===================================================================================
Hedge planning is a critical component for family offices looking to manage wealth, protect assets, and mitigate risks. Given their unique financial structures and goals, family offices need strategies that balance capital preservation, long-term growth, and risk management. In this article, we’ll explore the best hedge planning strategies for family offices, the methods and tools used in effective hedging, and how to evaluate and adapt hedging approaches to fit the specific needs of wealthy families.
What is Hedge Planning for Family Offices?
Understanding Hedge Planning
At its core, hedge planning involves using financial strategies to reduce or offset the risk of adverse price movements in a family office’s portfolio. These risks can come from market volatility, economic fluctuations, political instability, or sector-specific downturns. Hedge planning helps family offices manage these risks by using financial instruments such as options, futures, swaps, or other derivatives.
For family offices, hedge planning goes beyond just protecting investments—it also plays a role in tax efficiency, estate planning, and liquidity management. The objective is not only to preserve wealth but to ensure that assets are growing in a stable and secure environment, despite the changing market landscape.
Why Hedge Planning is Crucial for Family Offices
Family offices typically manage the wealth of high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) and multi-generational families. These entities often have complex financial needs, including the need for:
- Wealth preservation across generations
- Diversification of investments
- Protection from significant market losses
- Ensuring steady returns with minimal volatility
As such, effective hedge planning is vital to ensure the long-term sustainability of wealth, which requires a tailored approach based on the family office’s risk tolerance, investment horizon, and overall goals.
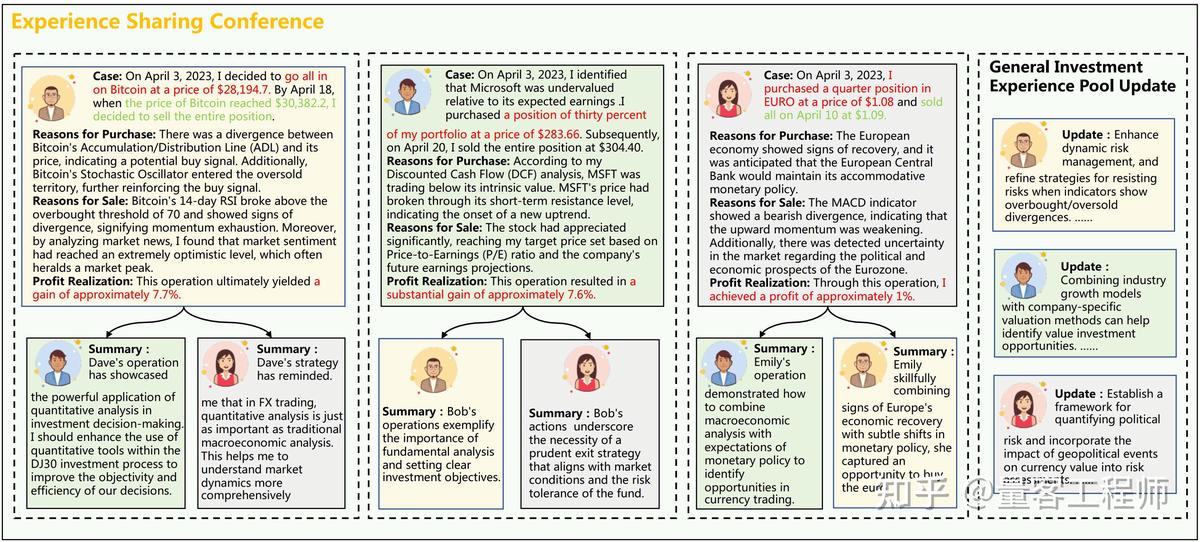
Key Strategies for Hedge Planning in Family Offices
1. Asset Allocation with Hedging Instruments
Overview of Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is the process of distributing investments among various asset classes—such as equities, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments—to optimize the balance between risk and return. For family offices, a strategic asset allocation can help create a well-diversified portfolio that mitigates risks while ensuring growth.
Using Hedging Instruments in Asset Allocation
- Options and Derivatives: Family offices often use options and derivatives as part of their hedging strategy. For example, buying put options on a large equity position can protect the family office from potential declines in stock prices.
- Futures Contracts: Futures contracts can be used to hedge against declines in commodities or interest rates. Family offices that have exposure to commodities (such as oil or agricultural products) might use futures to lock in prices and reduce volatility risk.
Benefits:
- Flexibility to hedge against specific risks.
- Enhanced portfolio protection during market downturns.
Drawbacks:
- Requires expertise in derivatives and options.
- Can be costly depending on market conditions and asset size.
2. Diversification Across Different Sectors and Geographies
Global Diversification as a Hedge
For family offices, one of the most effective ways to hedge risk is geographical diversification. By investing across multiple regions, such as North America, Europe, and Asia, family offices can reduce the impact of regional economic downturns, political instability, or currency devaluation.
Additionally, sectoral diversification helps protect against the risk of a particular industry underperforming. For example, technology may outperform during certain economic conditions, but financials or consumer staples may hold up better in others.
How to Achieve Global Diversification
- International Equities and Bonds: Investing in foreign stocks and bonds can provide exposure to high-growth markets while reducing risks tied to any single economy.
- Real Estate Investments in Multiple Countries: Real estate is a key asset for many family offices. By diversifying into international markets, family offices can hedge against local real estate cycles and benefit from growth in other regions.
Benefits:
- Reduces concentration risk.
- Potential to capture growth from emerging markets.
Drawbacks:
- Additional complexity in managing international assets.
- Currency risk when dealing with foreign investments.
3. Hedging with Private Equity and Venture Capital
Using Private Equity for Risk Mitigation
Family offices are often well-suited for private equity investments because of their ability to take a long-term view and hold illiquid assets. These investments can provide a hedge against public market volatility, as private equity companies are not subject to the same fluctuations as publicly traded companies.
Venture Capital as a Hedge Against Traditional Markets
Venture capital (VC) investments can also serve as an effective hedge. By investing in early-stage companies, family offices can access potentially high returns that are uncorrelated with the stock market. These investments can reduce exposure to traditional equity market risks and provide a source of alpha (excess returns above the market average).
Benefits:
- Protection from public market volatility.
- High return potential from private market investments.
Drawbacks:
- High illiquidity.
- Requires significant expertise and resources to evaluate investments.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Hedge Planning
Performance Metrics for Hedge Planning
For a family office to know whether its hedge planning is successful, it must measure the effectiveness of hedging strategies. Key performance indicators (KPIs) include:
- Risk-Adjusted Return (Sharpe Ratio): This metric helps assess the return of the portfolio in relation to the risk taken. A higher Sharpe ratio indicates that the family office is achieving better returns for the risk involved.
- Hedge Ratio: This refers to the proportion of the portfolio that is hedged using various instruments (such as options or futures). A family office may choose to hedge a portion of its equity portfolio or its entire holdings.
- Drawdown Analysis: The amount of loss in a portfolio from its peak to its lowest point helps in understanding how well the hedge strategies are protecting wealth during market downturns.
Review and Adjust Hedging Strategies
Over time, family offices should regularly review and adjust their hedge strategies based on changing market conditions, evolving family objectives, and asset performance. Risk management tools such as stress testing and scenario analysis can help identify vulnerabilities in the hedge plan and recommend adjustments.
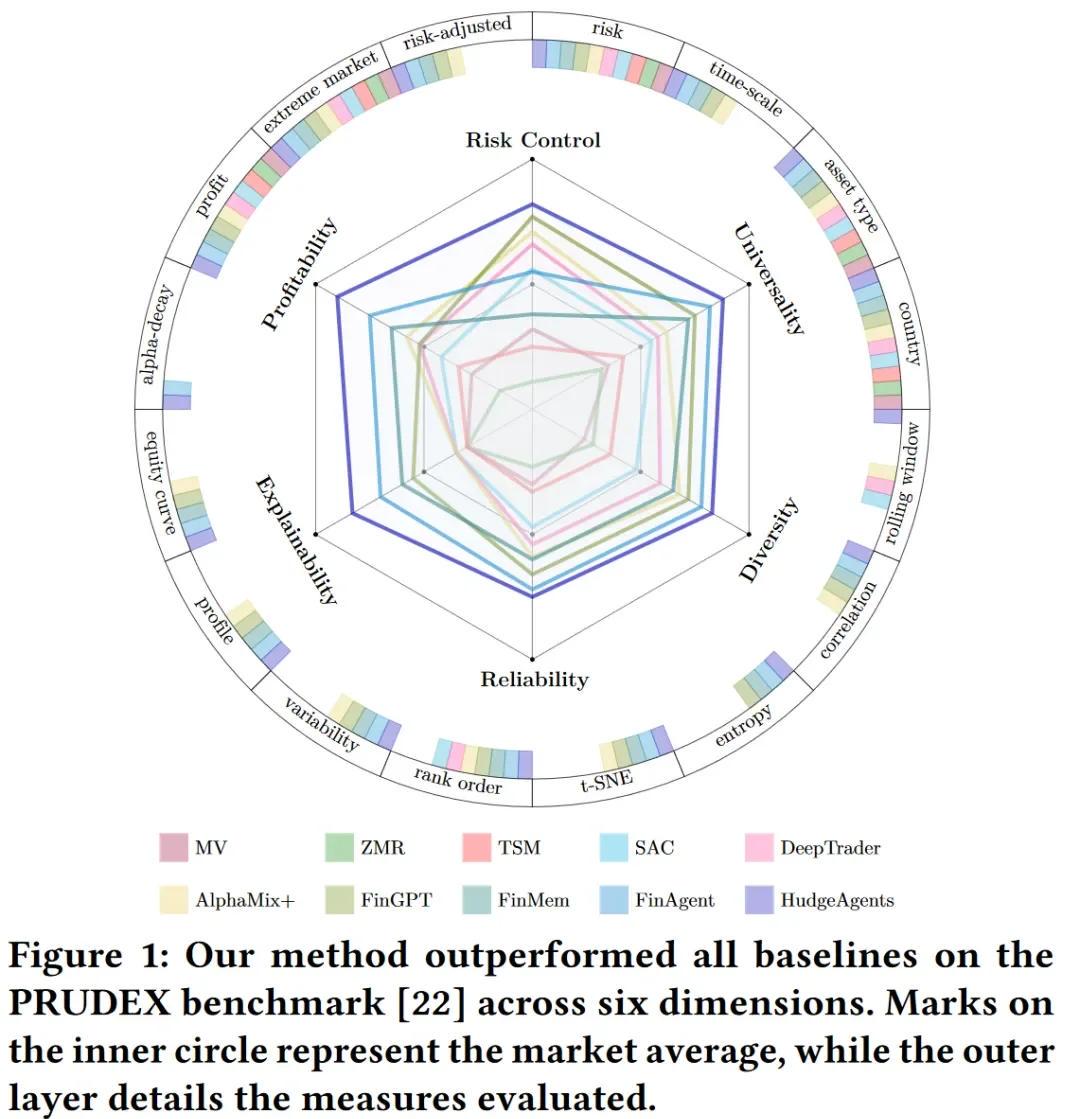
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why is hedge planning important for family offices?
Hedge planning is crucial for family offices because it helps protect wealth against market volatility and unforeseen risks, such as economic downturns, political instability, or natural disasters. By strategically hedging, family offices can preserve capital while pursuing long-term growth, ensuring that wealth is sustained across generations.
2. How can family offices implement hedging strategies effectively?
Family offices can implement hedging strategies by using a combination of asset allocation, diversification, and derivatives like options and futures. For riskier investments such as private equity or venture capital, the family office can also implement alternative investments to further hedge against traditional market risks.
3. What are the best hedging strategies for family offices in volatile markets?
In volatile markets, options-based hedging and diversification are effective strategies. Using protective puts can help family offices guard against significant market declines, while geographical and sectoral diversification reduces exposure to any one region or industry. For long-term growth, private equity investments can also act as a hedge.
Conclusion
Hedge planning is an essential tool for family offices looking to protect and grow wealth in uncertain times. By employing a combination of asset allocation, global diversification, and private equity investments, family offices can mitigate risks and secure their financial future. Whether you’re a family office just beginning to explore hedging or a seasoned investor looking for advanced strategies, understanding the key methods and approaches will allow you to make informed, risk-conscious decisions that align with your long-term financial goals.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment