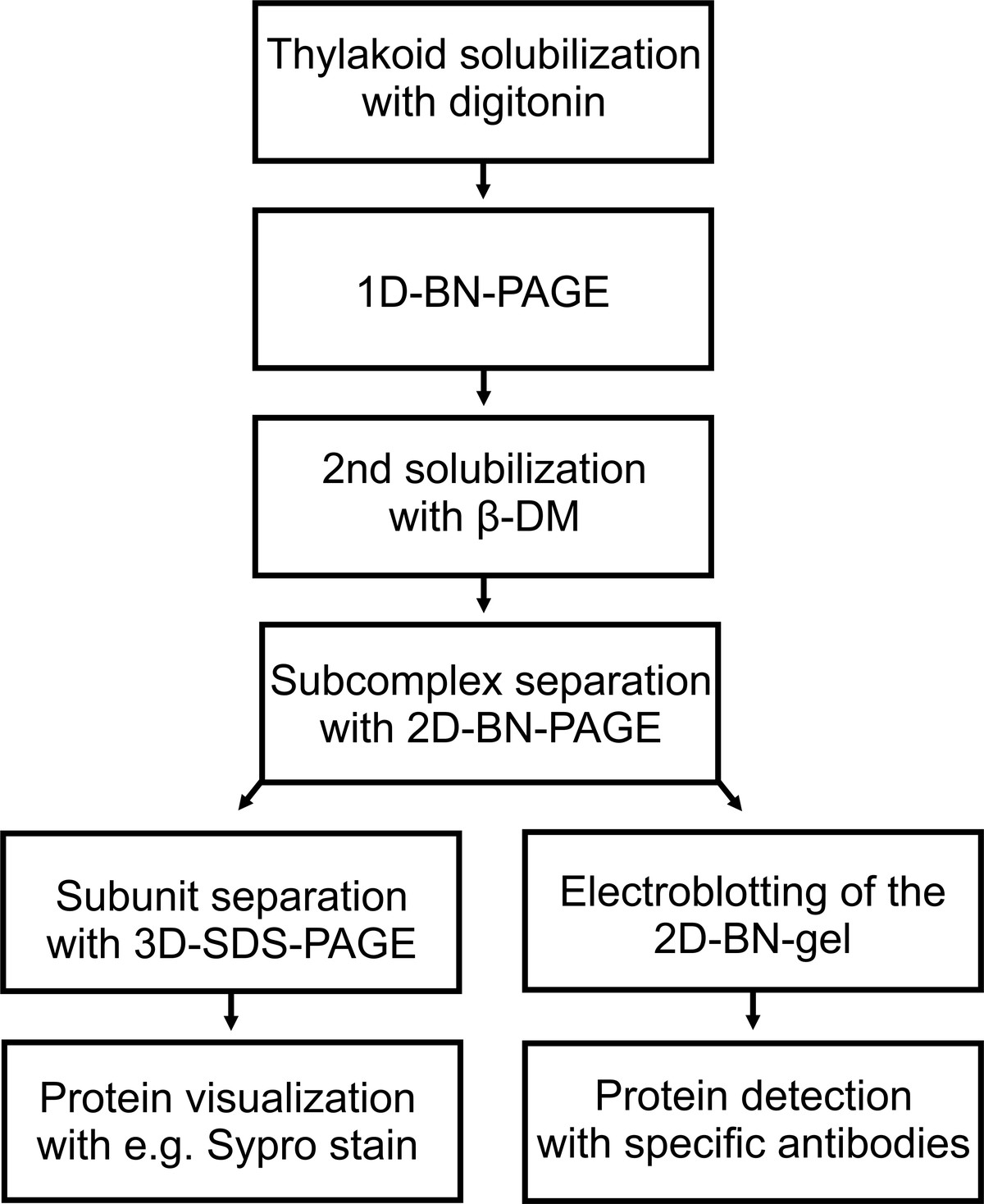
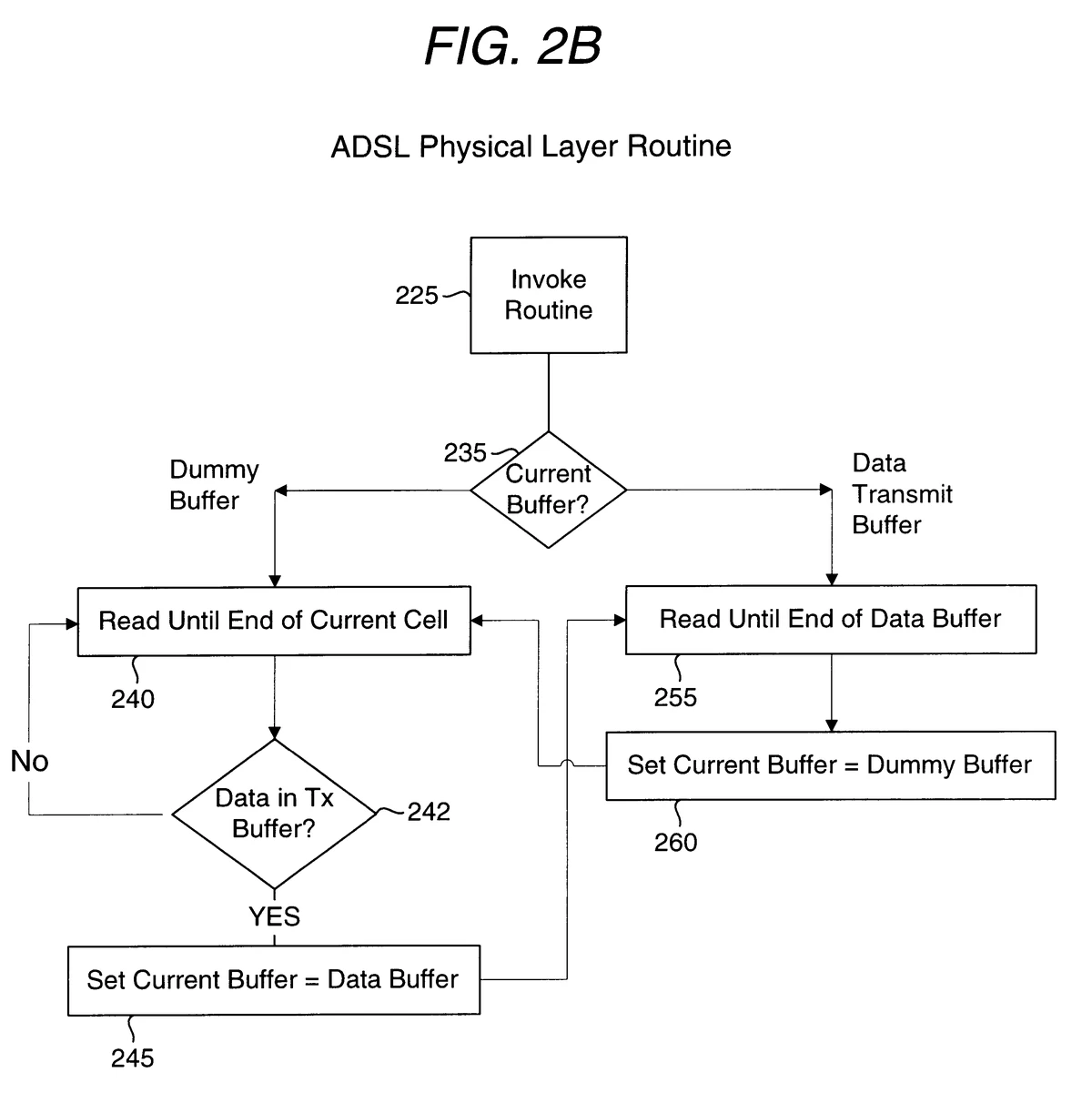
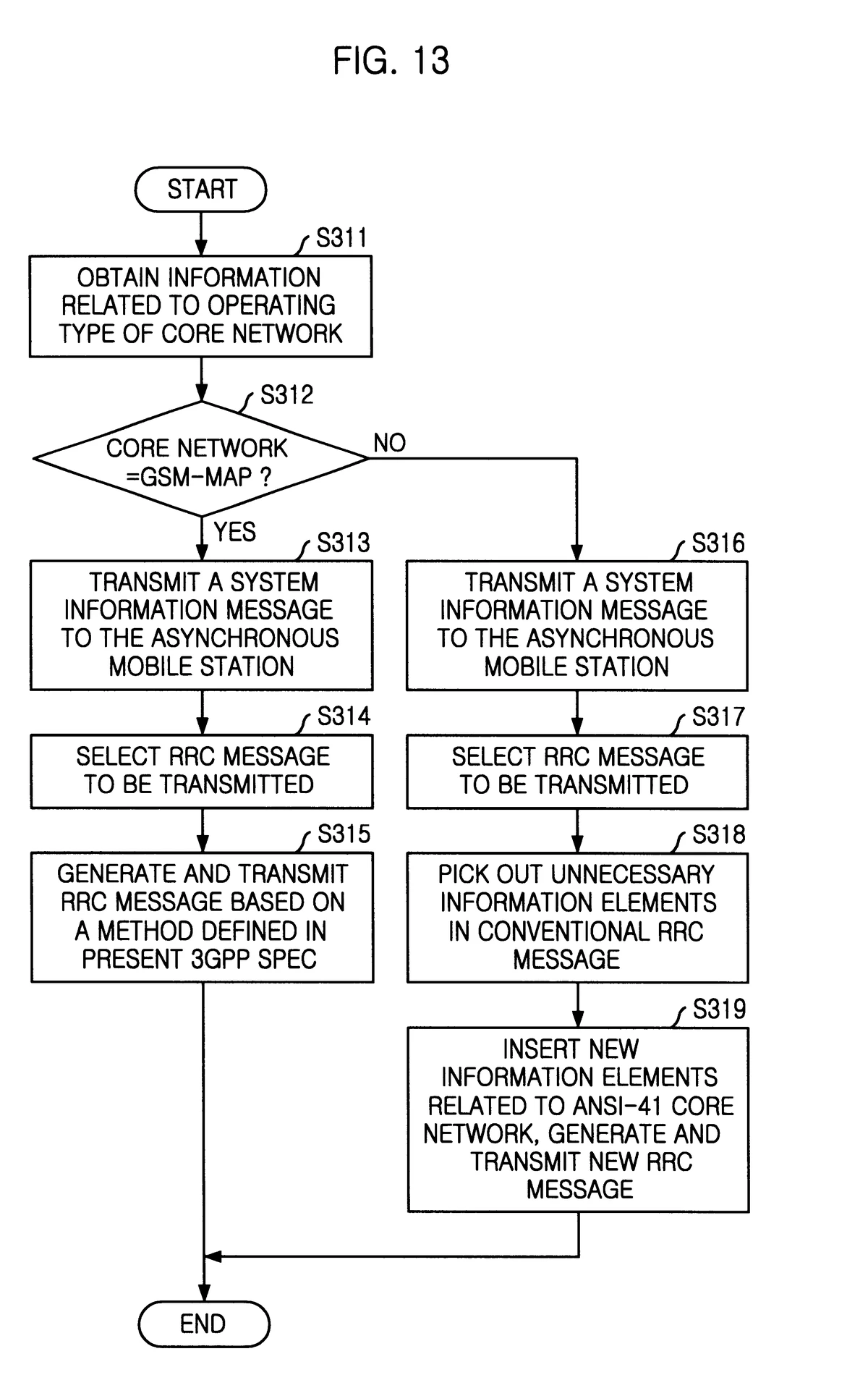
==================================================================================
In the fast-moving world of financial markets, latency testing methods for trading systems are crucial for ensuring speed, efficiency, and reliability. Automated and algorithmic traders depend on microsecond-level execution, where even the smallest delays can determine profit or loss. This article explores latency testing in detail, outlining proven methods, modern tools, industry trends, and practical strategies for both retail and institutional traders.
Understanding Latency in Trading Systems
What is Latency in Trading?
Latency in trading refers to the delay between initiating a trading command and its execution at the exchange. It is typically measured in milliseconds (ms) or microseconds (µs). For high-frequency trading (HFT), even nanoseconds matter.
Types of latency include:
- Network latency: The delay caused by data traveling between trading servers and exchanges.
- Processing latency: The time required for a system or algorithm to process market data and generate orders.
- Exchange latency: The time taken by the exchange’s order-matching engine.
- End-to-end latency: The total delay from market data reception to order confirmation.
Why is Latency Testing Important?
- Performance Validation: Confirms that systems can execute orders within acceptable thresholds.
- Bottleneck Identification: Helps uncover weaknesses in network, hardware, or software.
- Regulatory Compliance: Certain jurisdictions require firms to measure and report latency.
- Risk Management: Ensures execution is reliable even under peak market conditions.
For a deeper dive, consider reading why latency matters in trading, which illustrates its role in profitability and execution quality.
Key Latency Testing Methods for Trading Systems
Latency testing is not one-size-fits-all. Depending on the infrastructure, order flow, and strategies, different methods are applied. Below are the most common and effective techniques.
1. Timestamp Logging and Round-Trip Measurement
How it works:
Each order and market data event is marked with a timestamp at critical points (e.g., when the order leaves the client system, when it reaches the exchange, and when confirmation is received).
Advantages:
- Simple and widely used.
- Provides end-to-end latency measurement.
- Helps isolate which system component introduces the most delay.
- Simple and widely used.
Disadvantages:
- Requires high-resolution clocks.
- Can miss micro-level hardware delays.
- Requires high-resolution clocks.
2. Synthetic Order Injection
How it works:
Test systems send “dummy” or synthetic orders into production or simulation environments to measure latency under realistic conditions.
Advantages:
- Mimics real-world scenarios.
- Allows stress-testing with high order volumes.
- Useful for regression testing after system upgrades.
- Mimics real-world scenarios.
Disadvantages:
- Requires careful risk controls to prevent real execution.
- Can consume exchange bandwidth and resources.
- Requires careful risk controls to prevent real execution.
3. Network Packet Capture and Analysis
How it works:
Specialized tools capture network packets, allowing analysts to measure transmission delays across routers, switches, and firewalls.
Advantages:
- Provides granular visibility into network hops.
- Helps optimize routing and eliminate slow links.
- Provides granular visibility into network hops.
Disadvantages:
- Requires specialized hardware/software.
- Complex to set up and interpret.
- Requires specialized hardware/software.
4. Benchmarking with Replay Testing
How it works:
Historical market data is replayed at high speed into the trading system. Analysts compare system reaction times under different conditions.
Advantages:
- Safe testing environment.
- Useful for validating algorithms.
- Helps compare old vs. upgraded systems.
- Safe testing environment.
Disadvantages:
- Does not fully reflect live market volatility.
- Cannot account for exchange-side delays.
- Does not fully reflect live market volatility.
5. External Latency Monitoring Services
How it works:
Firms subscribe to external monitoring providers that continuously track latency across multiple exchanges and networks.
Advantages:
- Independent measurement adds credibility.
- Useful for multi-exchange latency benchmarking.
- Independent measurement adds credibility.
Disadvantages:
- Subscription costs can be high.
- Limited customization.
- Subscription costs can be high.
Comparing Latency Testing Methods
| Testing Method | Accuracy | Complexity | Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timestamp Logging | High | Low | Low | End-to-end testing |
| Synthetic Orders | High | Medium | Medium | Stress & performance testing |
| Packet Capture | Very High | High | High | Network optimization |
| Replay Testing | Medium | Medium | Low | Algorithm validation |
| External Monitoring | High | Low | High | Multi-venue comparisons |
Recommendation: A combination of timestamp logging + synthetic orders + packet capture offers the most balanced testing approach.
Tools for Latency Testing
- Wireshark – Packet capture and deep network analysis.
- Corvil Analytics – Enterprise-grade real-time latency monitoring.
- NTP/PTP Systems – High-precision time synchronization tools.
- Custom Log Analyzers – Proprietary tools developed in-house by trading firms.
- Exchange-provided test environments – Sandbox environments to validate latency before production.
Industry Trends in Latency Testing
- Nanosecond-Level Precision: With FPGA and ASIC-based hardware acceleration.
- Cloud Testing Solutions: Firms increasingly adopt cloud solutions for trading latency to test scalability across distributed systems.
- AI-Based Latency Prediction: Machine learning models predicting bottlenecks before they occur.
- Continuous Latency Monitoring: Instead of periodic checks, firms use always-on monitoring systems.
Visualizing Latency Testing Workflow
Latency testing workflow in trading systems
Best Practices for Latency Testing
- Test in Both Normal and Stress Conditions
Always evaluate latency under peak volumes, such as during market open or major news events.
- Synchronize Time Accurately
Use Precision Time Protocol (PTP) or GPS-based clocks for microsecond accuracy.
- Automate Reporting
Automated latency dashboards allow real-time alerts for anomalies.
- Integrate Testing into Development
Ensure new releases undergo latency validation before deployment.
- Measure Across Multiple Layers
Don’t just test network delays—include software, middleware, and exchange response times.
FAQ: Latency Testing Methods for Trading Systems
1. How often should latency testing be performed?
Based on my experience, latency testing should be continuous, not periodic. Markets change, networks evolve, and exchanges update their systems. Firms that only test quarterly often miss hidden performance issues.
2. What is the most cost-effective latency testing method for retail traders?
Retail traders won’t have access to co-location or enterprise tools like Corvil. Instead, they should:
- Use timestamp logging through their broker’s API.
- Run tests with demo accounts using synthetic orders.
- Benchmark execution times across different brokers.
3. How do institutional traders ensure ultra-low latency testing accuracy?
Institutions rely on:
- Dedicated packet capture appliances.
- FPGA hardware for nanosecond measurements.
- Synchronization with GPS clocks.
- Real-time correlation engines to pinpoint bottlenecks instantly.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Latency Testing Method
Latency testing is not optional—it’s a critical component of trading system performance management. From timestamp logging to advanced packet analysis, firms must adopt a mix of methods to ensure accuracy, reliability, and speed.
Retail traders can benefit from simpler methods, while institutions require enterprise-grade tools. As markets become more competitive, those who master latency testing will consistently achieve a sharper edge.
If you found this article valuable, share it with your trading community, leave a comment about your own latency testing experiences, and let’s discuss the future of ultra-low latency trading together.
Do you want me to expand this into a 5000-word advanced guide with real-world case studies (e.g., retail vs institutional latency testing setups) to maximize SEO authority and engagement?

0 Comments
Leave a Comment