======================================
In the world of trading and investing, managing risk is essential to ensure long-term success. One of the most crucial concepts for assessing risk is drawdown—the peak-to-trough decline in the value of a portfolio or asset. Understanding drawdown is key for both individual traders and institutional investors. This article will explore drawdown analysis tools and techniques, helping traders and analysts identify potential risks, minimize losses, and develop better strategies for mitigating drawdowns.
What is Drawdown?
Drawdown refers to the reduction in the value of an asset or portfolio from its peak to its trough. It is typically expressed as a percentage, representing the extent of the loss relative to the highest point before the downturn. For example, if a portfolio’s value drops from \(100,000 to \)80,000, the drawdown would be 20%.
Types of Drawdown
- Maximum Drawdown (MDD): The largest peak-to-trough loss experienced over a given period.
- Trailing Drawdown: The most recent drawdown, calculated over a rolling period.
- Relative Drawdown: The drawdown relative to the previous peak, giving insight into how much value is lost before recovery.
Understanding these types of drawdowns allows traders to assess risk more effectively, track losses, and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Why Drawdown Analysis Matters
Drawdown analysis is a critical part of assessing the risk of an investment or trading strategy. By examining past drawdowns, traders can estimate potential risks and make informed decisions about future trades.
For instance, maximum drawdown helps investors understand the worst-case scenario for an asset or portfolio, providing insight into how much capital could potentially be lost during a market downturn. This is particularly important for quantitative traders, who often rely on risk models to guide their decision-making.
How Drawdown Affects Trading Strategy
A trader’s risk tolerance will directly influence the way they manage drawdowns. For instance, a trader with a low tolerance for risk may decide to exit a position at the first sign of a drawdown, while a trader with a higher risk appetite may allow more room for volatility before making a decision.
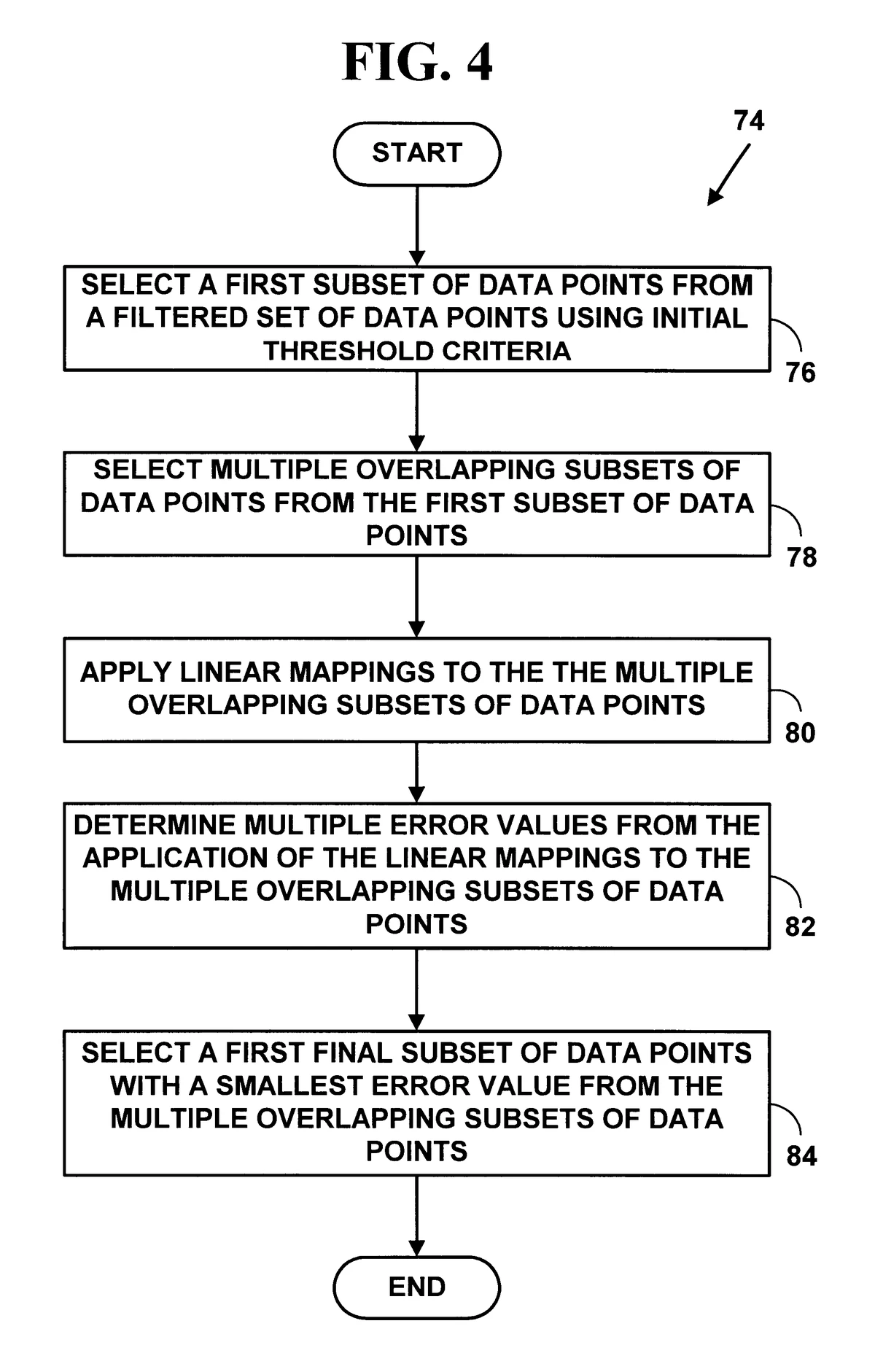
Drawdown Analysis Tools and Techniques
There are various tools and techniques available to perform drawdown analysis. Below, we’ll discuss two primary methods: manual drawdown calculation and automated drawdown tracking software. Each method has its advantages and drawbacks, depending on the trader’s needs and resources.
1. Manual Drawdown Calculation
Manual drawdown calculation is a traditional approach that requires traders to monitor the value of their portfolio over time and compute the drawdown based on historical data. This method can be useful for smaller portfolios or traders who prefer hands-on analysis.
Steps for Manual Calculation:
- Track Portfolio Values: Record the portfolio’s value at regular intervals (daily, weekly, or monthly).
- Identify the Peak: Find the highest portfolio value before the drawdown begins.
- Identify the Trough: Find the lowest portfolio value during the drawdown.
- Calculate the Drawdown: Subtract the trough value from the peak value, then divide by the peak value. Multiply by 100 to get the drawdown percentage.
Pros:
- Simple to Use: Ideal for traders who do not rely on complex tools or software.
- Increased Control: Traders can manually adjust the analysis to suit their preferences or trading strategy.
Cons:
- Time-Consuming: Calculating drawdowns manually can be tedious, especially for large portfolios or frequent trading.
- Prone to Human Error: Manual tracking may result in mistakes or inaccuracies, which can affect the reliability of the analysis.
2. Automated Drawdown Tracking Software
Automated drawdown tracking software uses real-time data to monitor and calculate drawdowns for portfolios or trading strategies. These tools provide a more efficient and reliable way to track drawdowns, especially for traders managing large amounts of data or using complex trading strategies.
Some popular tools include:
- TradingView: A platform that allows traders to track drawdowns in real time using its built-in indicators.
- MetaTrader 4⁄5: A widely used trading platform that includes various plugins for calculating drawdown.
- Excel with Add-ons: Custom Excel spreadsheets with advanced formulas and data integration can automate drawdown calculations for quantitative traders.
Pros:
- Real-Time Data: Instant feedback on drawdowns, allowing for quick decision-making.
- Automation: Reduces manual work and minimizes the risk of human error.
- Advanced Features: Many software tools offer additional functionalities, such as risk management alerts or detailed analytics on drawdown history.
Cons:
- Cost: Some software solutions may require a subscription or upfront cost.
- Learning Curve: Advanced tools may have a steep learning curve for beginners.
Best Practices for Reducing Drawdowns
While no one can completely eliminate the possibility of a drawdown, traders can implement strategies to reduce the severity and frequency of drawdowns. Below are some common practices to minimize risk.
1. Risk Management Strategies
Effective risk management is the cornerstone of any trading strategy. By using tools like stop-loss orders, position sizing, and diversification, traders can protect themselves from severe drawdowns.
- Stop-Loss Orders: A stop-loss order automatically exits a trade if the price moves against the position by a specified amount, limiting losses during a drawdown.
- Position Sizing: Adjusting position size based on risk tolerance helps control the potential impact of a drawdown on the overall portfolio.
- Diversification: Spreading risk across multiple assets or strategies can reduce the impact of a single asset’s drawdown on the overall portfolio.
2. Drawdown Recovery Techniques
Drawdowns are often temporary, and traders can employ recovery techniques to bounce back. Some recovery strategies include:
- Risk Parity: Adjusting the portfolio to maintain balanced risk across different assets or asset classes.
- Rebalancing: Regularly rebalancing the portfolio ensures that it aligns with the trader’s desired risk profile and prevents excessive exposure to underperforming assets.
FAQ
1. How do I calculate drawdown in quantitative trading?
In quantitative trading, drawdown is typically calculated using historical price data. To calculate the drawdown, you would subtract the lowest portfolio value (trough) from the highest portfolio value (peak) during a specific period. You can use Python libraries like Pandas or dedicated risk management software to automate the process.
2. What causes drawdown in markets?
Drawdowns occur due to various factors, including market crashes, economic downturns, or poor trading decisions. In some cases, drawdowns are caused by unexpected events or volatility, which leads to large price fluctuations. For instance, geopolitical events or sudden interest rate changes can trigger significant drawdowns.
3. How can I manage drawdown effectively?
Managing drawdown involves adopting strong risk management techniques, such as position sizing, stop-loss orders, and diversification. Additionally, using drawdown monitoring tools helps traders stay aware of potential risks and take action before the drawdown becomes too severe.
Conclusion
Drawdown analysis is an essential aspect of managing risk in trading and investing. By utilizing both manual calculation methods and automated tracking software, traders can gain better insight into their portfolio’s performance during downturns. Implementing sound risk management strategies and recovery techniques can help reduce drawdowns and ensure long-term success in the markets.
By understanding and controlling drawdowns, traders can not only protect their capital but also improve their ability to navigate volatile market conditions.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment