============================================
Quantitative trading, often called quant trading, is a data-driven approach to financial markets where strategies are built on mathematical models, algorithms, and statistical analysis. Many aspiring traders ask: How to learn quantitative trading strategies effectively? The journey requires structured learning, practical implementation, and ongoing adaptation to industry trends. This article provides a comprehensive guide, drawing from real-world practices, modern resources, and tested strategies.
What Are Quantitative Trading Strategies?
Quantitative trading strategies are systematic methods that use data analysis, mathematics, and algorithms to make trading decisions. Unlike discretionary trading, where emotions may dominate, quantitative strategies rely on rules, models, and backtested data.
Key elements include:
- Data Collection: Historical price data, volume, order-book depth, and alternative datasets.
- Modeling: Statistical or machine learning models used to predict market movements.
- Execution: Algorithmic implementation to automate trades with precision.
- Risk Management: Monitoring drawdowns, volatility, and position sizing.
Why Learn Quantitative Trading Strategies?
- Data-Driven Decisions: Eliminates emotional bias.
- Scalability: Strategies can be applied across multiple markets and asset classes.
- Consistency: Systematic execution ensures repeatable outcomes.
- Competitive Edge: Quant trading is widely adopted by hedge funds, prop firms, and institutional investors.
Learning quant strategies equips traders with the skills to thrive in both retail and institutional settings.
Step-by-Step Approach: How to Learn Quantitative Trading Strategies
1. Build a Strong Foundation in Mathematics and Statistics
Quantitative trading relies heavily on probability, linear algebra, and statistical inference. Topics like time-series analysis and stochastic processes are particularly relevant.
2. Learn Programming for Finance
Languages such as Python, R, C++, and Matlab are popular. Python dominates retail and institutional quant research due to its rich libraries (NumPy, Pandas, scikit-learn, TensorFlow).
3. Study Financial Markets and Instruments
Understanding equities, options, futures, and derivatives is essential. Without a solid grasp of market mechanics, even the best algorithm may fail in real-world trading.
4. Explore Educational Resources
From academic papers to structured online learning platforms, resources are abundant. For example, exploring Where to find quantitative trading courses helps aspiring traders connect with reputable programs tailored to different skill levels.
5. Practice Through Backtesting and Paper Trading
Backtesting against historical data allows traders to validate their strategies. Paper trading bridges theory and practice by simulating live trading without risking capital.
6. Develop Risk Management Skills
The best strategy can fail without sound risk controls. Master drawdown analysis, Value-at-Risk (VaR), and portfolio diversification techniques.

Two Major Quantitative Trading Strategies and Their Differences
1. Mean Reversion Strategy
This strategy assumes that asset prices eventually revert to their historical mean.
Pros:
- Works well in range-bound markets.
- Easy to implement using statistical indicators like Bollinger Bands.
- Can generate consistent small profits.
Cons:
- Fails in trending markets.
- Requires precise entry and exit rules.
- Vulnerable to structural market changes.
2. Momentum Strategy
Momentum strategies assume that assets that have performed well recently will continue to do so in the near future.
Pros:
- Highly effective in trending markets.
- Supported by strong academic evidence (momentum factor).
- Scalable across asset classes and geographies.
Cons:
- Sudden market reversals can lead to losses.
- High transaction costs if not optimized.
- Requires careful position sizing.
Comparative Analysis: Mean Reversion vs. Momentum
| Feature | Mean Reversion Strategy | Momentum Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Market Condition | Range-bound markets | Trending markets |
| Complexity | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Best Use Case | Short-term trades | Medium to long-term trades |
| Risk of Failure | Structural breaks | Sharp reversals |
| Adoption | Retail & prop traders | Hedge funds & institutions |
👉 Both strategies are useful. However, for long-term growth, blending them or applying portfolio-level factor diversification often produces stronger results.
Practical Tools and Platforms for Learning
- Backtesting Platforms: QuantConnect, Zipline, Backtrader.
- Data Providers: Quandl, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg Terminal.
- Coding Libraries: NumPy, Pandas, Statsmodels, scikit-learn, TensorFlow.
- Community Forums: Quantopian archives, Elite Trader, StackExchange Quant.
For beginners, it’s also useful to explore How to implement quantitative trading strategies, since practical execution is as critical as theoretical understanding.
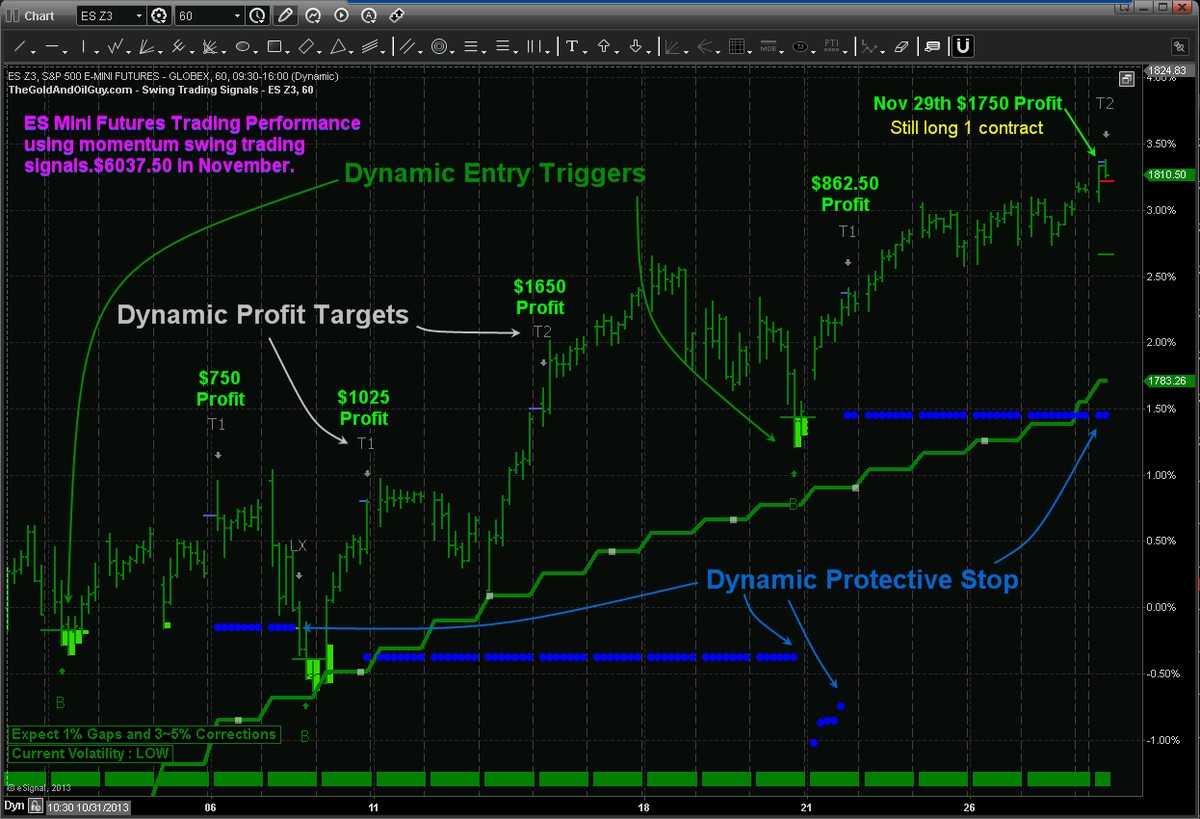
Industry Trends: Modern Approaches to Quant Strategies
- Machine Learning Integration: Predictive models that adapt to nonlinear market data.
- Alternative Data Usage: Incorporating social media sentiment, satellite data, and ESG metrics.
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT): Microsecond-level execution in highly liquid markets.
- Retail Quant Growth: Platforms now provide retail traders access to institutional-grade tools.
Visual Example
Quantitative Trading Learning Roadmap
A structured roadmap from theory to live trading for aspiring quantitative traders.
FAQs
1. How long does it take to learn quantitative trading strategies?
It depends on your background. Someone with math and programming knowledge may take 6–12 months to become proficient. Beginners may need 1–2 years of structured learning and practice.
2. Do I need advanced math to succeed in quant trading?
Not necessarily. Basic probability, statistics, and linear algebra are sufficient for most retail-level strategies. However, advanced institutional strategies (e.g., options pricing models, stochastic calculus) require deeper math knowledge.
3. Can beginners start with quant trading without prior finance experience?
Yes. Many retail traders learn by starting small with Quantitative trading for beginners guides and progressively moving into advanced models. Paper trading platforms make the transition smoother.
Conclusion: The Best Path to Learning Quantitative Trading
Learning how to master quantitative trading strategies requires discipline, continuous learning, and structured practice. Begin with fundamentals in math, programming, and market theory, then explore practical tools like backtesting and algorithmic platforms. Start small with mean reversion strategies, evolve into momentum and machine learning models, and always prioritize risk management.
Ultimately, success comes from combining theory, simulation, and live practice. By doing so, you not only learn how to trade quantitatively but also position yourself to thrive in a market where data-driven decision-making is the key to long-term profitability.
💡 Found this guide useful? Share it with your trading community, leave a comment with your learning journey, and join the conversation. Together, we can make quantitative trading more accessible and effective for everyone.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment