=============================================
Introduction
The order book is one of the most valuable resources for quantitative traders. It provides real-time insights into supply and demand dynamics, liquidity distribution, and potential price movements. Unlike historical price charts, which reflect completed trades, the order book reveals intentions—the bids and asks waiting to be executed. For algorithmic traders, hedge funds, and quantitative analysts, mastering order book data can be the difference between average execution and alpha generation.
In this article, we will explore how to use order book in quantitative trading, compare different methods of integrating order book signals, and provide actionable strategies with practical pros and cons. We will also embed insights from industry practices, reference advanced tools, and discuss how professional investors leverage order book dynamics for execution and strategy design.
Understanding the Order Book
What Is an Order Book?
An order book is a continuously updated list of buy and sell orders for a financial asset, organized by price levels. It typically includes:
- Bid side (demand): Buy orders placed at different price levels.
- Ask side (supply): Sell orders placed at different price levels.
- Spread: The difference between the best bid and best ask price.
- Depth: The cumulative size of orders across multiple levels.
The order book reflects not only market activity but also the latent intentions of traders.
Why the Order Book Matters in Quantitative Trading
The order book is crucial for market microstructure analysis, providing insights such as:
- Liquidity availability: Helps estimate how much size can be executed without significant slippage.
- Market impact: Assesses how aggressive orders might affect price.
- Order flow dynamics: Detects imbalance between buyers and sellers.
- Hidden signals: Identifies spoofing, layering, and other advanced trading behaviors.
Professional traders emphasize why order book matters in trading strategy because it bridges the gap between theory and execution.
Core Strategies for Using Order Book Data
1. Liquidity-Based Execution Strategy
One of the most common uses of the order book is to optimize trade execution.
How It Works
- Algorithms assess available liquidity at each price level.
- Orders are sliced into smaller chunks to minimize market impact.
- Execution strategies like VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price) or TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price) incorporate order book depth.
Advantages
- Reduces slippage for large trades.
- Provides smoother entry/exit points.
- Ideal for institutions and hedge funds.
Disadvantages
- May miss short-term price opportunities.
- Execution can become predictable and exploited by faster traders.
2. Order Flow Imbalance Strategy
This strategy uses the imbalance between bids and asks to forecast short-term price movements.
How It Works
- Compute Order Flow Imbalance (OFI):
OFI=Volumebids−VolumeasksVolumebids+VolumeasksOFI = \frac{Volume_{bids} - Volume_{asks}}{Volume_{bids} + Volume_{asks}}OFI=Volumebids+VolumeasksVolumebids−Volumeasks
- If bids dominate, the market may be bullish in the near term.
- If asks dominate, the market may be bearish.
Advantages
- Offers predictive signals for intraday trading.
- Useful for high-frequency trading models.
Disadvantages
- Noisy in highly liquid markets.
- Susceptible to spoofing and hidden liquidity.
3. Market Depth Analysis
Market depth refers to the aggregate supply and demand across price levels.
Application in Quantitative Models
- Identify support and resistance levels based on liquidity clusters.
- Adjust position sizing depending on available depth.
- Use for stress-testing strategies in illiquid markets.
This is closely related to why use order book for market depth analysis, a key concept for execution traders.
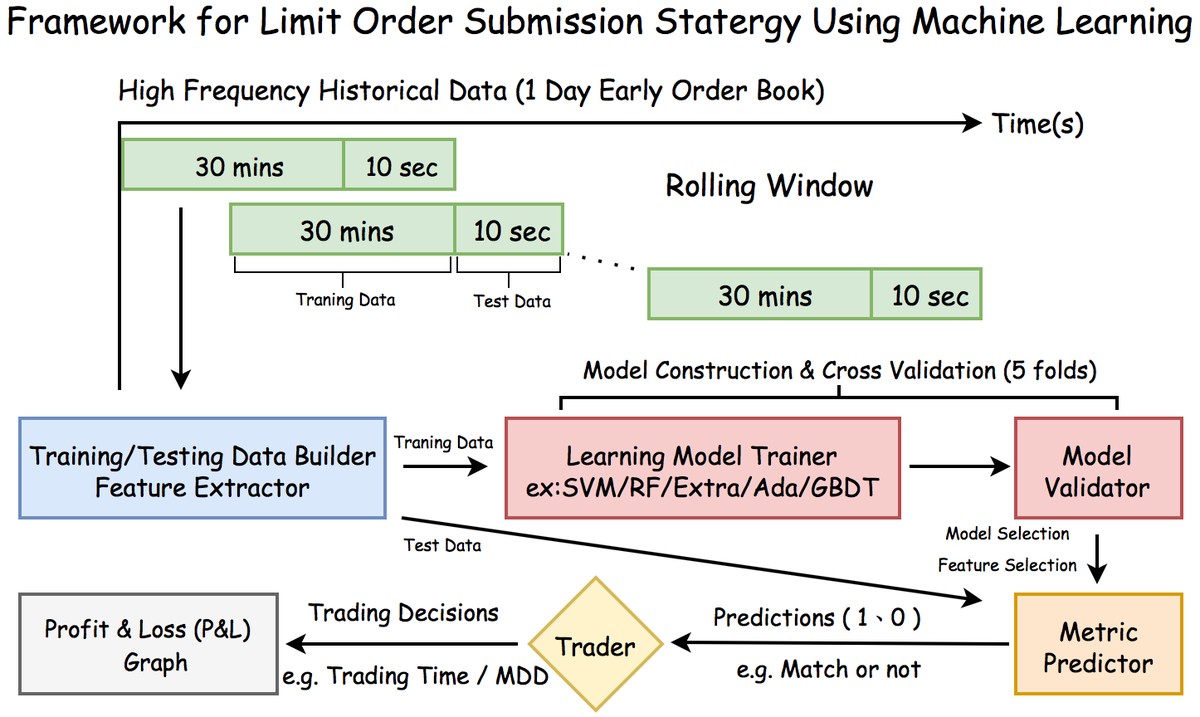
4. Machine Learning with Order Book Features
With advances in data science, order book features are now widely integrated into machine learning pipelines.
Example Features
- Spread width changes.
- Order cancellation rates.
- Depth imbalance ratios.
- Time-based liquidity evolution.
Benefits
- Captures nonlinear dynamics.
- Identifies microsecond-level trading patterns.
- Enhances predictive accuracy of price movement forecasts.
Limitations
- Requires high-quality tick-level data.
- Computationally expensive.
- Risk of overfitting if not carefully validated.
Case Study: Comparing Liquidity Execution vs. Order Flow Imbalance
Liquidity Execution
- Best for: Institutional investors, portfolio managers.
- Strength: Minimizes transaction costs.
- Weakness: Lacks predictive alpha.
Order Flow Imbalance
- Best for: High-frequency traders, prop desks.
- Strength: Provides directional edge.
- Weakness: Vulnerable to manipulation.
Recommendation:
For professional order book analysis tools for analysts, a hybrid approach works best—using liquidity-based execution for large trades while layering order flow imbalance signals for tactical entries.
Advanced Applications
Integration with Trading Algorithms
Traders increasingly integrate order book data directly into their automated systems. For example:
- Dynamic position sizing based on liquidity.
- Adaptive spreads in market making.
- Signal confirmation with order imbalance.
This reflects the growing trend of how to integrate order book data with trading algorithms.
Order Book in High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
HFT firms rely heavily on microstructure signals:
- Quote stuffing detection.
- Order cancellation speed analysis.
- Millisecond-level spread prediction.
These methods require nanosecond timestamped data and specialized infrastructure.
Visualization and Monitoring
Professional traders often use custom dashboards to visualize:
- Depth heatmaps.
- Liquidity walls.
- Dynamic spread evolution.
Order book depth heatmap visualizing liquidity layers

Practical Challenges in Using Order Book Data
- Data Volume: High-frequency order book data can reach terabytes per day.
- Latency Sensitivity: Delayed data loses predictive value.
- Market Manipulation: Fake orders may distort signals.
- Infrastructure Costs: Requires specialized servers and data storage solutions.
FAQ: Using Order Book in Quantitative Trading
1. How can beginners start learning order book trading?
Beginners should start with a beginner’s guide to reading order books, focusing on concepts like bids, asks, spread, and depth. Simulation platforms and free data providers can help develop intuition before moving to real trading.
2. How do institutional traders use the order book?
Institutional traders rely on order book management techniques for portfolio managers. They use it to minimize market impact, identify liquidity pools, and optimize execution costs. Advanced algorithms automatically adapt to changing depth conditions.
3. Is order book data reliable for predicting price direction?
Order book signals can be predictive in short timeframes, especially when analyzing imbalances. However, they are noisy and can be manipulated. Combining them with other signals, such as volume flow or machine learning models, increases reliability.
Conclusion
Understanding how to use order book in quantitative trading is essential for traders seeking an edge in modern markets. From liquidity-based execution strategies to order flow imbalance analysis and machine learning applications, the order book remains at the core of quantitative market microstructure.
Professional traders combine multiple approaches—balancing execution efficiency with predictive insights—to optimize their performance. Whether you are a beginner exploring visualization tools or an institutional analyst deploying algorithmic execution, mastering order book dynamics will significantly improve your trading edge.
If you found this guide useful, share it with your network, leave a comment with your own experiences, and join the conversation on how order book strategies are evolving in the era of algorithmic trading.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment