=====================================================
In today’s fast-paced financial markets, how to use data visualization in quantitative trading has become an essential skill for traders, analysts, and portfolio managers. Data visualization transforms complex numerical data into actionable insights, enabling traders to detect patterns, anomalies, and market trends with ease. This article provides a comprehensive guide to implementing effective data visualization strategies in quantitative trading, blending professional experience with the latest industry trends.
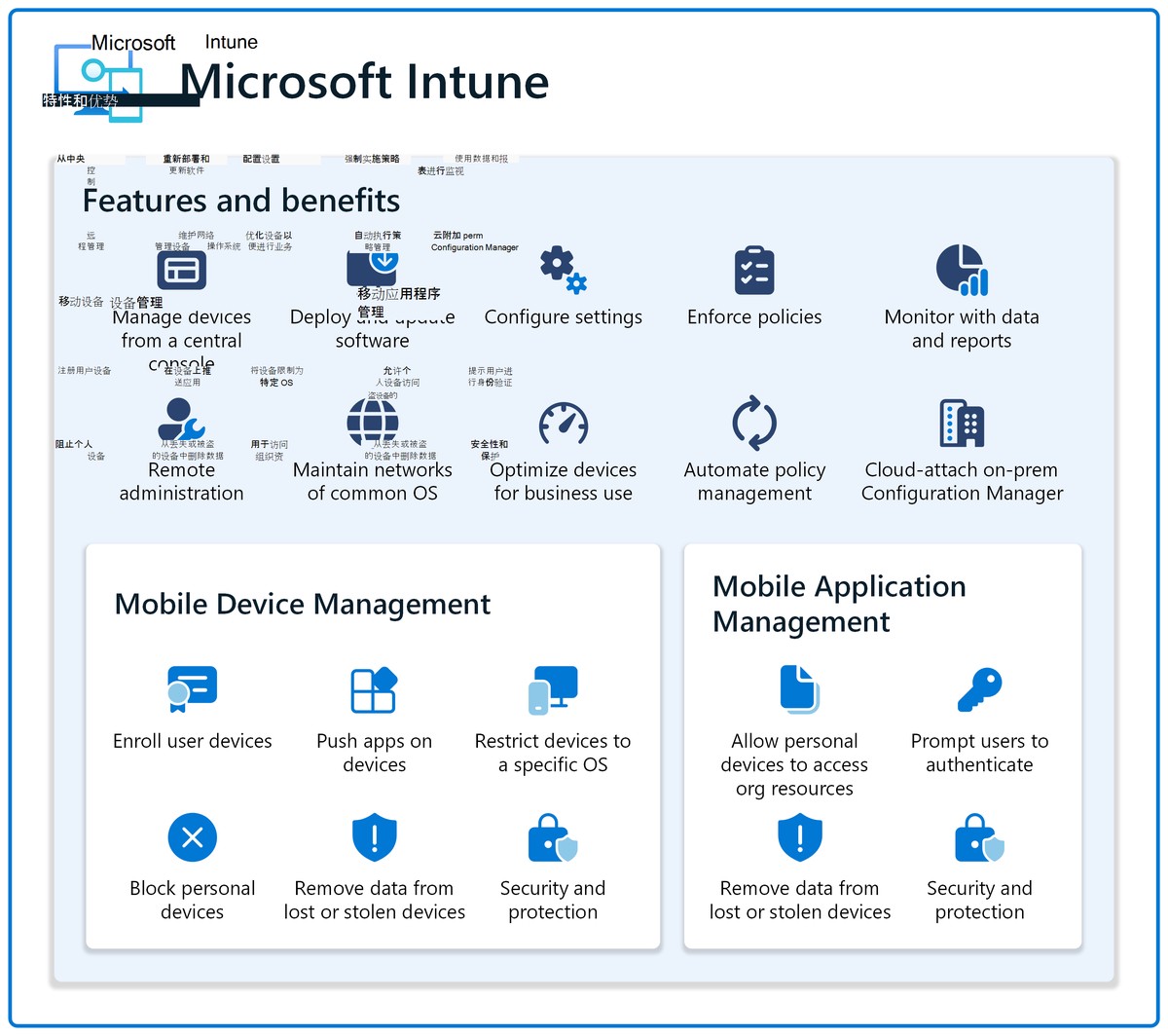
Understanding Data Visualization in Quantitative Trading
What is Data Visualization?
Data visualization is the practice of representing financial data in graphical or visual formats such as charts, heatmaps, scatter plots, and dashboards. In quantitative trading, visualization tools help interpret massive datasets generated from market prices, order books, trading volumes, and algorithmic outputs.
Why Data Visualization Matters for Quantitative Traders
- Enhances decision-making speed by presenting complex data intuitively.
- Reveals hidden correlations and market patterns that might be missed in raw data.
- Supports risk management, helping traders quickly identify outliers or potential market shocks.
- Facilitates backtesting and strategy optimization by visually tracking performance over time.
Visual representations like candlestick charts allow traders to identify patterns quickly.
Key Data Visualization Techniques for Quantitative Trading
1. Time-Series Analysis Visualization
Candlestick and OHLC Charts
Candlestick and Open-High-Low-Close (OHLC) charts provide traders with essential price movement data over a specified period. They are fundamental for recognizing patterns like head-and-shoulders, flags, or triangles, which are critical for trading strategy development.
Line and Area Charts
For trend analysis, line and area charts visualize closing prices over time, highlighting upward or downward trends and volatility clusters.
Advantages:
- Offers quick interpretation of price trends and reversals.
- Widely supported in all trading platforms.
Disadvantages:
- May not reflect volume or order book depth without additional overlays.
Example:
Traders often overlay moving averages or Bollinger Bands on time-series charts to visualize trend strength and potential entry/exit points.
2. Multivariate and Advanced Analytics Visualization
Heatmaps
Heatmaps can display correlations between multiple assets or the performance of sectors in real-time. For instance, a correlation heatmap allows traders to quickly identify diversification opportunities or systemic risks.
Scatter Plots and Bubble Charts
Scatter plots show the relationship between two variables, such as volatility vs. return, while bubble charts add a third dimension like trading volume. This is particularly useful for portfolio optimization and risk-reward analysis.
Advantages:
- Reveals complex relationships among multiple variables.
- Supports quantitative strategy refinement and risk assessment.
Disadvantages:
- Requires careful scaling and normalization to avoid misleading visualizations.
Heatmaps visually highlight correlations across a portfolio for better risk management.
Integrating Data Visualization into Quantitative Workflows
Step 1: Data Collection and Preprocessing
Before visualization, ensure that data from sources like market feeds, historical datasets, and alternative data are cleaned, normalized, and structured. Data preprocessing is crucial for accurate representation.
Step 2: Selecting Appropriate Visualization Tools
Choosing the right tools impacts clarity and usability. Some widely used platforms include:
- Python Libraries: Matplotlib, Seaborn, Plotly
- R Libraries: ggplot2, Shiny dashboards
- Trading Platforms: Bloomberg Terminal, TradingView
Where to find best tools for data visualization in trading: Professional forums, GitHub repositories, and vendor reviews provide curated recommendations for quantitative traders.
Step 3: Strategy Development and Backtesting
Visualizations allow traders to backtest strategies, highlighting patterns, drawdowns, and performance metrics over historical periods. Interactive dashboards can simulate different scenarios to stress-test trading models.
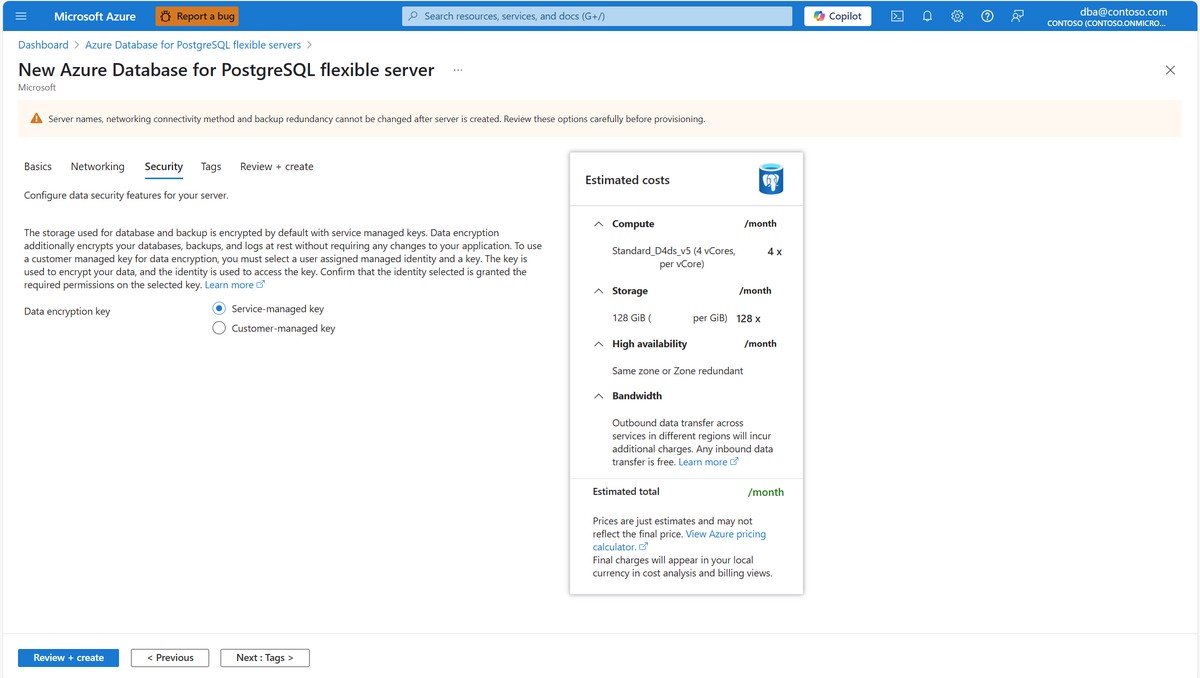
Comparing Visualization Methods
| Technique | Use Case | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Candlestick/OHLC | Price trends | Intuitive, widely used | Limited multivariate insights |
| Line/Area Chart | Trend analysis | Simple, clear | Oversimplifies market dynamics |
| Heatmaps | Correlations, risk | Multidimensional, actionable | Requires large datasets |
| Scatter/Bubble | Portfolio risk/return | Shows relationships | Can be misleading if scaled poorly |
The choice of visualization depends on the complexity of the data and the specific trading strategy. For algorithmic trading, multivariate visualizations often provide more actionable insights.
Advanced Data Visualization Strategies
Interactive Dashboards
Interactive dashboards allow traders to filter, zoom, and drill down into specific data segments, improving decision-making speed. Platforms like Tableau, Power BI, or custom Python dashboards can integrate real-time market data for live analysis.
Predictive Visualization Models
By combining machine learning with visualization, traders can project market trends, visualize predicted returns, and identify probable risk events. For example, a predictive heatmap might indicate which assets are likely to correlate strongly in the next trading session.
Advantages:
- Enables forward-looking insights beyond historical analysis.
- Improves strategy refinement and risk-adjusted returns.
Disadvantages:
- Requires high-quality data and advanced technical expertise.
- Risk of overfitting or misinterpretation if models are poorly validated.
Interactive dashboards help traders analyze live market trends and portfolio health efficiently.
Case Study: Hedge Funds Using Visualization in Quantitative Trading
Hedge funds rely heavily on data visualization to:
- Track high-frequency trading patterns in real-time.
- Identify tail-risk exposures across diversified portfolios.
- Optimize algorithmic strategies by visualizing backtesting outcomes.
For example, a scatter plot matrix can reveal correlations among thousands of assets, enabling quant analysts to reduce systemic exposure.
Best Practices for Effective Data Visualization
- Clarity and Simplicity: Avoid cluttered visuals; focus on actionable insights.
- Consistency: Maintain uniform scales, colors, and symbols across charts.
- Interactivity: Use filters, sliders, and zoom features to explore large datasets.
- Integration: Embed visualizations into trading platforms or dashboards for seamless workflow.
- Validation: Cross-check visual outputs with quantitative metrics to ensure accuracy.
How data visualization enhances quantitative trading strategies: Integrating these best practices allows traders to identify market anomalies, optimize positions, and react faster to changing market conditions.
FAQs
1. How does data visualization improve trading decision-making?
Visualization converts complex datasets into intuitive charts and dashboards, enabling traders to identify trends, anomalies, and correlations that inform precise, timely decisions.
2. What are the best tools for data visualization in quantitative trading?
Python libraries (Matplotlib, Seaborn, Plotly), R packages (ggplot2), and platforms like Tableau or Bloomberg Terminal are highly effective. Choosing a tool depends on your data size, interactivity needs, and integration requirements.
3. Can data visualization help in algorithmic trading?
Yes, visualizing order book depth, price trends, and backtesting outcomes helps algorithm developers refine models, detect potential risks, and optimize strategy execution in real-time.
Conclusion
Mastering how to use data visualization in quantitative trading is no longer optional—it is essential for modern traders seeking an edge. By leveraging time-series charts, heatmaps, interactive dashboards, and predictive models, traders can make faster, more informed decisions while mitigating risk. Integrating visualization into quantitative workflows enhances strategy development, backtesting, and live market analysis.
Investing in high-quality visualization tools and adopting best practices ensures that both retail and institutional traders can convert complex financial data into actionable insights, ultimately improving trading performance and portfolio resilience.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment