
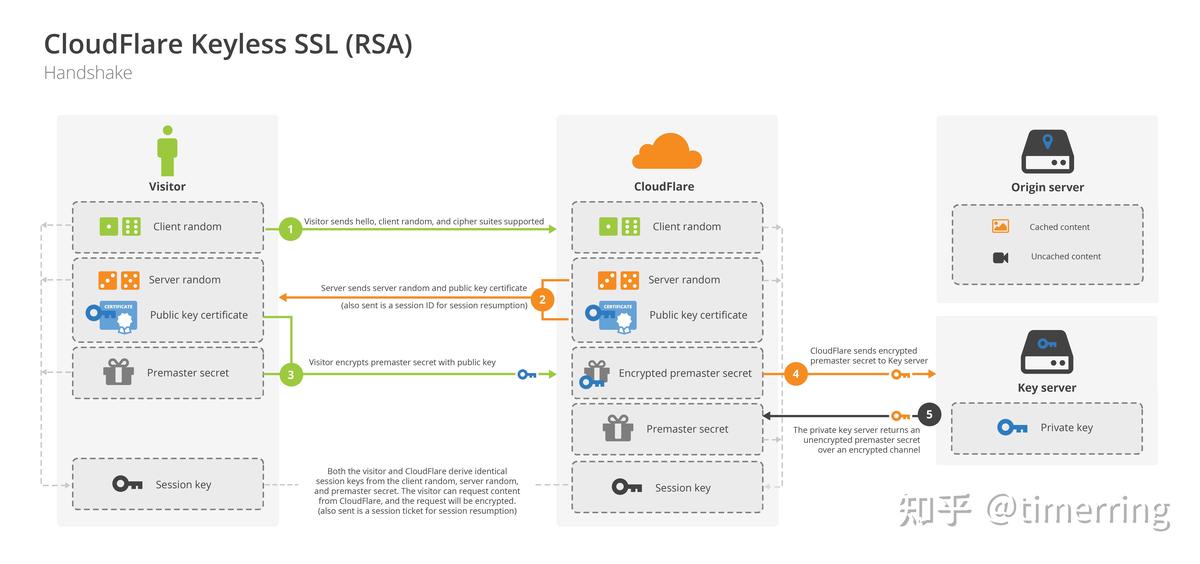
======================================
In the world of trading, signals are crucial tools that help traders make informed decisions. However, the accuracy of trading signals can greatly vary, and traders must be able to verify them before committing to any trades. Inaccurate signals can lead to significant financial losses. This article will provide an in-depth guide on how to verify trading signals, explore the different methods for ensuring their reliability, and share tips on how to make informed decisions based on verified signals.
- Understanding Trading Signals
——————————–
1.1 What Are Trading Signals?
Trading signals are indicators or alerts that help traders decide when to enter or exit a trade. These signals can be based on technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or algorithmic models. Trading signals provide traders with crucial information such as the right price to buy or sell, the market condition, and potential trends.
1.1.1 Types of Trading Signals:
- Technical Signals: Based on chart patterns, indicators, or oscillators (e.g., moving averages, RSI, MACD).
- Fundamental Signals: Based on economic data or news (e.g., earnings reports, GDP growth).
- Algorithmic Signals: Generated by trading bots or automated systems that use quantitative analysis to generate trade signals.
1.2 Importance of Verifying Trading Signals
Given that trading signals are essential for making timely and profitable decisions, it’s crucial to verify them to avoid costly mistakes. A signal that seems promising at first may not always be accurate, and failing to validate the signal can lead to impulsive trading decisions.
1.2.1 Risks of Relying on Unverified Signals:
- False Positives: A signal may incorrectly indicate a buy or sell opportunity, leading to a bad trade.
- Lagging Indicators: Some signals are delayed, and acting on them may cause you to miss out on profitable opportunities.
- Signal Scams: Not all signal providers are trustworthy; some may offer low-quality or fraudulent signals.
- Methods to Verify Trading Signals
————————————
2.1 Backtesting the Signal Strategy
One of the most effective methods to verify the accuracy of a trading signal is through backtesting. Backtesting involves applying the signal to historical data to see how well it would have performed in the past.
2.1.1 Steps for Backtesting Trading Signals:
- Select a Signal: Choose the signal that you wish to test.
- Collect Historical Data: Gather historical price and market data for the asset you’re analyzing.
- Apply the Signal: Implement the trading signal on the historical data to simulate past trades.
- Evaluate Performance: Analyze key performance metrics such as profit, win rate, and drawdown.
2.1.2 Pros of Backtesting:
- Data-Driven: Provides insights based on past performance.
- Objective Analysis: Removes emotional decision-making, relying solely on historical data.
- Predictive Power: Can help forecast the potential future success of a trading signal.
2.1.3 Cons of Backtesting:
- Overfitting: There is a risk of over-optimizing a strategy based on historical data, which might not perform well in live markets.
- Data Quality: Backtesting is only as good as the data used, and poor-quality data can lead to misleading results.
2.2 Forward Testing the Signals
Forward testing, also known as paper trading, involves testing trading signals in real-time using a demo account or virtual capital. This allows traders to evaluate how well the signal performs in current market conditions without the risk of actual capital.
2.2.1 Steps for Forward Testing:
- Set Up a Demo Account: Open a demo account with your broker to test signals in real-time.
- Apply the Signal: Use the trading signal to place orders in the demo account.
- Monitor Performance: Track the accuracy and profitability of the signal over a period of time.
2.2.2 Pros of Forward Testing:
- Real-Time Market Conditions: Signals are tested in live market conditions.
- No Financial Risk: Since you’re using virtual capital, there is no real risk involved.
2.2.3 Cons of Forward Testing:
- Psychological Differences: The absence of real money might not provide a true picture of how you would behave under pressure.
- Limited Timeframe: A short testing period may not capture all market conditions.
2.3 Evaluating the Source of the Trading Signal
Not all signal providers are created equal. It’s essential to evaluate the credibility of the source that provides the trading signal. Reliable providers typically have a track record, transparent methodologies, and a history of successful trades.
2.3.1 Factors to Consider When Evaluating a Signal Provider:
- Reputation: Look for reviews and testimonials from other traders.
- Track Record: Check if the provider has a documented history of successful signals.
- Methodology: Understand the approach used by the provider, whether it’s based on technical analysis, algorithmic strategies, or other methods.
2.3.2 Pros of Evaluating Signal Providers:
- Trustworthiness: Ensures that the signals come from a reliable and reputable source.
- Consistency: A reputable provider is more likely to offer consistent and high-quality signals.
2.3.3 Cons of Evaluating Signal Providers:
- Bias: Some providers may highlight only their successes while downplaying failures.
- Cost: High-quality signal services may charge a premium for their expertise.
- Additional Verification Methods
———————————-
3.1 Signal Comparison
Compare multiple signals for the same trade from different sources or strategies. If several signals agree, it may increase the likelihood that the trade is a valid opportunity.
3.1.1 Tools for Signal Comparison:
- Trading Platforms: Many trading platforms allow you to follow multiple signal providers and compare their performance.
- Signal Aggregators: Some services aggregate signals from various providers, enabling traders to compare them easily.
3.2 Using Advanced Tools and Indicators
Advanced tools, such as automated trading bots and algorithmic trading strategies, can help verify signals by analyzing multiple factors, such as market trends, volume, and volatility. These tools can also help filter out false signals and provide confirmation before acting on them.
3.2.1 Key Tools for Signal Verification:
- Machine Learning Models: AI-powered models can predict the accuracy of signals based on historical patterns.
- Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing market sentiment can help validate signals by assessing whether they align with the overall market mood.
- Price Action Confirmation: Watching for price action patterns that confirm the signal can help improve the reliability of the trade.
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
———————————–
4.1 How do I know if a trading signal is reliable?
To verify if a trading signal is reliable, you should backtest it using historical data, forward test it in a demo account, and evaluate the credibility of the signal provider. Additionally, comparing signals from different sources can provide additional validation.
4.2 Can trading signals be automated?
Yes, trading signals can be automated using algorithmic trading systems or trading bots. These systems can automatically execute trades based on pre-defined signals, reducing the need for manual intervention.
4.3 Why are trading signals important for beginners?
Trading signals are important for beginners as they provide guidance on when to enter or exit trades, reducing the complexity of decision-making. Signals help beginners make informed decisions and can boost confidence while learning the ropes of trading.
- Conclusion
————-
Verifying the accuracy of trading signals is crucial for ensuring consistent success in trading. Whether you choose to backtest, forward test, evaluate the signal provider, or use advanced verification tools, it’s essential to use multiple methods to validate the reliability of a signal. By adopting these practices, traders can improve their accuracy, minimize risks, and make more informed trading decisions.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment