security measures. 3. Coding knowledge helps, but not required. |
| Final Thoughts | APIs are a powerful tool for beginners. Start small, use secure APIs, and gradually build technical knowledge for more advanced setups. |

0 Comments
Leave a Comment