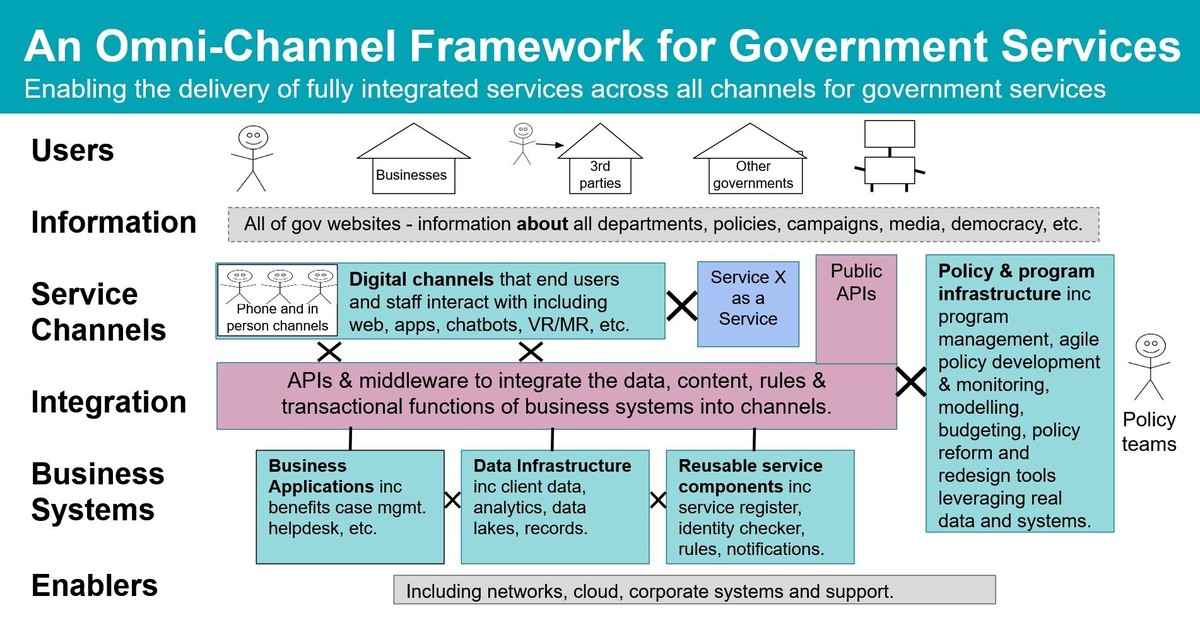
==============================================
Institutional investors—such as pension funds, hedge funds, insurance companies, and sovereign wealth funds—are constantly seeking sophisticated tools to manage risk and optimize portfolio returns. One of the most influential models for capturing volatility dynamics in financial markets is the Generalized Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity (GARCH) model. In this article, we explore the GARCH applications for institutional investors, highlighting practical strategies, real-world examples, and advanced methodologies.
By the end, you will gain a clear understanding of how GARCH fits into institutional decision-making, its benefits and limitations, and best practices for implementation.
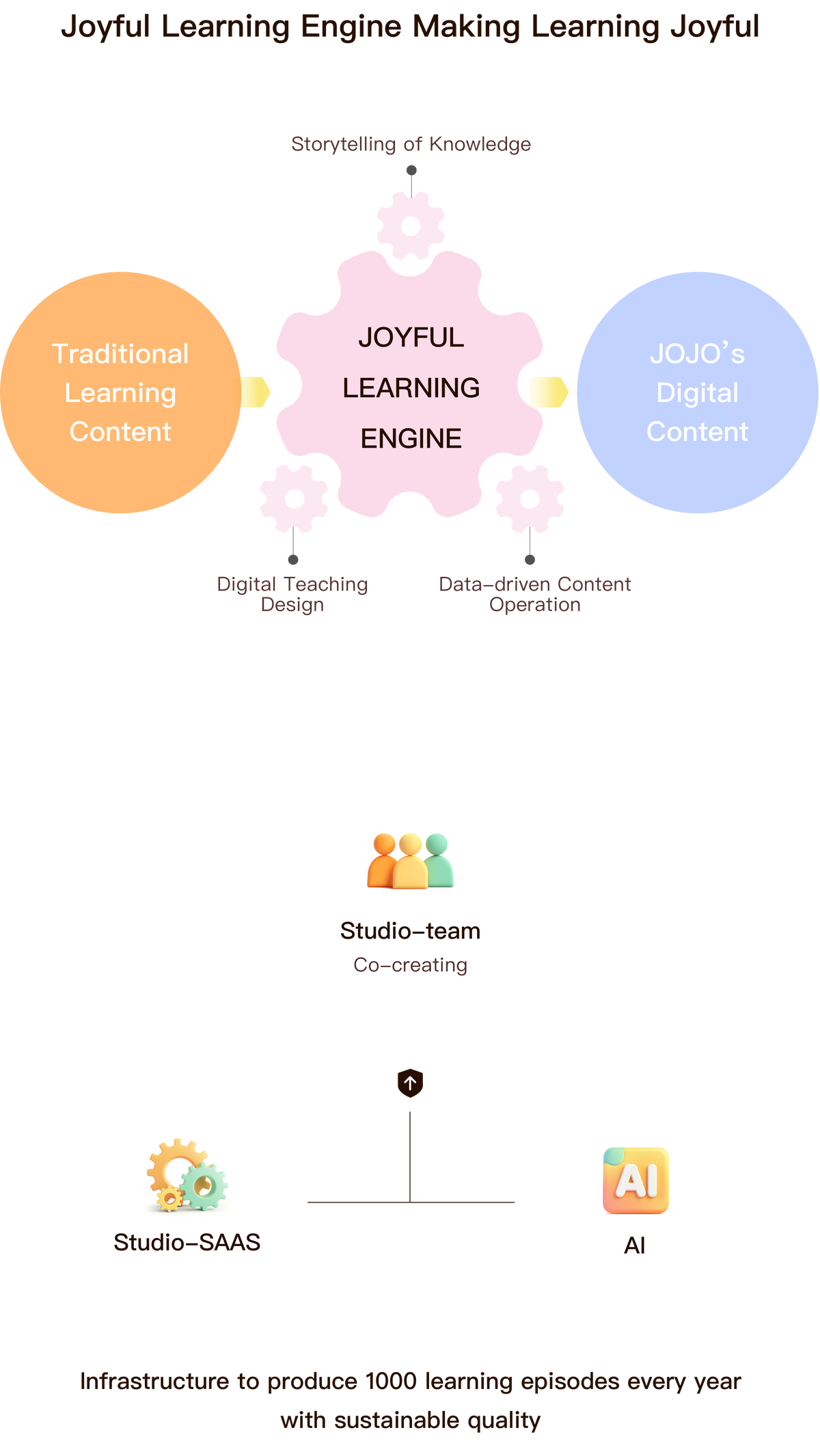
Understanding GARCH in Institutional Context
What Is GARCH?
The GARCH model, developed by Tim Bollerslev in 1986, extends the ARCH model by capturing conditional heteroskedasticity in time-series data. It models volatility clustering—a key feature in financial markets where high-volatility events are followed by more volatility.
Why It Matters to Institutional Investors
- Risk Management: Helps institutions forecast Value-at-Risk (VaR).
- Portfolio Optimization: Adjusts asset allocation dynamically based on volatility forecasts.
- Derivatives Pricing: Improves accuracy in pricing options and structured products.
- Stress Testing: Simulates extreme market conditions.
In practice, institutions often integrate GARCH models into broader quantitative pipelines that include factor models, Monte Carlo simulations, and machine learning.
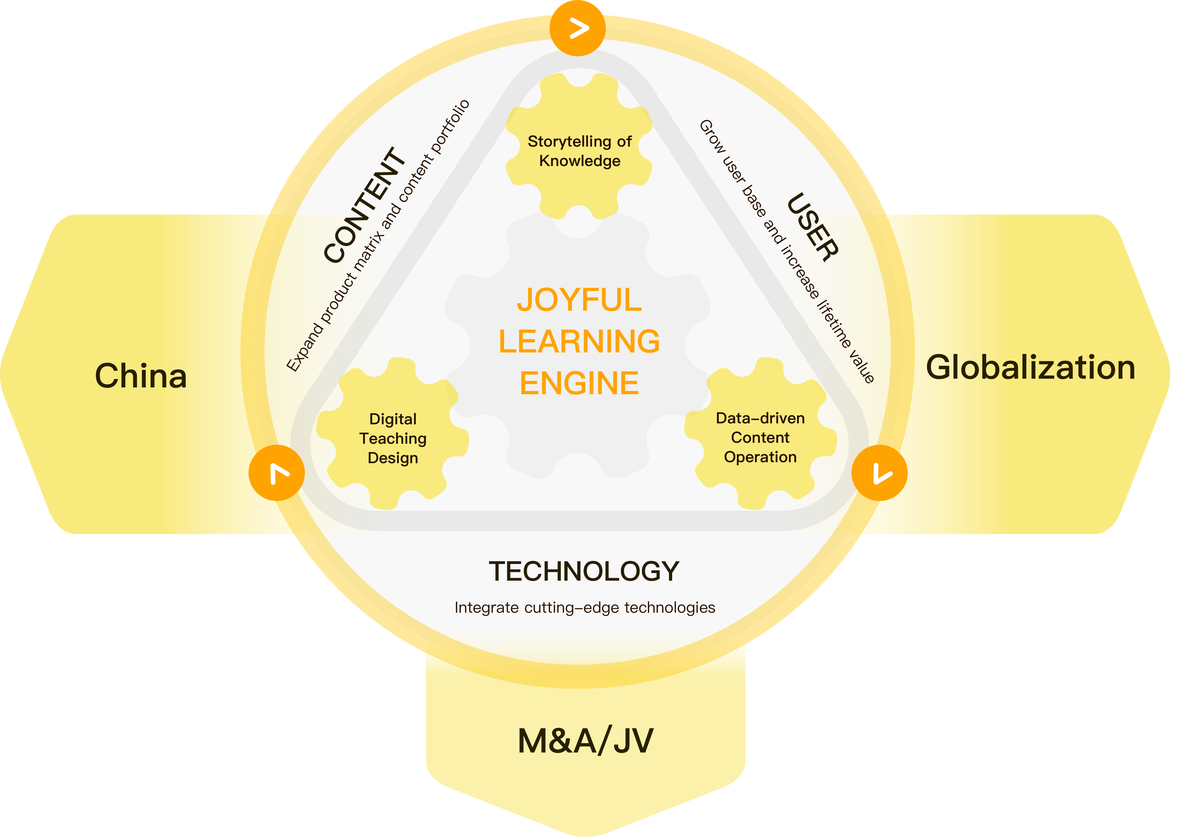
Key GARCH Applications for Institutional Investors
1. Volatility Forecasting for Portfolio Risk Control
Institutional investors rely heavily on volatility forecasts to rebalance portfolios. GARCH captures both persistence and mean reversion in volatility, making it highly effective.
- Benefit: Anticipates short-term volatility spikes, reducing portfolio drawdowns.
- Limitation: Can underperform during regime shifts (e.g., COVID-19 market crash).
2. Value-at-Risk (VaR) Calculations
Banks and funds use VaR to measure the worst expected loss over a certain time horizon at a given confidence level. GARCH models improve VaR estimates by accounting for conditional volatility.
- Use Case: A hedge fund running leveraged strategies can integrate GARCH forecasts to dynamically adjust capital buffers.
- Challenge: Overconfidence in parameter stability may underestimate tail risks.
3. Derivatives and Options Pricing
Options pricing relies on volatility inputs. Unlike the Black-Scholes model, which assumes constant volatility, GARCH provides time-varying estimates.
- Advantage: Produces more realistic implied volatility surfaces.
- Drawback: Computationally intensive for large derivatives portfolios.
Volatility clustering captured by GARCH models
4. Asset Allocation and Hedging
Institutional investors often use GARCH-based forecasts in tactical asset allocation strategies. For example, during heightened volatility, exposure to equities may be reduced, while allocations to bonds or alternative assets increase.
- Pros: Adaptive, responsive to market shocks.
- Cons: Frequent rebalancing can lead to transaction costs.
5. Stress Testing and Scenario Analysis
By modeling conditional variance, GARCH enables institutions to simulate different market shocks and stress scenarios.
- Application: Insurance firms test solvency under rare but severe volatility events.
- Limitation: GARCH assumes historical patterns will persist, which may not hold during black swan events.
Comparing Two Institutional GARCH Strategies
Strategy 1: Standard GARCH(1,1) for Risk Forecasting
- Description: The most widely used model, focusing on short-term volatility forecasting.
- Strengths: Simplicity, accuracy in capturing volatility clustering.
- Weaknesses: Fails during structural breaks and does not capture asymmetries well.
Strategy 2: GJR-GARCH for Asymmetric Volatility
- Description: Extends GARCH to capture leverage effects (negative returns often increase volatility more than positive returns).
- Strengths: More realistic for equity and derivative markets.
- Weaknesses: Requires more data, complex to calibrate.
Recommendation: For institutional investors managing equity-heavy portfolios, GJR-GARCH provides superior risk insights. For general fixed-income portfolios, standard GARCH(1,1) suffices.
Institutional investors applying GARCH for portfolio risk management
Integrating GARCH With Modern Quantitative Frameworks
Machine Learning + GARCH
Institutions increasingly combine GARCH with machine learning models to enhance predictive accuracy. ML captures nonlinearities, while GARCH anchors volatility dynamics.
Factor Models + GARCH
Multi-factor models (e.g., Fama-French) can integrate GARCH volatility forecasts to refine portfolio construction.
Backtesting GARCH-Based Strategies
Evaluating model robustness through backtesting is essential. Institutions often combine GARCH with rolling-window simulations to validate predictive power. Understanding how to backtest GARCH trading models ensures the strategy is stress-tested before implementation.
Institutional Case Studies
Hedge Fund Example
A hedge fund applied GJR-GARCH for equity trading. By anticipating volatility spikes, they reduced leverage exposure during turbulent markets, cutting drawdowns by 15%.
Pension Fund Example
A pension fund integrated GARCH-based VaR estimates into its risk management framework, resulting in more accurate capital allocation under Basel III compliance.
Limitations of GARCH for Institutional Investors
- Parameter Instability: Estimates may shift rapidly across regimes.
- Tail Risk Blindness: Extreme market events often exceed GARCH predictions.
- Computational Complexity: Scaling across multi-asset portfolios can be resource-intensive.
This explains why GARCH models fail in certain markets, especially during periods of structural breaks or unprecedented events.
Best Practices for Institutions Using GARCH
- Model Comparison: Always test multiple variants (e.g., EGARCH, TGARCH).
- Combine with Other Tools: Use alongside Monte Carlo and stress testing.
- Regular Recalibration: Update parameters frequently to reflect market conditions.
- Risk Governance: Integrate into enterprise-wide risk systems with human oversight.
- Scenario Planning: Simulate extreme scenarios beyond GARCH forecasts.
FAQ: GARCH Applications for Institutional Investors
1. How does GARCH improve institutional risk management?
By forecasting volatility dynamically, GARCH provides early warnings of market stress. This allows institutions to adjust leverage, hedge exposure, and meet regulatory capital requirements more effectively.
2. Can GARCH be applied across all asset classes?
Yes, but with caveats. It works well for equities, FX, and commodities. For illiquid markets like private equity, GARCH has limited application due to lack of high-frequency data.
3. How do institutions optimize GARCH models?
Institutions typically perform parameter tuning, rolling-window recalibration, and model comparison across variants. Understanding how to optimize GARCH parameters for best results is critical for achieving reliable forecasts.
Conclusion
The GARCH applications for institutional investors extend far beyond simple volatility forecasting. From portfolio risk control to derivatives pricing and stress testing, GARCH models remain indispensable in modern finance. However, they must be applied carefully—supplemented with robust backtesting, alternative models, and governance frameworks.
For institutions seeking to balance sophistication with reliability, GARCH provides a foundation, but not a silver bullet. Its true power lies in integration with advanced quantitative tools and risk management strategies.
If you found this analysis insightful, share it with colleagues or add your perspective in the comments: How has GARCH impacted your institutional trading or risk management framework?
GARCH applications in institutional portfolio optimization

0 Comments
Leave a Comment