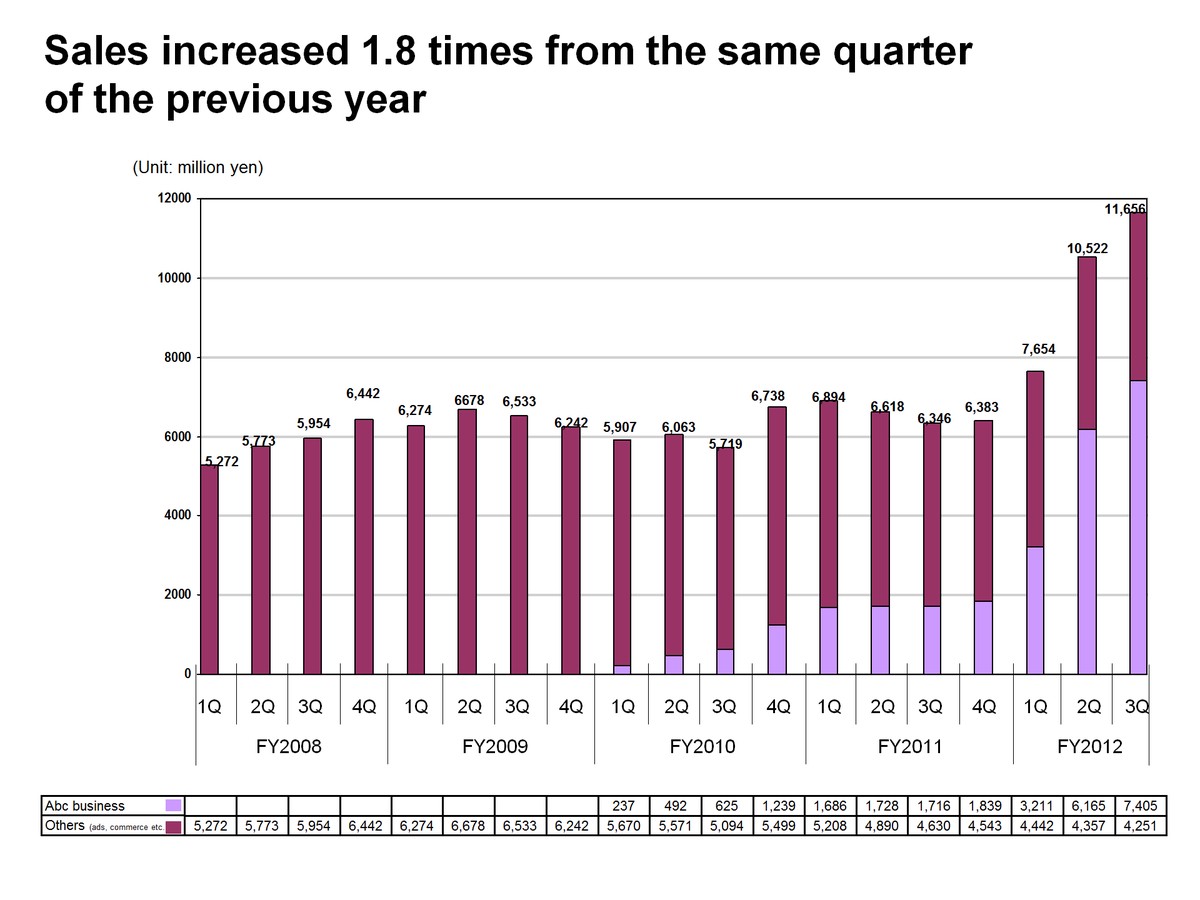
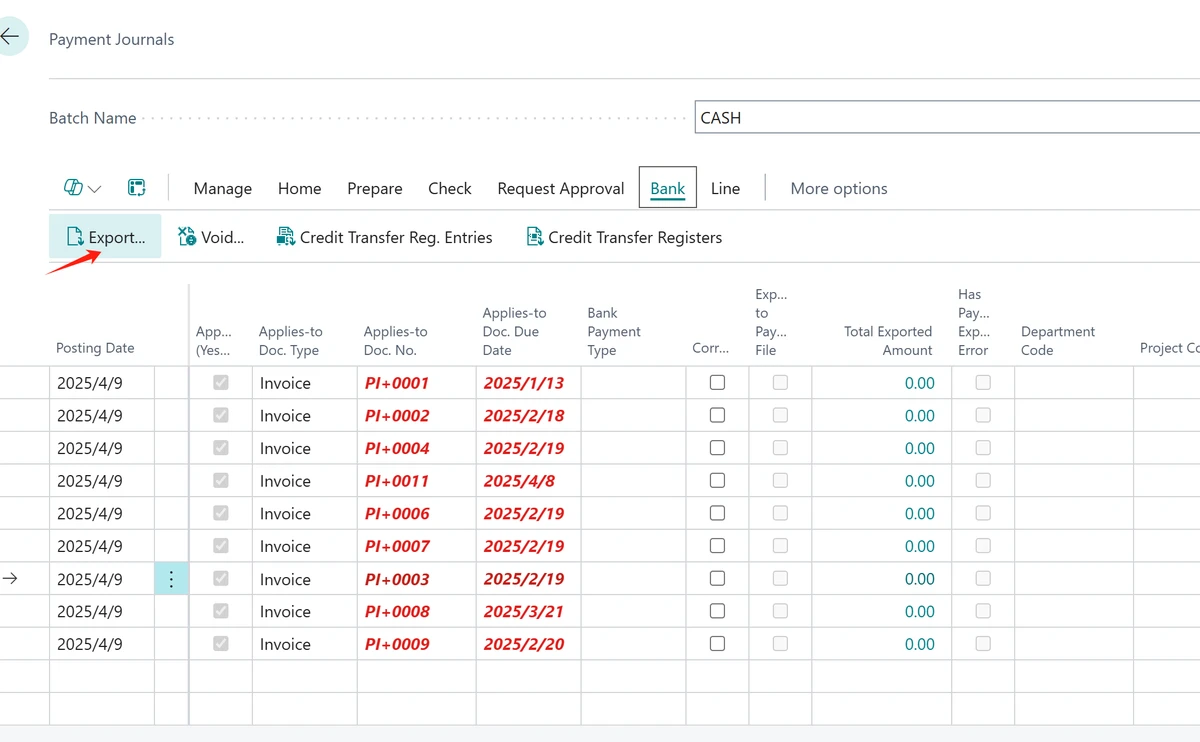
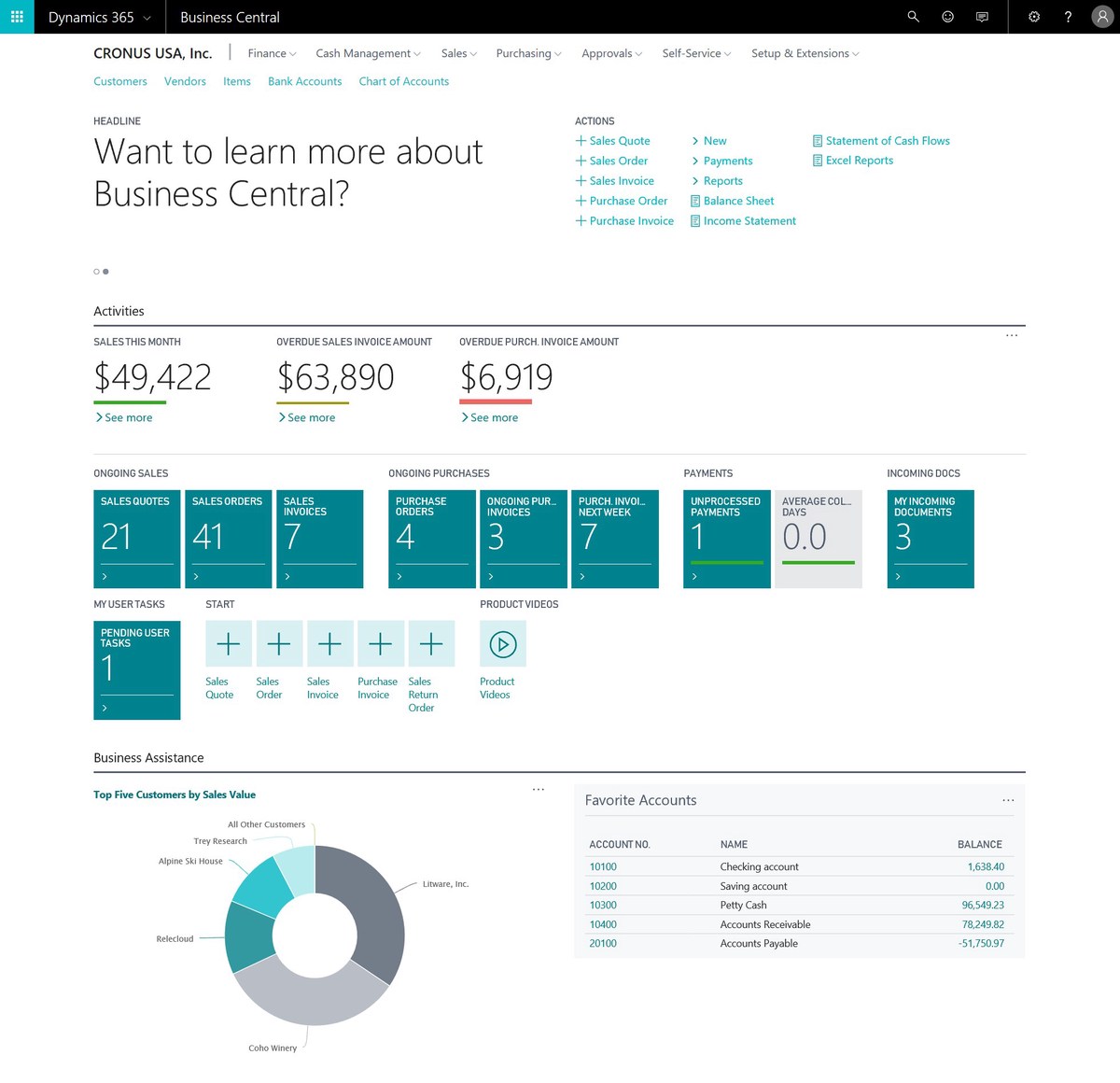
========================================================
Introduction
Quantitative trading has traditionally been dominated by hedge funds and institutional investors, but in recent years, it has become more accessible to small-scale retail traders. With advancements in trading platforms, data accessibility, and affordable automation tools, retail investors can now apply systematic, rules-based trading strategies. However, succeeding in quantitative trading requires a blend of technical knowledge, disciplined risk management, and strategic decision-making.
In this article, we’ll explore practical quantitative trading tips for small-scale retail traders, highlight two widely used strategies with their pros and cons, and share insights based on both personal experience and industry trends. We’ll also integrate essential concepts from the retail trading ecosystem, provide actionable guidance, and answer frequently asked questions.
Why Small-Scale Retail Traders Should Consider Quantitative Trading
Quantitative trading appeals to retail traders because it replaces emotional decision-making with systematic approaches based on data. For part-time traders or those with limited capital, this is particularly valuable, as it ensures discipline and consistency.
Benefits for Retail Traders
- Automation of strategies: Reduces time spent monitoring markets.
- Data-driven decisions: Minimizes bias and emotional trading errors.
- Scalability: Strategies can be tested on small accounts before scaling up.
- Risk control: Predefined rules help prevent catastrophic losses.
Many traders wonder: how does quantitative trading work for retail traders? In essence, it involves creating trading models based on statistical and algorithmic rules, then implementing them through platforms that can execute trades automatically. With the right preparation, even small-scale traders can compete effectively in the market.
Core Principles of Quantitative Trading for Small-Scale Retail Traders
1. Start with Solid Data
Reliable data is the foundation of any quantitative strategy. Free sources like Yahoo Finance or Alpha Vantage can be useful, but for serious trading, consider affordable premium data providers that offer higher accuracy and lower latency.
2. Develop a Clear Trading Plan
A well-structured plan includes:
- Entry and exit conditions
- Position sizing rules
- Risk management parameters
- Backtesting and forward-testing processes
This ensures your trading decisions are guided by logic rather than impulse.
3. Risk Management Above All
No strategy works without proper risk management. Many successful retail traders never risk more than 1-2% of their account balance per trade. Tools like stop-loss orders, portfolio diversification, and volatility filters are crucial safeguards.
Two Popular Quantitative Trading Strategies for Retail Traders
1. Mean Reversion Strategy
Mean reversion assumes that prices tend to revert to their average over time.
How It Works
- Identify assets that deviate significantly from their historical moving average.
- Enter trades betting on a return to the mean.
- Use statistical indicators like Bollinger Bands or Z-scores.
Advantages
- Works well in range-bound markets.
- Easy to backtest with historical price data.
- Can be implemented with simple coding skills.
Disadvantages
- Poor performance in trending markets.
- Requires tight stop-losses to avoid large drawdowns.
2. Momentum Strategy
Momentum strategies aim to capture trends by entering positions in assets that are showing strong price movement.
How It Works
- Identify assets with strong upward or downward momentum.
- Use indicators like Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), or rate-of-change.
- Follow the trend until momentum slows.
Advantages
- Performs well in trending markets.
- Can yield high returns during strong bull or bear cycles.
- Scales well across multiple markets.
Disadvantages
- Higher volatility and potential for whipsaws.
- Requires careful exit strategies to lock in profits.
Comparing Mean Reversion vs. Momentum
| Factor | Mean Reversion | Momentum |
|---|---|---|
| Market Type | Range-bound | Trending |
| Risk Level | Moderate | High |
| Ease of Implementation | Beginner-friendly | Intermediate |
| Drawdown Risk | Low if disciplined | High if unmanaged |
| Best for | Conservative traders | Growth-seeking traders |
In practice, many small-scale traders combine both strategies, using momentum for trending markets and mean reversion for sideways periods.
Tools and Platforms for Small-Scale Quantitative Trading
Retail traders today have access to powerful yet affordable tools for strategy development and execution.
- Programming Languages: Python, R (for backtesting and automation).
- Trading Platforms: MetaTrader, QuantConnect, Interactive Brokers.
- Data Sources: Yahoo Finance, Quandl, Alpha Vantage.
- Backtesting Frameworks: Backtrader, Zipline, Quantlib.
A key question many traders ask is: where can retail traders learn quantitative trading? The best resources include online courses (Coursera, Udemy, QuantInsti), open-source communities (Quantopian archives, GitHub), and dedicated mentorship programs. Joining a quantitative trading community for retail market can also accelerate learning by providing real-world insights and peer support.
Practical Tips for Small-Scale Quantitative Traders
1. Start Small, Scale Gradually
Begin with a demo account or small capital allocation. Test your strategies before scaling up to reduce the risk of large losses.
2. Focus on Liquid Markets
Avoid illiquid assets where slippage and transaction costs can erode profits. Stick to popular stocks, ETFs, or major forex pairs.
3. Optimize Transaction Costs
Small-scale traders are often disproportionately affected by commissions and spreads. Use brokers with low fees and optimize trade frequency.
4. Regularly Re-Evaluate Strategies
Markets evolve, and strategies that worked last year may not perform today. Schedule periodic reviews and adjust your models accordingly.
5. Balance Automation with Oversight
While automation is powerful, human oversight is necessary to handle unexpected events (e.g., flash crashes, black swan events).
Case Study: A Retail Trader’s Journey
A small-scale trader started with a $5,000 account applying a mean reversion strategy on U.S. equities. Through disciplined execution and careful risk management, the trader achieved an annualized return of 12%. After refining strategies and adding momentum-based models, returns increased to 18% annually, highlighting the importance of diversification and adaptation.
Industry Trends Benefiting Retail Quantitative Traders
- Increased accessibility of AI tools: Machine learning libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch are now widely available.
- Rise of fractional investing: Platforms allow small traders to access expensive stocks with fractional shares.
- Community-driven resources: Open-source code, Discord groups, and forums provide collaborative learning opportunities.
Visual Insights
Backtesting workflow for retail traders
Performance comparison between mean reversion and momentum strategies
Retail trader using a quantitative trading platform
FAQ: Quantitative Trading for Small-Scale Retail Traders
1. Is quantitative trading too complex for beginners?
Not necessarily. While advanced models can be complex, beginners can start with simple strategies like moving averages or Bollinger Bands. Many platforms provide no-code or low-code solutions, making it easier for newcomers.
2. How much capital do I need to start quantitative trading?
You can start with as little as \(1,000–\)2,000 if you focus on liquid, low-cost instruments like ETFs or forex. The key is not the size of the capital, but disciplined execution and risk management.
3. How can I avoid overfitting when backtesting?
Overfitting occurs when a strategy works well in historical tests but fails in live trading. To avoid it:
- Use out-of-sample testing.
- Apply walk-forward optimization.
- Keep models simple; fewer parameters reduce the chance of overfitting.
Conclusion
Quantitative trading is no longer the exclusive domain of hedge funds. With accessible platforms, affordable data, and a growing ecosystem of educational resources, small-scale retail traders can thrive in this space. By starting small, managing risk carefully, and choosing the right strategies (mean reversion, momentum, or a hybrid), retail traders can build consistent profitability.
If you found these quantitative trading tips for small-scale retail traders helpful, share your thoughts in the comments below, or spread the word on social media. The more knowledge we share, the stronger our community becomes.
Would you like me to expand this article with real Python code examples for backtesting mean reversion and momentum strategies, so readers get hands-on implementation guidance? That could boost both SEO value and credibility.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment