

===================================================================================
Taking profits is a critical element of successful trading, and understanding the best strategies to implement it can significantly impact your overall profitability. For beginners, mastering take profit strategies is essential for not just securing gains, but also for managing risk effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various take profit strategies, how to choose the best levels for taking profits, and answer key questions to help you achieve consistent trading success.
- What is a Take Profit Strategy?
————————————–
1.1 Understanding Take Profit in Trading
A take profit strategy is a predefined plan set by a trader to lock in profits once a trade reaches a specific price level. This strategy is designed to help traders avoid emotional decision-making and to secure profits before the market reverses. Essentially, take profit orders are limit orders placed at a specific price point, ensuring that profits are captured as soon as that level is hit.
1.2 Why is Take Profit Important?
Using a take profit strategy offers several advantages:
- Prevents Emotional Decisions: Traders can avoid the fear of losing profits by automatically taking profits at set levels.
- Locks in Gains: By setting realistic targets, traders can ensure that profits are taken at optimal points, reducing the risk of price reversals.
- Improves Risk Management: Setting take profit levels helps to balance potential rewards with acceptable risks.
- Common Take Profit Strategies for Beginners
————————————————–
2.1 Fixed Percentage Take Profit Strategy
The fixed percentage take profit strategy is one of the most straightforward and widely used methods by beginners. This approach involves setting a specific percentage gain on a trade, after which profits will be taken automatically.
How it Works:
- For example, a trader might decide to set a 10% take profit level. Once the asset’s price rises by 10% from the entry point, the take profit order is triggered, and the position is closed.
Advantages:
- Simple to Implement: This strategy requires minimal analysis and is easy for beginners to understand.
- Clear Expectations: Traders can easily calculate their profit targets.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Flexibility: The fixed percentage approach does not account for market volatility or changing market conditions.
- Missed Opportunities: If the asset continues to rise after hitting the take profit level, you may miss out on further gains.
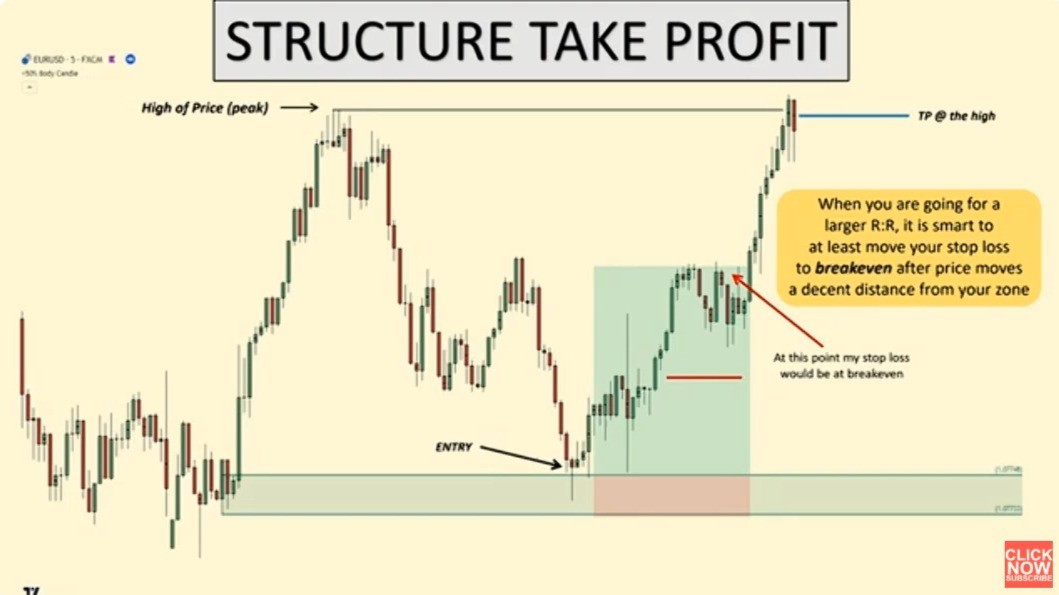
2.2 Support and Resistance-Based Take Profit Strategy
A more advanced strategy involves setting take profit levels based on technical analysis of support and resistance levels. This method aims to capture profits when the price reaches key levels identified through chart patterns.
How it Works:
- Traders will analyze the asset’s chart to identify major support and resistance levels. They will then set take profit orders just before a resistance level (if buying) or just above a support level (if shorting).
Advantages:
- Higher Probability of Success: By using support and resistance, traders are more likely to exit a trade at points where price reversals are expected.
- Adaptable: This strategy allows traders to account for market conditions, adjusting their targets based on live price action.
Disadvantages:
- Requires Technical Knowledge: Traders need to be comfortable with chart analysis and identifying key price levels.
- Risk of False Breakouts: Price can sometimes break through support or resistance levels, leading to missed opportunities or losses.
- How to Choose Take Profit Levels
—————————————
3.1 Evaluating Market Conditions
The choice of take profit levels is highly dependent on market conditions. In a volatile market, it might be better to use tighter profit-taking targets, while in a trending market, broader take profit levels may be more suitable.
Market Conditions to Consider:
- Trending Markets: In a strong uptrend or downtrend, consider setting take profit levels further away from the entry point.
- Range-bound Markets: When the market is moving sideways, use tighter profit targets to capitalize on smaller price swings.
3.2 Risk-Reward Ratio
A good rule of thumb is to aim for a favorable risk-reward ratio. For beginners, a 2:1 or 3:1 ratio is often recommended. This means that for every unit of risk, your potential reward should be two or three units. By using this method, traders can ensure they are not only targeting profits but also managing risk appropriately.
Example:
- If a trader is risking \(50 on a trade, they might set a take profit level that yields \)100 in profit, achieving a 2:1 risk-reward ratio.
3.3 Using Fibonacci Retracement Levels
Fibonacci retracement is a technical analysis tool that identifies potential support and resistance levels based on the Fibonacci sequence. Traders often use these levels to set take profit points. Fibonacci retracement levels like 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8% can serve as potential take profit targets.
Advantages:
- Widely Recognized Levels: Fibonacci levels are commonly used in technical analysis and are recognized by many traders, making them reliable.
- Dynamic Adjustment: Fibonacci retracement levels can be adjusted as the market evolves.
Disadvantages:
- Subjective: The choice of which Fibonacci levels to use can be subjective and may not always provide perfect predictions.
- Advanced Take Profit Strategies
————————————–
4.1 Trailing Stop Loss with Take Profit
A trailing stop loss strategy is a dynamic method where the stop loss is adjusted as the market moves in the trader’s favor. This allows for profits to be locked in if the market reverses, but it also gives room for further gains if the market continues in the desired direction.
How it Works:
- A trailing stop loss is set a specific distance below (for long trades) or above (for short trades) the current market price. As the price moves in the trader’s favor, the stop loss moves up (for longs) or down (for shorts), ensuring that profits are locked in as the market continues to move in the trader’s favor.
Advantages:
- Profit Protection: The trailing stop ensures that profits are secured if the market reverses.
- Flexibility: This strategy allows the trader to capture larger moves without having to adjust the take profit manually.
Disadvantages:
- Requires Monitoring: The trailing stop may not be ideal for traders who do not have the time to monitor the markets regularly.
4.2 Partial Take Profit Strategy
The partial take profit strategy involves closing a portion of a trade once a profit target is hit, while leaving the remaining position open to capture additional gains.
How it Works:
- A trader might decide to take profit on 50% of their position once the asset reaches a predefined level. The remaining 50% of the position is held in case the asset continues to move in the trader’s favor.
Advantages:
- Lock in Profits and Stay Involved: This strategy allows traders to secure profits while still benefiting from potential further price movements.
- Risk Reduction: By closing a portion of the position, traders can reduce their exposure and lock in some profits.
Disadvantages:
- Less Simple: This strategy requires more decision-making and management than a full take profit strategy.
- FAQ: Take Profit Strategies for Beginners
————————————————
5.1 How do I set take profit in trading?
To set a take profit, you should determine a price level at which you want to exit the trade. This can be based on technical analysis (support and resistance, Fibonacci levels), a fixed percentage, or a dynamic strategy like trailing stops.
5.2 What is the best take profit strategy for beginners?
The fixed percentage strategy is the best take profit strategy for beginners as it is simple and easy to implement. It provides a clear exit point based on the trader’s desired profit target.
5.3 Why is take profit important in trading?
Take profit helps traders lock in profits and avoid emotional decision-making. It is an essential tool for managing risk, ensuring that gains are secured before market conditions reverse.
- Conclusion
—————–
Mastering take profit strategies is essential for any beginner trader looking to achieve consistent profits and minimize risk. Whether you choose to use fixed percentage targets, support and resistance levels, or more advanced techniques like trailing stops and partial take profits, understanding how to effectively implement take profit strategies will significantly improve your trading outcomes. By combining these strategies with sound risk management principles, you can enhance your chances of long-term success in the markets.

0 Comments
Leave a Comment