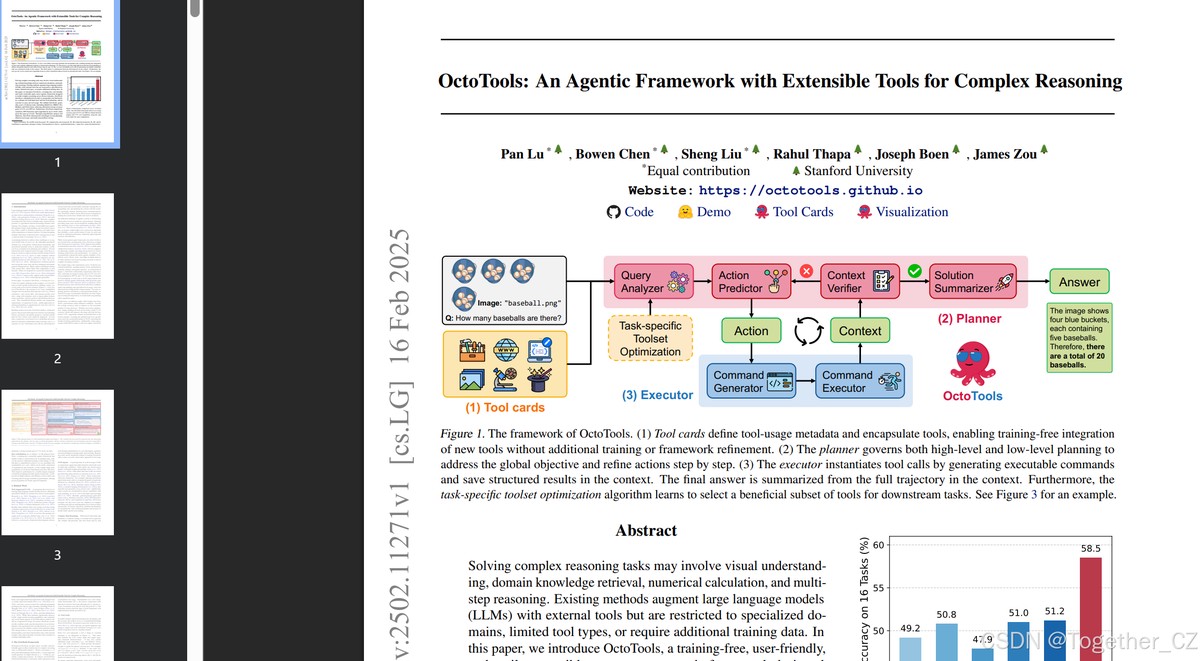
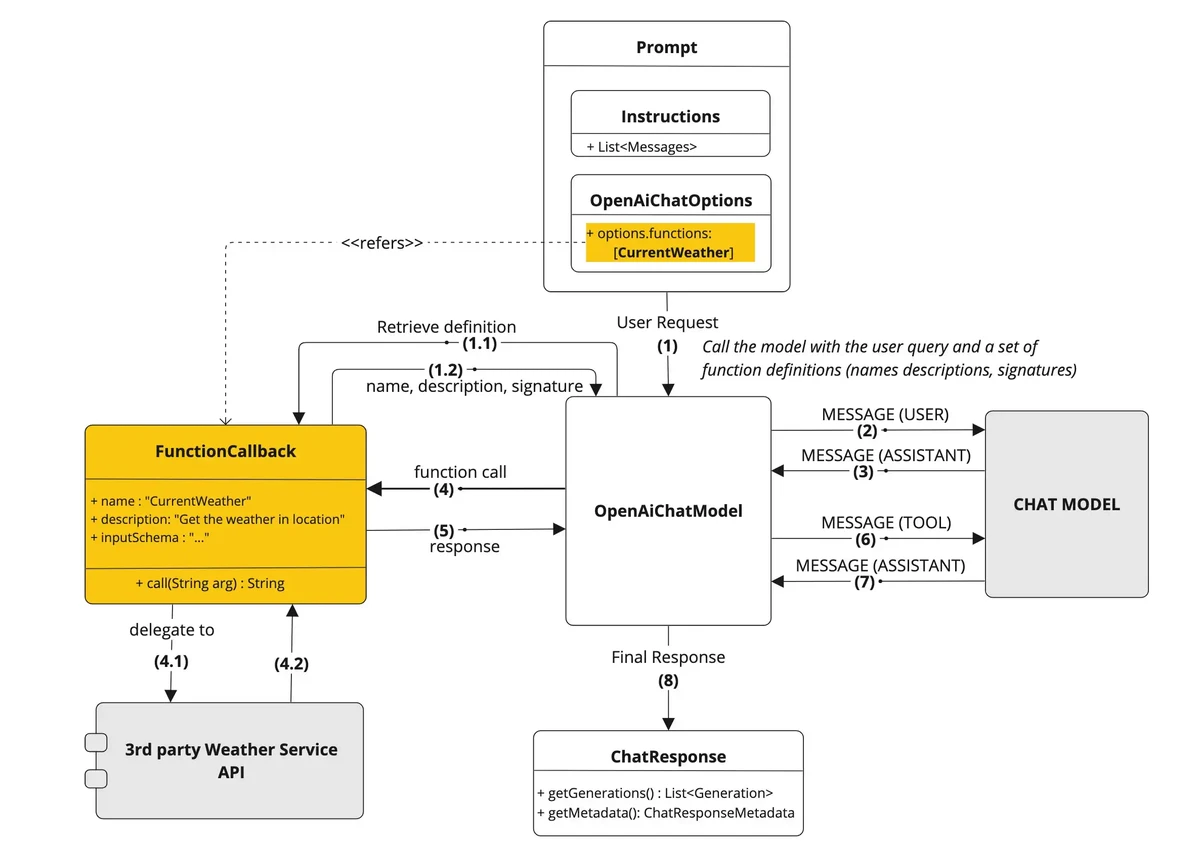
=============================================================
Introduction
In quantitative finance and professional trading, understanding market momentum is pivotal for achieving consistent profitability. Momentum analysis tools allow analysts to detect trend strength, anticipate price movements, and optimize trading strategies. For both institutional and retail professionals, leveraging these tools can distinguish high-performing portfolios from mediocre ones.
This article delves into the most effective momentum analysis tools for analysts, compares two major methodologies, explores real-world applications, and provides actionable insights for both beginners and experienced traders.
Internal link integration: Knowing “how does momentum affect quantitative trading” is essential for analysts aiming to enhance their strategy performance and risk management.
Understanding Momentum in Financial Markets
What Is Momentum?
Momentum is the tendency of asset prices to continue moving in the same direction for a certain period. It is a core concept in both quantitative trading and discretionary investment strategies.
- Positive momentum: Prices trending upwards
- Negative momentum: Prices trending downwards
- Neutral momentum: Lack of a significant trend
Analysts use momentum to assess whether a security is likely to continue its trend or reverse, often using technical indicators, price change rates, and statistical models.
Why Momentum Matters
- Trend recognition: Helps identify strong market movements early
- Portfolio optimization: Enhances risk-adjusted returns
- Strategy development: Supports algorithmic and discretionary trading decisions
- Timing: Critical for entry and exit points in short-term and long-term strategies
Method 1: Technical Momentum Indicators
Overview
Technical momentum indicators quantify price movement trends using historical data. Commonly used indicators include:
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the magnitude of recent price changes
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): Identifies trend direction and potential reversals
- Rate of Change (ROC): Measures percentage change over a defined period
- Momentum Oscillators: Track short-term fluctuations relative to historical averages
Implementation Techniques
- Combine multiple indicators for confirmation of trends
- Apply to different timeframes for multi-scale analysis
- Integrate with trading algorithms to automate momentum-based signals
Advantages
- Easy to implement: Most platforms support these indicators
- Visual insights: Analysts can see trends and reversals
- Backtesting compatibility: Indicators can be tested against historical data
Disadvantages
- Lagging signals: Some indicators may react late to trend changes
- False positives: High volatility can trigger misleading signals
- Over-reliance risk: Requires combination with other analytical methods
Momentum indicators such as MACD and RSI help analysts detect trend reversals and strength
Internal link integration: Understanding “how momentum indicators work in trading” enables analysts to design more precise algorithmic strategies and validate trading signals effectively.
Method 2: Statistical Momentum Models
Overview
Statistical models apply quantitative methods to measure momentum beyond traditional indicators. These include:
- Linear regression on price changes to identify persistent trends
- Autoregressive models (AR) to forecast momentum continuation
- Machine learning techniques for pattern recognition in price movements
- Factor-based approaches incorporating volume, volatility, and macro variables
Implementation Techniques
- Use Python or R libraries to perform backtesting and predictive analysis
- Integrate real-time data feeds to dynamically adjust model parameters
- Combine with risk management frameworks to optimize position sizing
Advantages
- Predictive capability: Models can anticipate trend continuation or reversals
- Customizable: Analysts can tailor models for specific asset classes
- High accuracy potential: Advanced models capture subtle patterns in price action
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Requires expertise in statistics and coding
- Overfitting risk: Models may fail in unseen market conditions
- Data dependency: Requires high-quality and timely data
Statistical momentum models provide predictive insights for quantitative trading strategies
Comparative Analysis of Methods
| Method | Pros | Cons | Ideal Users |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Indicators | Simple, visual, easy to implement | Lagging signals, potential false positives | Retail analysts, beginners, discretionary traders |
| Statistical Models | Predictive, customizable, scalable | Complex, data-dependent, risk of overfitting | Quantitative analysts, hedge funds, algorithmic traders |
Recommendation: A hybrid approach is often ideal. Use technical indicators for trend visualization and immediate signal confirmation while applying statistical models for predictive insights and algorithmic integration.
Best Practices for Using Momentum Analysis Tools
1. Multi-Timeframe Analysis
- Combine short-term and long-term momentum to avoid false signals
- Ensure alignment across timeframes before executing trades
2. Data Quality Assurance
- Use reliable market data providers
- Clean historical data to reduce noise
3. Integrate Risk Management
- Apply stop-loss and take-profit rules based on momentum strength
- Use position sizing proportional to momentum signal confidence
4. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
- Monitor strategy performance and adjust momentum thresholds
- Stay updated on new indicators, machine learning techniques, and market behavior
5. Automation and Real-Time Monitoring
- Use automated tools for real-time momentum alerts
- Implement dashboard solutions for quick decision-making
FAQ
1. How do I measure momentum in trading systems?
Momentum can be measured using percentage price changes, momentum oscillators, or statistical models. Analysts often combine multiple tools to capture both trend strength and reliability.
2. Why use momentum analysis in trading?
Momentum analysis identifies strong trends and anticipates reversals, helping traders optimize entry and exit points. This reduces risk and enhances profitability in both short-term and long-term trading strategies.
3. Can momentum strategies work in volatile markets?
Yes, but signal filtering and adaptive thresholds are critical. Combining multiple indicators and statistical models helps reduce false signals during high volatility periods.
4. Are momentum tools suitable for beginners?
Absolutely. Basic indicators like RSI and MACD provide a user-friendly entry point. Beginners can gradually incorporate more advanced statistical models as they gain experience.
Conclusion
Momentum analysis tools are essential for analysts seeking to optimize trading strategies and manage risk effectively. By combining technical indicators with statistical models, analysts can gain both visual insights and predictive capabilities, enhancing both discretionary and algorithmic trading performance.
Embracing a hybrid approach, continuously monitoring market conditions, and integrating risk management practices ensures that momentum analysis tools translate into tangible portfolio benefits.
Momentum analysis is not just about tracking price changes; it is a strategic framework for anticipating market behavior, validating strategies, and achieving consistent trading performance.
Investors and analysts who master these tools will be well-positioned to capture market trends, outperform benchmarks, and stay competitive in dynamic financial markets.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment