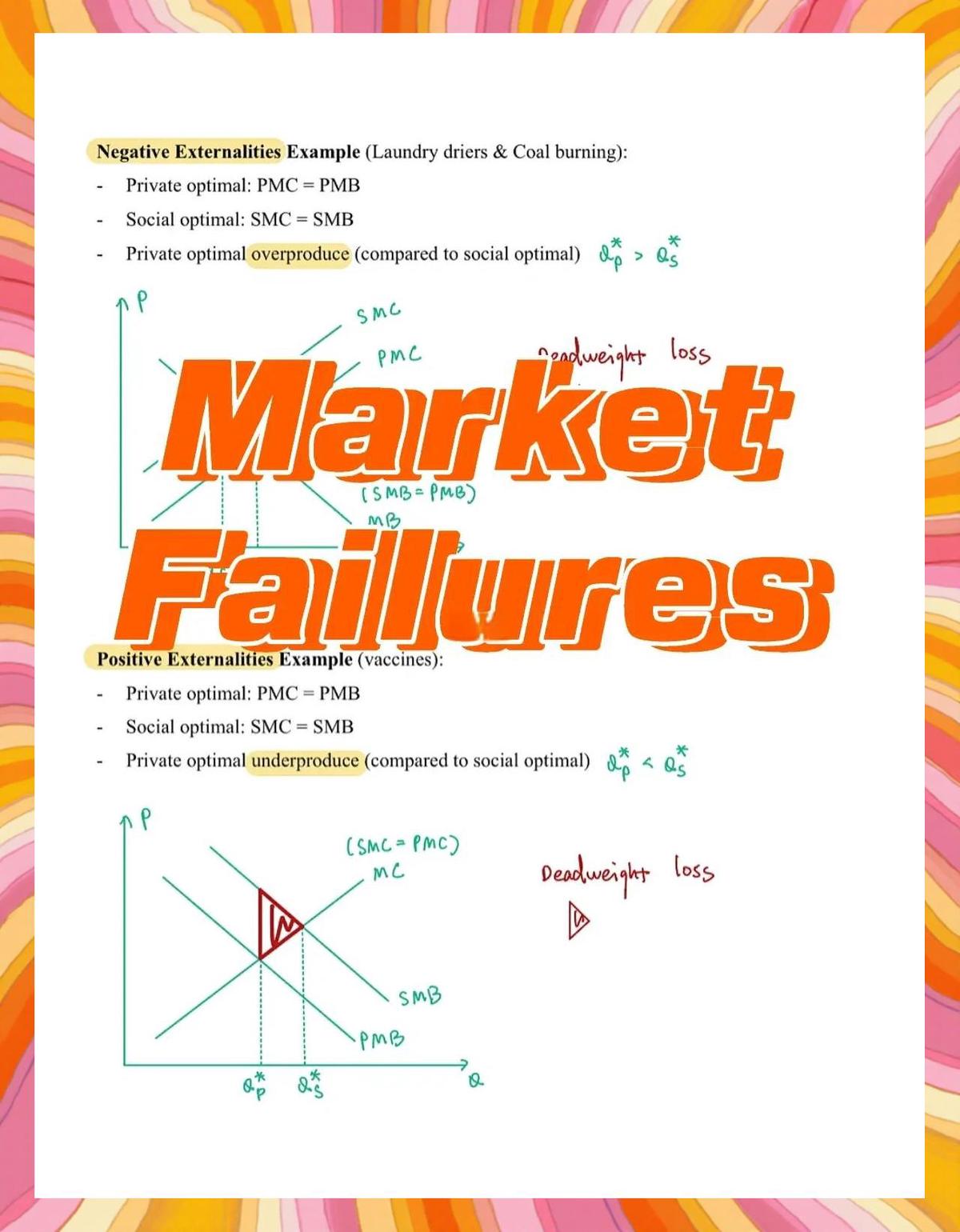
=====================================
Introduction
Financial markets are often viewed as simple platforms where buyers and sellers meet. In reality, the underlying mechanics are far more complex. The market microstructure examines the processes, trading rules, order flows, and participant behaviors that determine how securities are traded and how prices evolve.
Understanding how to analyze market microstructure is vital for traders, institutional investors, regulators, and academics. For traders, it offers insights into order execution and liquidity costs. For researchers, it reveals the dynamics behind volatility and efficiency. For regulators, it highlights how rules shape fairness and transparency.
This article provides a complete guide to analyzing market microstructure, exploring multiple methods, comparing their strengths and weaknesses, and offering practical insights into applying them in trading strategies.
What is Market Microstructure?
Market microstructure is the study of the processes and mechanisms through which securities prices are formed and trades are executed. It focuses on aspects like:
- Order types: Market orders, limit orders, stop orders.
- Order books: Depth, bid-ask spreads, liquidity levels.
- Trading venues: Exchanges, dark pools, electronic communication networks (ECNs).
- Participant behavior: Institutional traders, retail investors, market makers, and high-frequency traders.
- Price dynamics: How orders interact to move prices, reflecting supply and demand.
Unlike macro-level finance theories, microstructure deals with frictions and real-world trading mechanics, such as transaction costs, slippage, and asymmetric information.
Why Market Microstructure is Important?
Studying market microstructure helps market participants:
- Improve execution quality – Traders can reduce costs by choosing optimal order types and timing.
- Understand liquidity – Identifying when markets are deep or thin prevents overpaying for trades.
- Manage volatility – Microstructure analysis reveals how large trades affect short-term price swings.
- Regulatory oversight – Regulators monitor microstructure to ensure fairness and transparency.
For example, algorithmic traders depend heavily on microstructure analysis to design systems that exploit inefficiencies in order books and spreads.
Core Elements of Market Microstructure Analysis
1. Order Book Dynamics
The order book lists all outstanding buy and sell orders. Key indicators include:
- Bid-Ask Spread: The difference between the highest bid and lowest ask price. A tight spread signals high liquidity.
- Depth: The quantity of orders available at each price level. Deeper markets are more resilient.
- Order Imbalance: When buy and sell orders are uneven, it may foreshadow price movements.
2. Trading Costs
Microstructure analysis identifies explicit and implicit costs:
- Explicit costs: Commissions, exchange fees.
- Implicit costs: Market impact, slippage, opportunity costs.
3. Information Flow
Market microstructure is heavily influenced by information asymmetry. Some traders (e.g., institutional investors) may have superior insights, affecting how prices adjust.
Methods of Analyzing Market Microstructure
Method 1: Statistical Analysis of High-Frequency Data
High-frequency tick data captures every trade, quote, and order submission. Analysts use it to:
- Measure volatility clustering.
- Identify liquidity shocks.
- Quantify order flow persistence.
Advantages:
- Provides precise insights into intraday trading.
- Captures real-time shifts in liquidity.
Disadvantages:
- Requires expensive data sources and advanced computational tools.
- Can be overwhelming without proper models.
Method 2: Order Flow and Liquidity Models
Order flow models analyze how buy/sell pressure affects prices. Liquidity models measure resilience and depth of the market.
For example, Kyle’s (1985) model links order flow to price impact, while Amihud’s measure quantifies illiquidity based on volume and price changes.
Advantages:
- Explains the mechanics of price discovery.
- Useful for designing trading algorithms.
Disadvantages:
- Relies on assumptions that may not hold in all markets.
- Complex for retail traders without advanced finance knowledge.
Method 3: Market Impact Studies
These studies measure how trades of different sizes affect short-term price movements. Institutional investors use them to minimize slippage when executing large orders.
Advantages:
- Directly applicable to trade execution strategies.
- Reveals optimal trade scheduling.
Disadvantages:
- Results vary by market condition.
- Requires historical transaction-level data.
Method 4: Simulation and Agent-Based Models
Simulations replicate trading environments where artificial agents (e.g., market makers, HFTs, retail traders) interact.
Advantages:
- Allows testing of hypothetical scenarios.
- Useful for stress testing and regulatory studies.
Disadvantages:
- Model outcomes depend on assumptions.
- Computationally intensive.
Practical Example: Analyzing Market Microstructure in Equities
Consider analyzing a stock’s order book:
- Step 1: Measure average bid-ask spread during trading hours.
- Step 2: Track order book depth before and after earnings announcements.
- Step 3: Identify periods of high order imbalance.
Findings may reveal that spreads widen significantly around news events, suggesting higher trading costs during those times. Institutional traders might delay large trades until spreads normalize.
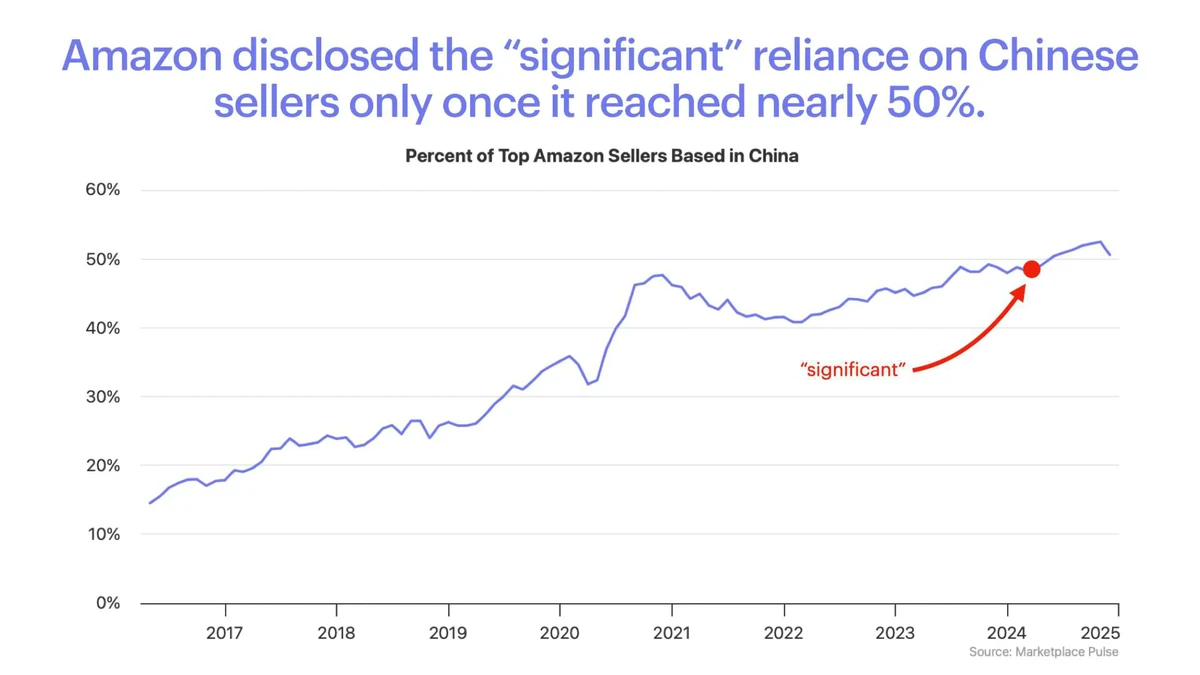
Visual Guide
Example of a limit order book showing bid/ask prices, depth, and potential imbalance signals.
Comparing Methods
| Method | Best For | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Frequency Data Analysis | Quantitative analysts | Granular insights, volatility tracking | Costly data, complex tools |
| Order Flow & Liquidity Models | Institutional investors | Price discovery mechanics, algorithm design | Relies on theoretical assumptions |
| Market Impact Studies | Hedge funds, brokers | Execution strategy optimization | Market-specific, data-intensive |
| Simulation & Agent-Based Models | Regulators, academics | Scenario testing, policy evaluation | Computationally heavy, assumption-driven |
How Does Market Microstructure Impact Trading?
Microstructure directly influences trading outcomes:
- Execution speed – Faster markets reduce slippage.
- Liquidity costs – Thin markets penalize large orders.
- Algorithmic strategies – HFTs exploit microstructure inefficiencies.
For retail traders, understanding these dynamics prevents overpaying due to wide spreads or poor order placement.
Where to Learn Market Microstructure?
Aspiring professionals can deepen their knowledge through:
- University courses in finance and quantitative economics.
- Specialized certifications (CFA, CQF).
- Market microstructure research papers from academic journals.
- Online platforms offering simulations and market microstructure visualizations.
My personal experience suggests that hands-on analysis of live order book data is more impactful than theoretical study alone.
FAQs: How to Analyze Market Microstructure
1. Is market microstructure relevant for retail traders?
Yes. Even small orders face spreads and slippage. By analyzing microstructure, retail traders can improve execution, avoid illiquid times, and better understand price movements.
2. How does market microstructure affect pricing?
Prices are not determined solely by supply and demand fundamentals. Instead, microstructure—through order flow, liquidity, and participant behavior—affects short-term price formation and volatility.
3. What data is needed to study market microstructure?
Typically, high-frequency tick data (quotes, trades, and order book updates) is required. Some platforms offer simplified order book views, which are enough for retail-level analysis.
Conclusion
Understanding how to analyze market microstructure provides a competitive edge in modern trading. By studying order book dynamics, liquidity models, and execution costs, traders can improve performance and reduce risk.
- For retail traders, focusing on spreads and timing is crucial.
- For institutional investors, advanced models and impact studies are necessary.
- For regulators and academics, simulations help shape policy.
Market microstructure is not just theory—it’s the real battlefield where prices are made. Whether you are a retail trader or a hedge fund manager, analyzing it can be the difference between average and exceptional results.
💬 Do you already analyze order book dynamics in your trades, or do you rely mainly on technical indicators? Share your experience below, and don’t forget to pass this guide along to others interested in market structure insights!

0 Comments
Leave a Comment