=====================================
Introduction
Understanding how to analyze market microstructure has become one of the most critical skills for traders, institutional investors, and researchers. Market microstructure is the study of how trades are executed, how prices are formed, and how liquidity is provided within financial markets. Unlike traditional finance theories that assume frictionless markets, microstructure focuses on the real mechanics of trading—including order books, bid-ask spreads, transaction costs, and the behavior of different market participants.
This guide will provide a comprehensive framework for analyzing market microstructure, compare different strategies, discuss tools and data sources, and offer actionable insights for traders and analysts.
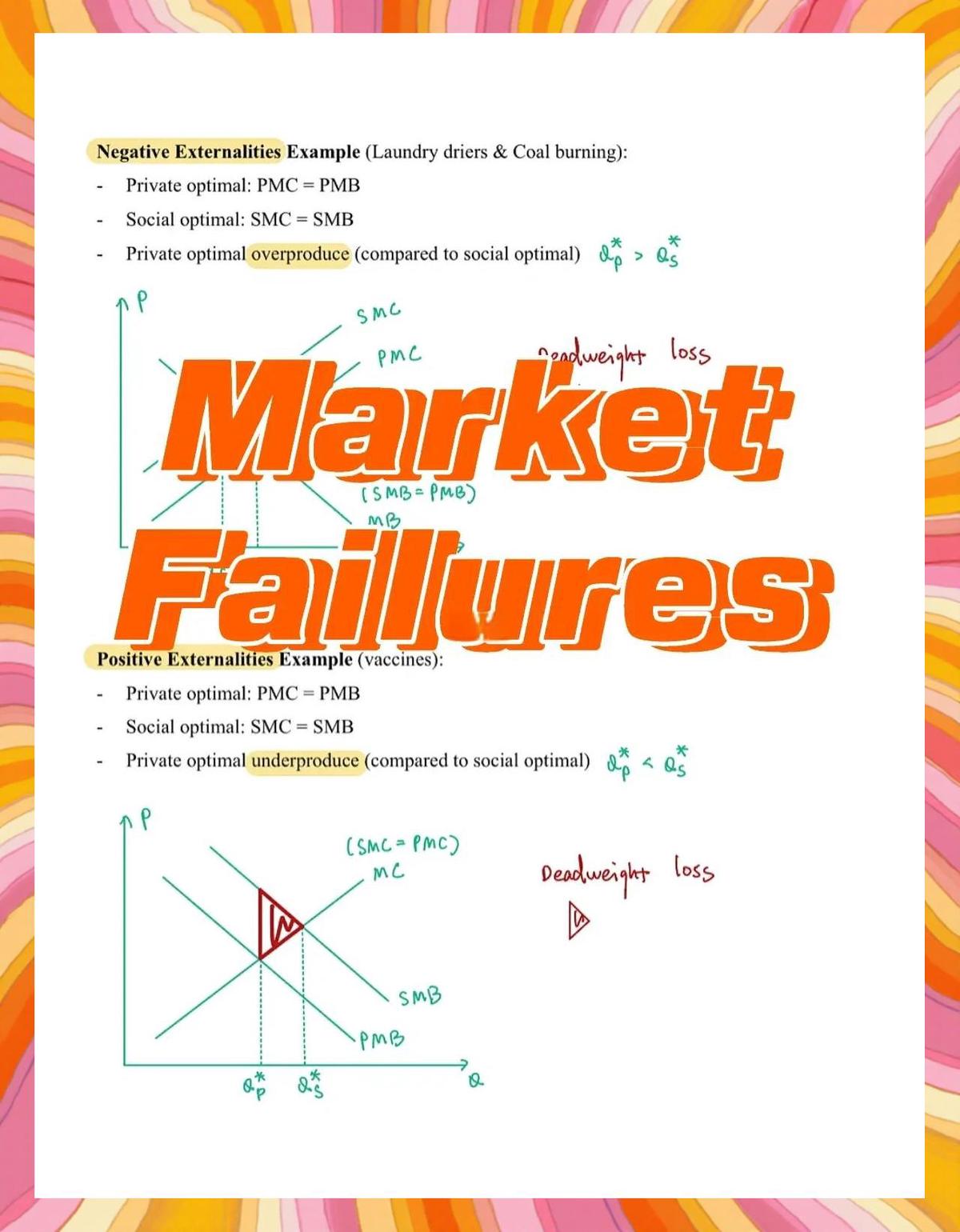
What is Market Microstructure?
Market microstructure examines the processes and outcomes of exchanging assets under explicit trading rules. It studies how market participants—such as retail traders, institutional investors, market makers, and algorithmic trading firms—interact within order-driven or quote-driven systems.
Key elements include:
- Order types (market, limit, stop-loss, iceberg, hidden orders).
- Bid-ask spreads (the cost of immediate execution).
- Liquidity (depth of the order book and ease of executing trades without moving the market).
- Price discovery (how information gets reflected in asset prices).
- Transaction costs (explicit costs like fees and implicit costs like slippage).
Why Analyze Market Microstructure?
Analyzing microstructure provides insights into:
- Execution efficiency: Minimizing slippage and market impact.
- Liquidity conditions: Identifying when markets are liquid or illiquid.
- Behavior of high-frequency traders (HFTs): Understanding how algorithms interact with slower participants.
- Risk management: Anticipating short-term volatility and order flow risks.
For investors, recognizing these dynamics can significantly improve trading performance and risk-adjusted returns. This is also why many institutions emphasize why market microstructure is important in trading education and execution research.
Methods to Analyze Market Microstructure
1. Order Book Analysis
Order book analysis involves examining the real-time supply and demand for a financial instrument. Analysts track:
- Depth of the order book (liquidity on each side).
- Large hidden or iceberg orders.
- Imbalances between buyers and sellers.
Advantages:
- Provides granular insights into liquidity.
- Detects potential support and resistance levels.
Disadvantages:
- Data-heavy and requires specialized platforms.
- Can be manipulated by spoofing or layering (though illegal, these practices still occur).
2. Trade and Quote (TAQ) Data Analysis
TAQ data captures every transaction and quote update in the market. Analysts measure:
- Trade initiation (buyer vs. seller-initiated trades).
- Quote changes (spread dynamics and order cancellations).
- Market impact (price movements caused by order flow).
Advantages:
- Precise measurement of liquidity and trading costs.
- Essential for quantitative modeling.
Disadvantages:
- Expensive to access (institutional-grade data).
- Requires advanced statistical knowledge.
3. Statistical and Econometric Models
Researchers apply models such as:
- Roll’s model: Estimates the effective bid-ask spread.
- Kyle’s model: Measures market depth and price impact of trades.
- Glosten-Milgrom model: Explains how asymmetric information affects spreads.
Advantages:
- Provides theoretical foundations.
- Useful for academic and institutional research.
Disadvantages:
- Requires large datasets.
- Less actionable in fast-paced trading environments.
4. Algorithmic Trading & Microstructure Simulation
Quantitative traders often use market microstructure simulation tools to backtest strategies under realistic execution conditions. These models incorporate:
- Latency effects.
- Market maker behavior.
- Adaptive liquidity conditions.
Advantages:
- Helps design execution algorithms.
- Can reveal hidden costs not visible in backtesting without microstructure.
Disadvantages:
- Requires high computational resources.
- Dependent on assumptions about trader behavior.
Comparing Methods
| Method | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Order Book Analysis | Day traders, HFT | Real-time liquidity insights | Data-intensive, subject to spoofing |
| TAQ Data Analysis | Institutional investors | Precise trade-level data | Expensive, complex analysis |
| Statistical Models | Researchers | Theoretical rigor | Less practical for fast trading |
| Simulation Tools | Algorithmic traders | Strategy testing | High complexity, costly |
From experience, order book analysis combined with TAQ data provides the most balanced approach for professional traders. Institutions, however, often lean on econometric models for policy and strategy evaluation.
Practical Strategies for Traders
Strategy 1: Liquidity Detection for Execution
By analyzing depth and spreads, traders can identify the best times to execute large trades with minimal impact.
Strategy 2: Price Impact Modeling
Using models like Kyle’s, institutions estimate how their trades might move the market and adjust order slicing accordingly.
Strategy 3: Algorithmic Execution (VWAP, TWAP, POV)
Algorithms execute trades incrementally based on volume, time, or participation rates—reducing signaling risk.

Real-World Applications
- Institutional Investors: Use microstructure to reduce trading costs by optimizing order execution.
- Hedge Funds: Analyze liquidity to exploit short-term inefficiencies.
- Brokers: Provide execution quality reports for regulatory compliance.
- Retail Traders: Learn how does market microstructure impact trading to avoid trading in thin markets with wide spreads.
Image Example: Market Microstructure Visualization
Order book depth showing liquidity at different price levels.
FAQ Section
1. How do I start analyzing market microstructure as a beginner?
Begin with order book and trade data available on most trading platforms. Focus on spreads, liquidity depth, and trade volumes. Over time, integrate advanced tools such as TAQ datasets or econometric models.
2. Why is market microstructure crucial for institutional investors?
Institutions trade in large volumes, where execution costs significantly impact returns. Microstructure analysis helps them minimize market impact, optimize order routing, and maintain competitive performance.
3. Where can I find market microstructure data?
Data can be sourced from exchanges (e.g., Nasdaq TotalView, CME MDP), data vendors (Bloomberg, Refinitiv), and academic libraries. Many platforms also offer market microstructure for quantitative analysts who need high-frequency trade datasets.
Conclusion
Learning how to analyze market microstructure is essential for anyone who wants to gain a competitive edge in trading or research. From order book analysis to econometric models, each method offers unique insights.
For traders, combining real-time liquidity monitoring with data-driven models provides the most actionable framework. For institutions, robust econometric analysis ensures long-term execution efficiency.
If you found this guide insightful, share it with colleagues or leave a comment below. Engaging with others helps refine our collective understanding of market mechanics and strengthens trading strategies across all levels.
Would you like me to also create a visual flowchart of market microstructure analysis steps (from order book monitoring to econometric modeling) to complement this article?

0 Comments
Leave a Comment